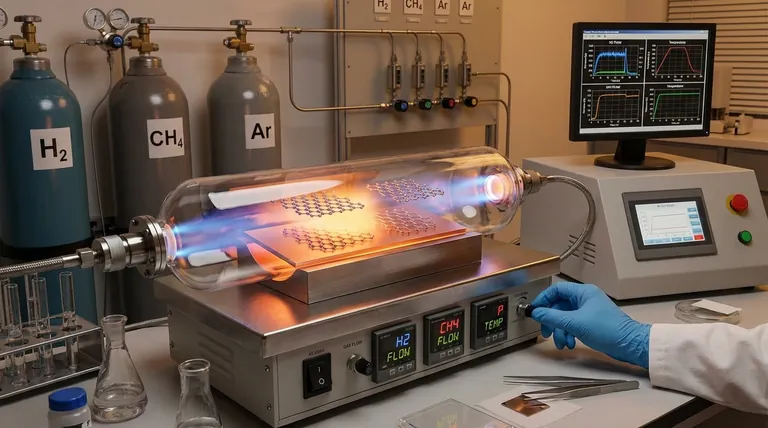
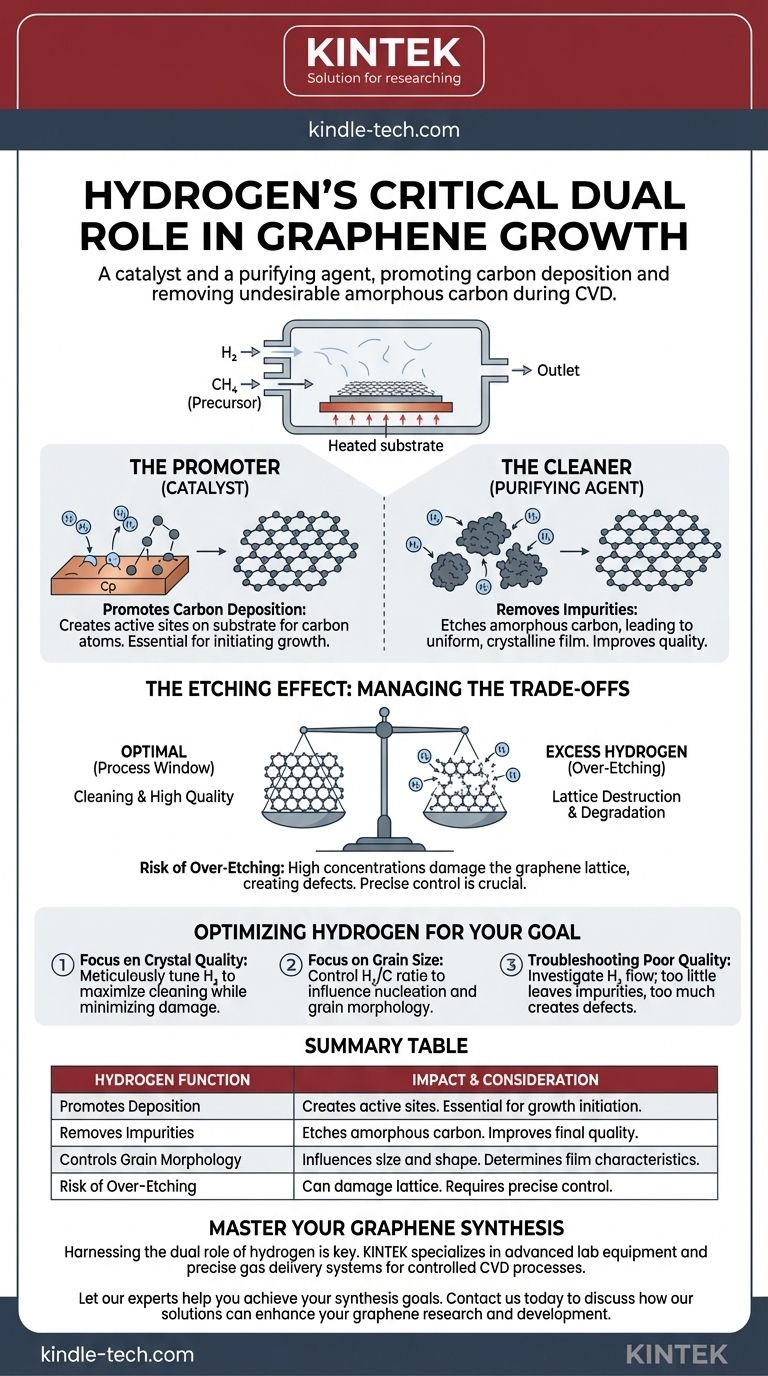
In short, hydrogen plays a critical dual role in graphene growth. During chemical vapor deposition (CVD), it acts as both a catalyst and a purifying agent by promoting carbon deposition on the substrate while simultaneously removing undesirable amorphous carbon, which improves the final quality of the graphene sheet.
The core challenge in using hydrogen for graphene growth is managing its contradictory nature. It is essential for cleaning the growth surface and producing high-quality crystals, but an excess will actively etch and destroy the very graphene lattice you are trying to create.

The Two Faces of Hydrogen in Graphene Growth
Understanding how to control hydrogen is fundamental to mastering graphene synthesis. Its impact is not monolithic; it serves distinct purposes at different stages and concentrations, directly influencing the final material's structure and properties.
Promoting Carbon Deposition
Hydrogen is required to prepare the metallic substrate (often copper) for growth. It helps create active sites where carbon atoms from the precursor gas (like methane) can effectively deposit and begin forming the graphene lattice.
The "Cleaner" - Removing Impurities
One of hydrogen's most crucial functions is purification. It provides reactive H atoms that selectively etch, or corrode, amorphous carbon—a disordered, non-crystalline form of carbon that is a common impurity and degrades graphene quality.
By removing these imperfections, hydrogen ensures that the resulting film is a more uniform, crystalline structure.
Influencing Grain Morphology
The concentration of hydrogen significantly impacts the formation of individual graphene grains. By controlling the hydrogen-to-carbon ratio, you can influence the size and shape (morphology) of these grains, which ultimately determines the characteristics of the continuous graphene film.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Etching Effect
While hydrogen is a powerful tool for improving quality, its reactive nature presents a significant risk. The same mechanism that removes impurities can also damage the product.
The Risk of Over-Etching
The process of etching is not perfectly selective. If the concentration of hydrogen is too high or the exposure time is too long, the hydrogen atoms will begin to attack and corrode the desirable graphene itself.
Lattice Destruction and Quality Degradation
This over-etching leads to the destruction of the hexagonal crystal lattice that defines graphene. The result is a film with defects, holes, and a deteriorated structure, compromising its exceptional electronic and mechanical properties.
Finding the "Process Window"
Success in graphene synthesis relies on finding the optimal process window. This is the narrow range of hydrogen concentration and flow rate that is strong enough to remove amorphous carbon but not so aggressive that it damages the graphene lattice.
Optimizing Hydrogen for Your Synthesis Goal
Your approach to using hydrogen should be dictated by your end goal. The balance is delicate and requires precise control over the CVD process parameters.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible crystal quality: You must meticulously tune the hydrogen concentration to maximize the removal of amorphous carbon while minimizing damage to the graphene sheet.
- If your primary focus is controlling grain size: The hydrogen-to-methane ratio will be your most critical parameter, as it directly governs the nucleation and growth dynamics of the graphene domains.
- If you are troubleshooting poor-quality graphene: Investigate your hydrogen flow as a primary cause; too little may leave impurities, while too much may be creating defects.
Mastering the role of hydrogen transforms graphene growth from a simple deposition into a precise materials engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Hydrogen Function | Impact on Graphene Growth | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Promotes Deposition | Creates active sites on the substrate for carbon atoms to form the graphene lattice. | Essential for initiating growth. |
| Removes Impurities | Etches amorphous carbon, leading to a more uniform and crystalline film. | Improves final material quality. |
| Controls Grain Morphology | Influences the size and shape of graphene grains by adjusting the H₂/C ratio. | Determines film characteristics. |
| Risk of Over-Etching | High concentrations can damage the graphene lattice, creating defects and holes. | Requires precise control to avoid quality degradation. |
Master Your Graphene Synthesis Process
Harnessing the dual role of hydrogen is key to producing high-quality, uniform graphene films. The precise balance between promoting growth and preventing etching requires expert control over Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) parameters.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science research, including precise gas delivery systems essential for controlled CVD processes. Whether you are optimizing for maximum crystal quality, specific grain size, or troubleshooting defects, the right tools make the difference.
Let our experts help you achieve your synthesis goals. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your graphene research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is zirconia fiber wool utilized in high-temperature CVD systems to improve insulation and safety?
- What are the techniques used in graphene synthesis? Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Methods Explained
- What are the physical properties of carbon nanotubes? Unlock Unmatched Strength & Conductivity
- What are sputtering targets made of? From Pure Metals to Ceramics for Your Thin Film
- What are the precursors for carbon nanotubes? Optimize Your CNT Synthesis for Cost and Efficiency
- How is plasma formed in sputtering? Ignite a Stable Plasma for Superior Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps in thin film formation? Master the Atomic-Level Process for Superior Coatings
- What is the unit of deposition rate? Mastering Thin-Film Control for Precision Manufacturing



















