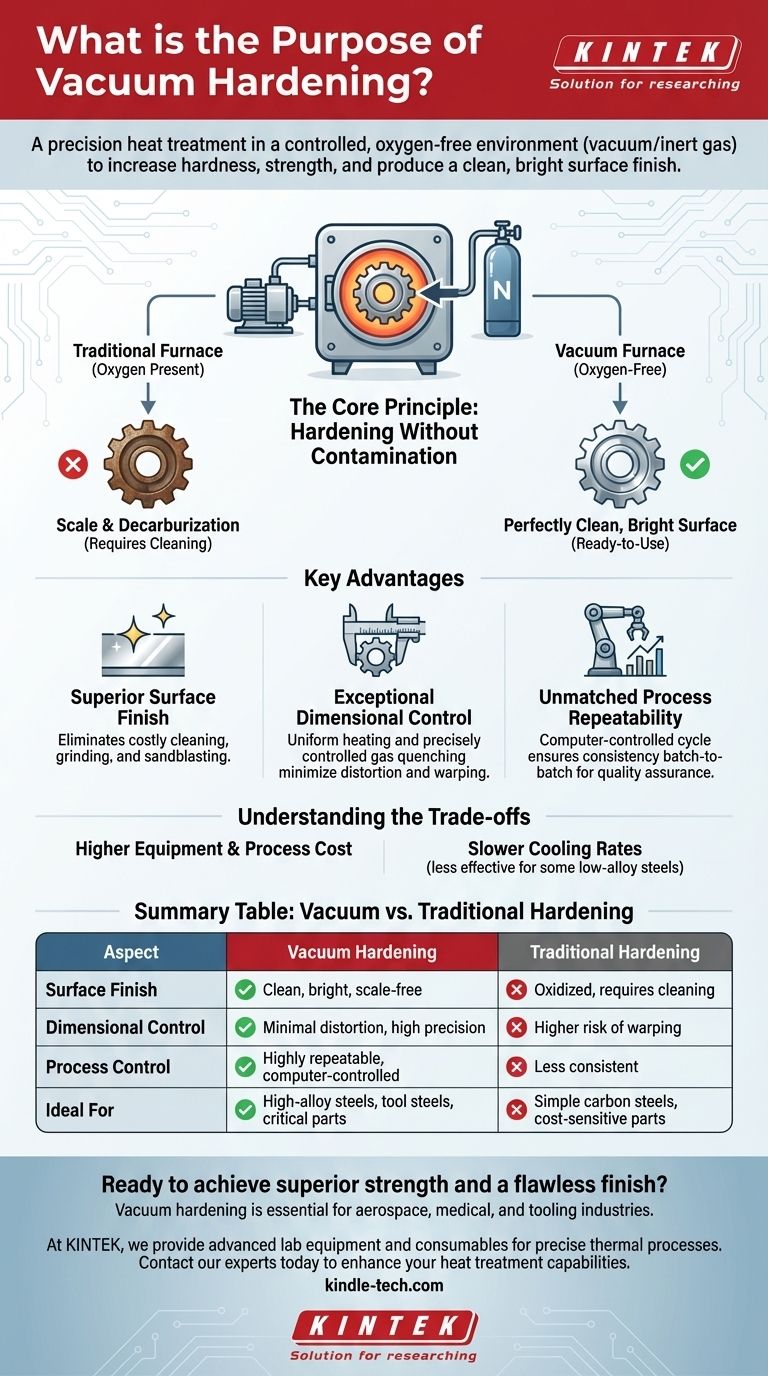
At its core, vacuum hardening is a process of precision. It is a specialized heat treatment method that heats a metal part in a controlled, oxygen-free environment—either a near-perfect vacuum or an inert gas like nitrogen. Its primary purpose is to increase the hardness and strength of the material while simultaneously producing a perfectly clean, bright surface finish, which often eliminates the need for any subsequent mechanical cleaning or polishing.
The true value of vacuum hardening isn't just strengthening the metal, but achieving that strength with exceptional surface quality and dimensional stability. It trades a higher initial process complexity for a superior, often final-form, component.

The Core Principle: Hardening Without Contamination
Vacuum hardening fundamentally redefines heat treatment by removing the variable of atmospheric reaction. This control is the source of all its primary benefits.
Creating an Oxygen-Free Environment
In a traditional furnace, the high heat causes oxygen in the air to react with the metal's surface, forming a layer of scale (oxidation). Vacuum furnaces prevent this by removing the air or replacing it with an inert gas.
This process ensures the surface chemistry of the material remains unchanged.
The Heating and Quenching Cycle
Parts are heated to temperatures as high as 1,300°C using radiation and convection. Once the material reaches the correct temperature for the desired transformation, it is rapidly cooled (quenched).
This quench is typically performed using a high-pressure stream of inert gas, most commonly nitrogen. The cooling rate can be precisely managed by adjusting gas pressure and flow, ensuring uniform hardening.
Why This Matters for Material Integrity
Beyond preventing simple oxidation, the controlled atmosphere stops carburization and decarburization. These are a gain or loss of carbon on the steel's surface, which can compromise its designed hardness and wear resistance.
By preserving the material's intended surface carbon content, vacuum hardening ensures the part performs exactly as engineered.
Key Advantages Driving Adoption
Engineers and manufacturers choose vacuum hardening when the final quality of the component is paramount. The process delivers several distinct advantages over traditional methods.
Superior Surface Finish
The most immediate benefit is a clean, bright, and decorative surface finish. Because no oxidation occurs, parts emerge from the furnace ready for use or final assembly.
This eliminates costly and time-consuming secondary operations like sandblasting, grinding, or chemical cleaning.
Exceptional Dimensional Control
Uniform heating and precisely controlled gas quenching minimize the thermal stress on a component. This results in minimal distortion, warping, and dimensional change.
For complex geometries or parts with tight tolerances, such as injection molds or aerospace gears, this level of stability is critical.
Unmatched Process Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled, allowing for the precise regulation of temperature, pressure, and quench rates.
This guarantees an extremely high degree of repeatability from part-to-part and batch-to-batch, a non-negotiable requirement for quality assurance in critical industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hardening is not a universal solution. Its benefits must be weighed against its specific requirements and limitations.
Equipment and Process Cost
Vacuum furnace systems are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. This often translates to a higher per-piece cost.
Slower Cooling Rates
Quenching with nitrogen gas is generally less severe than quenching in a liquid like oil or water. This controlled, slower cooling rate is what reduces distortion.
However, this can be a limitation for some low-alloy steels that require an extremely fast quench to achieve maximum hardness.
Best Suited for Specific Alloys
The process is ideal for air-hardening tool steels, high-alloy steels, and specialized materials like heat-resistant nickel-based alloys. It is less effective or economical for simple carbon steels that depend on a rapid water quench.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if vacuum hardening is appropriate depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, finish, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface quality and minimal distortion: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice, as it eliminates post-treatment cleaning and preserves tight tolerances.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production of simple parts: Traditional atmospheric hardening may be more economical, provided the resulting surface oxidation and need for cleaning are acceptable.
- If your primary focus is treating high-alloy or heat-resistant materials for critical applications: The process control, cleanliness, and repeatability of vacuum hardening are often non-negotiable requirements for industries like aerospace and medical.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum hardening is an investment in process control to achieve a flawless final component right out of the furnace.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Hardening | Traditional Hardening |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Clean, bright, scale-free | Oxidized, requires cleaning |
| Dimensional Control | Minimal distortion, high precision | Higher risk of warping |
| Process Control | Highly repeatable, computer-controlled | Less consistent |
| Ideal For | High-alloy steels, tool steels, critical parts | Simple carbon steels, cost-sensitive parts |
Ready to achieve superior strength and a flawless finish for your critical metal components?
Vacuum hardening is the solution for manufacturers and engineers who demand precision, repeatability, and a ready-to-use part straight from the furnace. This process is essential for industries like aerospace, medical, and tooling where component integrity is non-negotiable.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to implement and support precise thermal processes like vacuum hardening. Our expertise helps you ensure material performance and eliminate costly secondary finishing steps.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your heat treatment capabilities and deliver the high-quality results your projects demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components



















