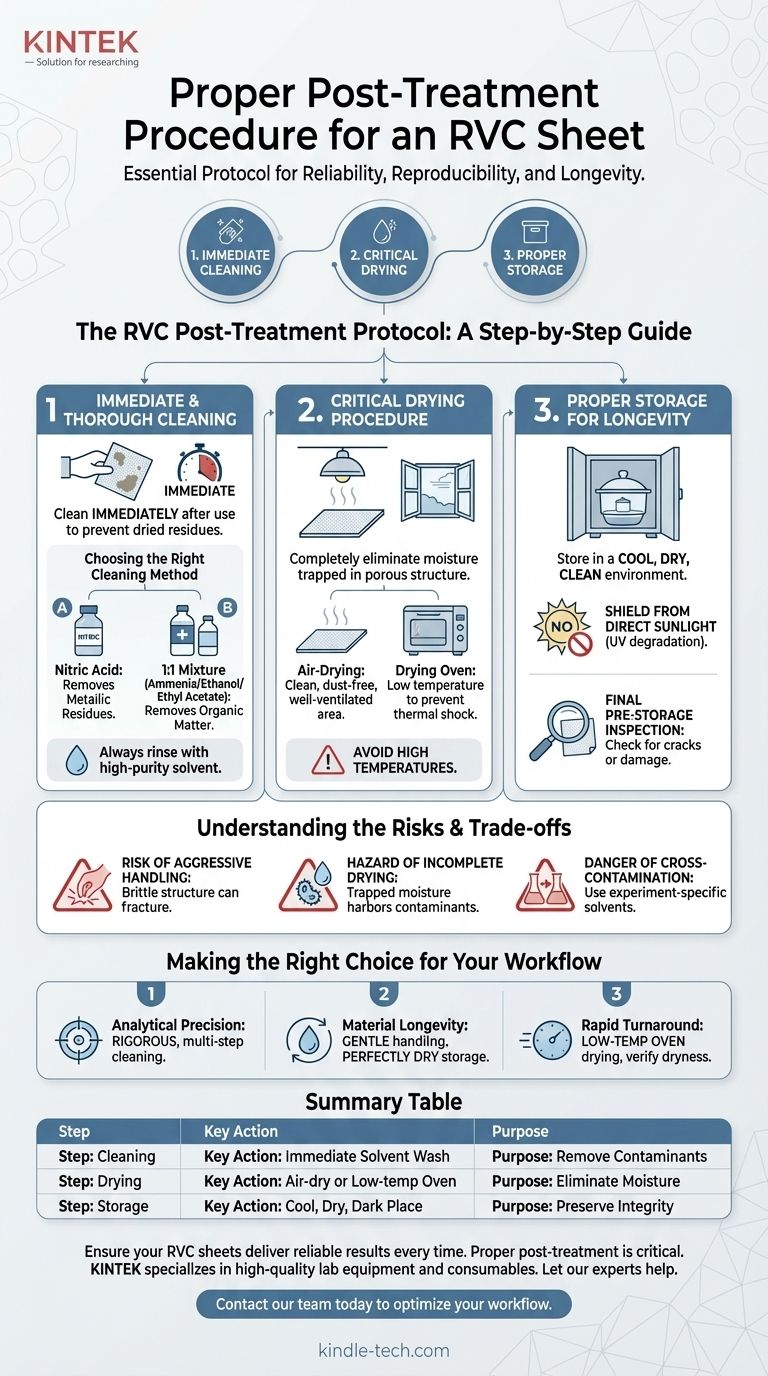
The proper post-treatment procedure for an RVC sheet involves three critical stages: immediate cleaning after use, thorough drying to remove all moisture, and correct storage to preserve its integrity. This process is essential for removing experimental reactants and contaminants, ensuring the sheet is in a pristine state for its next use.
The core purpose of post-treatment is not merely to clean the RVC sheet, but to restore its unique, high-surface-area porous structure to a known, uncontaminated state. Failure to do so directly compromises the reliability and reproducibility of future experimental results.
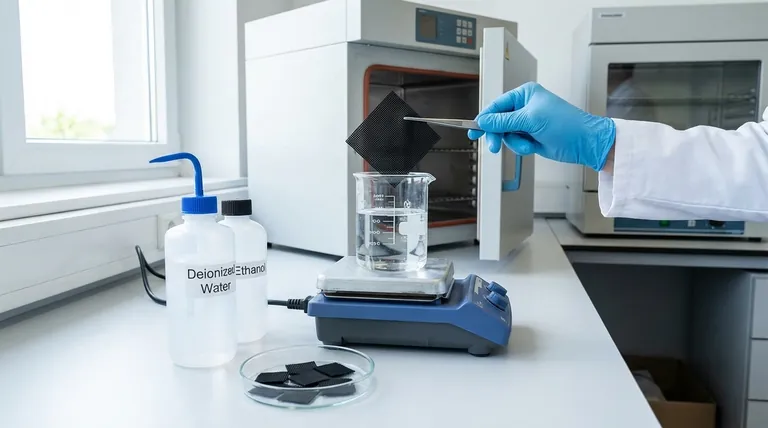

The RVC Post-Treatment Protocol: A Step-by-Step Guide
Properly caring for your Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) extends its lifespan and, more importantly, guarantees the validity of your work. The process can be broken down into two main actions: cleaning and drying.
Step 1: Immediate and Thorough Cleaning
The single most important step is to clean the RVC sheet immediately after an experiment concludes. Allowing reactants or byproducts to dry on the surface can make them significantly more difficult to remove and may permanently contaminate the material.
The goal is to eliminate all residual reactants, impurities, and contaminants that were introduced during your procedure.
Choosing the Right Cleaning Method
Your post-use cleaning protocol should mirror the methods used for pre-treatment. The choice of solvent depends on the nature of the contaminants you need to remove.
Common cleaning approaches involve soaking and gentle scrubbing with one of the following:
- Nitric Acid: Effective for removing metallic residues.
- A 1:1 mixture: Combining ammonia water, anhydrous ethanol, or ethyl acetate is often used for removing organic matter.
Always rinse thoroughly with a high-purity solvent (like deionized water or ethanol) after the primary cleaning step to remove any remaining cleaning agent.
Step 2: Critical Drying Procedure
Once cleaned, the RVC sheet must be completely dried. Its porous, sponge-like structure can trap moisture, which can interfere with future experiments or lead to material degradation during storage.
You have two primary options for drying:
- Air-Drying: Place the sheet in a clean, dust-free, and well-ventilated area.
- Drying Oven: For faster results, use a drying oven at a low temperature. High temperatures can risk thermal shock or material damage.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
Handling RVC requires a balance between thoroughness and care. Applying the wrong technique can be as damaging as skipping the process entirely.
The Risk of Aggressive Handling
While cleaning is vital, the intricate vitreous carbon network is brittle. Overly aggressive scrubbing can fracture the internal struts, destroying the porous structure and rendering the electrode useless. Always handle with care.
The Hazard of Incomplete Drying
Trapped moisture is a hidden danger. It can harbor contaminants, support microbial growth, or introduce unwanted water into your next experiment, which is especially problematic in non-aqueous electrochemistry.
The Danger of Cross-Contamination
Failing to clean the RVC sheet with a solvent specific to your last experiment's contaminants can lead to cross-contamination. Residues from a previous experiment can leach into your next one, invalidating your results.
The Final Step: Proper Storage for Longevity
A cleaned and fully dried RVC sheet is ready for storage. The environment you store it in is crucial for maintaining its ready-to-use state.
Creating the Ideal Environment
Store the RVC sheet in a cool, dry, and clean environment. A desiccator or a sealed container in a cabinet is ideal. This protects it from ambient humidity and dust.
Critically, you must shield it from direct sunlight, as UV radiation can potentially degrade the material over long periods.
Final Pre-Storage Inspection
Before putting the sheet away, perform a quick visual inspection. Look for any new cracks, chips, or signs of damage that may have occurred during use or cleaning. It is better to identify a compromised sheet now than right before your next experiment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Workflow
Your specific experimental needs should guide your post-treatment priorities.
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: Prioritize a rigorous, multi-step cleaning regimen using solvents chosen specifically to dissolve your experiment's residues.
- If your primary focus is material longevity: Emphasize gentle handling during cleaning and ensure the storage environment is perfectly dry and protected from light and dust.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround: Utilize a low-temperature drying oven to speed up the process, but verify the sheet is completely dry before storage or reuse.
Adhering to a disciplined post-treatment protocol is the key to ensuring your RVC materials deliver consistent, reliable, and reproducible performance.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Cleaning | Immediate solvent wash (e.g., Nitric Acid for metals) | Remove contaminants and prevent residue buildup. |
| 2. Drying | Air-dry or use a low-temperature oven | Eliminate moisture to prevent degradation and contamination. |
| 3. Storage | Store in a cool, dry, dark place (e.g., desiccator) | Preserve structural integrity for future use. |
Ensure your RVC sheets deliver reliable results every time. Proper post-treatment is critical for the success of your electrochemical experiments. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including RVC materials, designed for demanding laboratory environments. Let our experts help you maintain peak performance and extend the life of your vital lab materials. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and optimize your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
People Also Ask
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- What are 3 products that carbon nanotubes can be used in? Enhancing Batteries, Tires, and Composites
- How should carbon cloth used for high-temperature electrolysis be handled after operation? Prevent Irreversible Oxidative Damage
- Why are high surface area materials preferred for BES anodes? Maximize Microbial Power and Efficiency



















