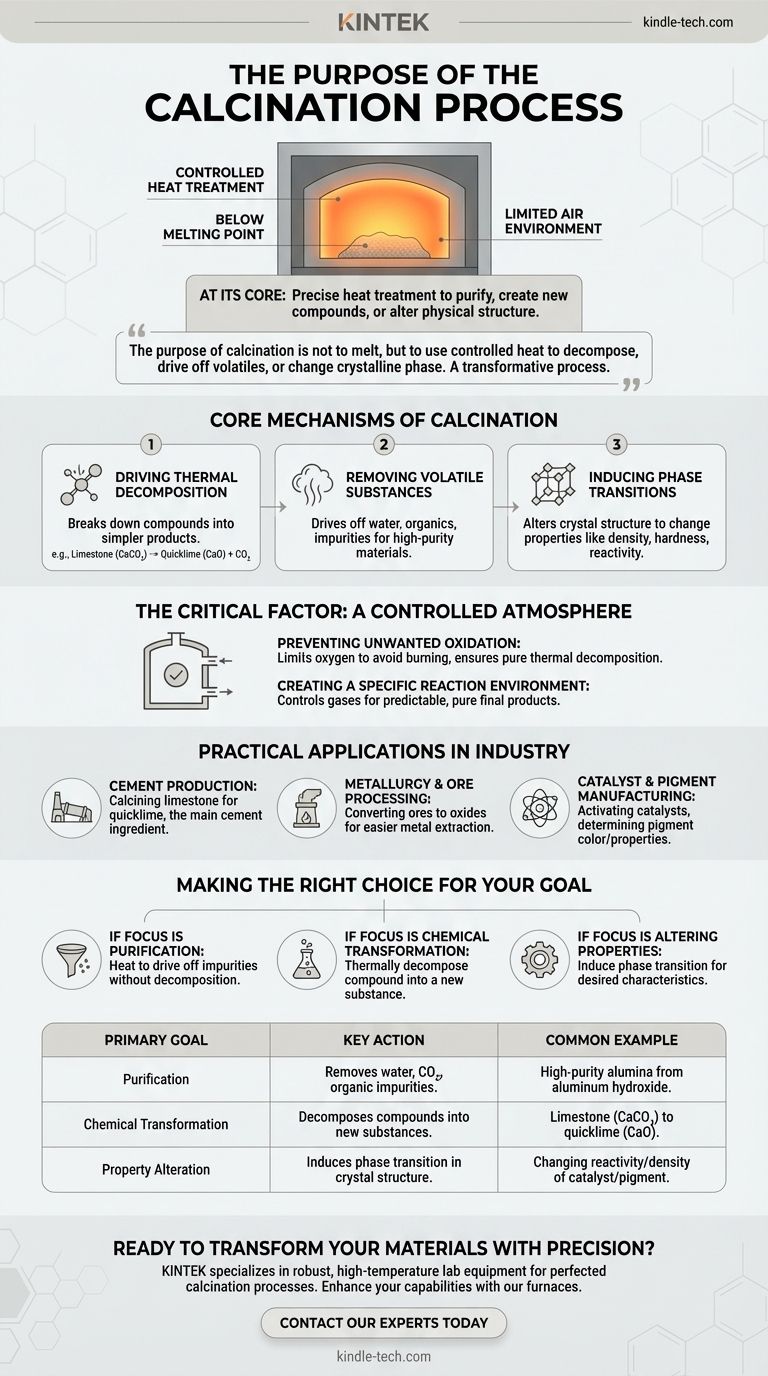
At its core, calcination is a precise heat treatment process used to induce chemical or physical changes in a solid material. It involves heating the material to a high temperature, but always below its melting point, often in an environment with little to no air to control the reaction. This process is fundamental to purifying materials, creating new compounds, or altering a substance's physical structure.
The purpose of calcination is not to melt a material, but to use controlled heat to decompose it, drive off volatile components like water or CO₂, or change its crystalline phase. It is a transformative process, not a destructive one.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To truly understand calcination, you must look beyond the simple application of heat. The process leverages high temperatures to trigger specific, predictable changes within the material's structure and composition.
Driving Thermal Decomposition
The most common goal of calcination is to break down chemical compounds. Heat provides the energy needed to sever chemical bonds, causing a substance to decompose into simpler products.
A classic example is the production of quicklime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). When heated, the limestone doesn't melt; instead, it breaks down, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind the desired calcium oxide.
Removing Volatile Substances
Many raw materials contain unwanted volatile components, such as physically trapped water, chemically bound water (hydrates), or organic impurities.
Calcination heats the material sufficiently to drive these substances off as gas, effectively purifying the solid that remains. This is crucial for creating stable, high-purity materials for industrial use.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Sometimes, the goal isn't to change the chemical composition but to alter the physical structure. Heat can cause a material's atoms to rearrange into a different crystal lattice, known as a phase transition.
This change can dramatically alter the material's properties, such as its density, hardness, or chemical reactivity, making it suitable for a new application.
The Critical Factor: A Controlled Atmosphere
A defining feature of calcination is that it occurs in the absence or a very limited supply of air (oxygen). This is not an accident; it is a critical control parameter that distinguishes it from other heat treatments like roasting.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
By limiting oxygen, calcination prevents the material from burning or reacting with oxygen (oxidizing). This is essential when the goal is pure thermal decomposition.
In contrast, processes like roasting often intentionally introduce air to promote oxidation, such as converting sulfide ores into oxides.
Creating a Specific Reaction Environment
The atmosphere inside the calcination furnace is a key variable. By controlling the gases present, engineers can ensure that only the desired chemical reactions occur, leading to a more predictable and pure final product.
Understanding the Practical Applications
Calcination is not just a laboratory technique; it is a large-scale industrial process that forms the backbone of several major industries.
Cement Production
The entire cement industry is built on calcination. Limestone is calcined in massive kilns to produce quicklime, the primary ingredient in cement.
Metallurgy and Ore Processing
As the references note, calcination is a key step in metallurgy. It is used to convert metal ores, particularly carbonates and hydrates, into their oxide forms. These oxides are then more easily reduced to the pure metal in a subsequent smelting process.
Catalyst and Pigment Manufacturing
In the chemical industry, calcination is used to activate catalysts by creating a specific surface structure and porosity. It is also used to produce inorganic pigments, where the final color and properties are determined by the precise temperature and atmosphere of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters of calcination are tailored to the desired outcome. Understanding your primary objective is key to applying the process correctly.
- If your primary focus is purification: Use calcination to heat the material enough to drive off water, organic matter, or other volatile impurities without causing decomposition.
- If your primary focus is chemical transformation: Use calcination to thermally decompose a compound into a new substance, such as converting a carbonate into an oxide.
- If your primary focus is altering material properties: Use calcination to induce a phase transition, changing the crystal structure to achieve desired characteristics like increased density or reactivity.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational tool for manipulating matter, enabling the conversion of raw materials into the highly engineered products that define our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Primary Goal | Key Action | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purification | Removes water, CO₂, and organic impurities. | Producing high-purity alumina from aluminum hydroxide. |
| Chemical Transformation | Thermally decomposes compounds into new substances. | Converting limestone (CaCO₃) into quicklime (CaO). |
| Property Alteration | Induces a phase transition in the crystal structure. | Changing the reactivity or density of a catalyst or pigment. |
Ready to Transform Your Materials with Precision?
Calcination is a critical step for achieving material purity and desired properties. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust, high-temperature lab equipment you need to perfect your calcination processes. Whether you are developing catalysts, processing ores, or manufacturing advanced ceramics, our furnaces offer the precise temperature control and atmospheric management essential for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? Maximize Uniformity & Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment



















