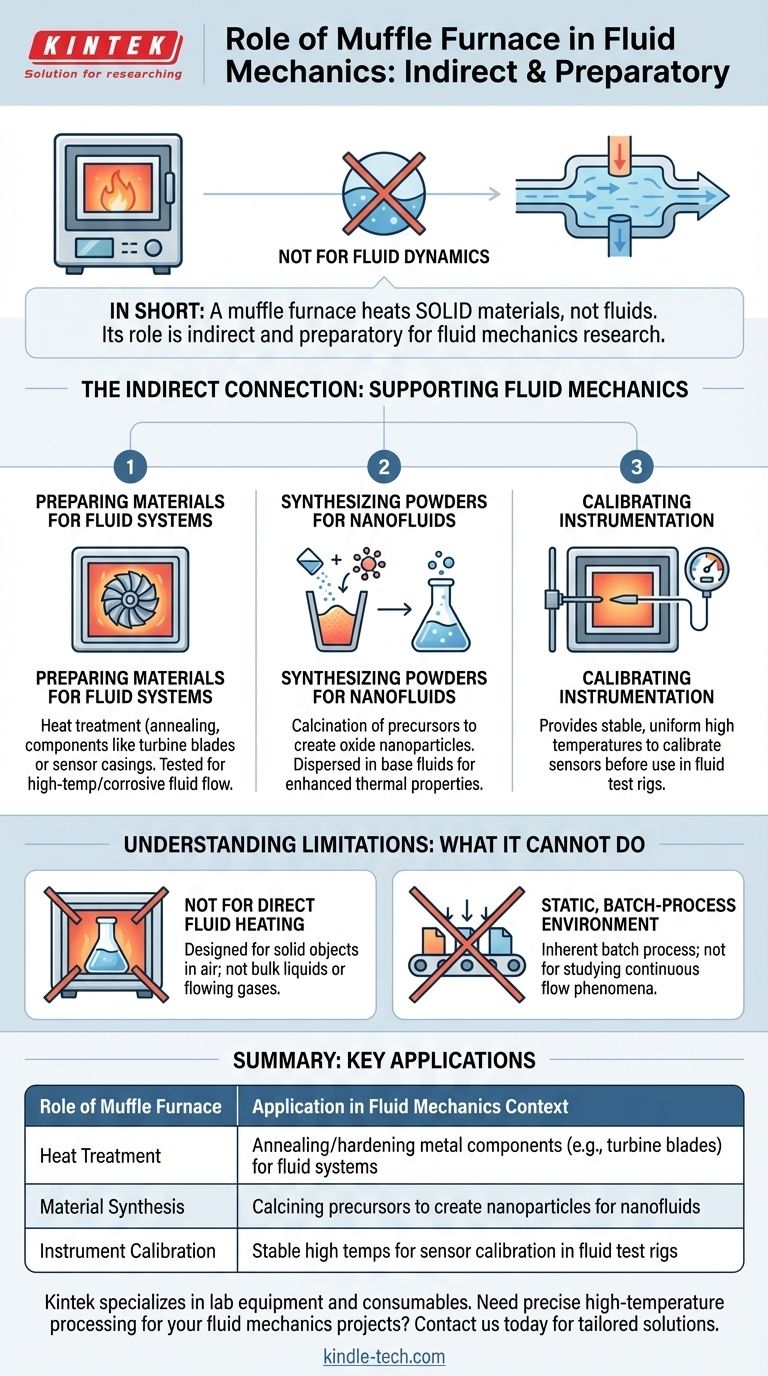
In short, a muffle furnace has no direct operational role within the field of fluid mechanics. Its function is to heat solid materials to very high temperatures in a controlled chamber, a process fundamentally separate from the study of fluid motion, pressure, and flow.
A muffle furnace is not a tool for studying fluid dynamics. Instead, its role is indirect and preparatory, primarily used in materials science to create or test components that will later be used in fluid systems.

What is a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is a type of high-temperature oven. Its defining feature is a "muffle," an insulated chamber that separates the material being heated from the heating elements and any combustion byproducts.
Modern electric furnaces use this principle to create a self-contained, energy-efficient cabinet for rapid heating and cooling.
The Principle of Operation
A muffle furnace operates by converting electrical energy into heat. This is achieved through Joule heating, where an electric current passes through high-resistance heating elements (often made of Nichrome).
These elements heat the chamber walls through radiation and convection. The chamber, made of refractory material, holds the heat, allowing the temperature to rise and be precisely regulated.
Key Components
The system consists of three main parts:
- Heating Chamber: The insulated box containing the heating elements where the sample is placed.
- Insulation: Layers of ceramic or firebrick that prevent heat from escaping, ensuring efficiency and safety.
- Control System: A thermocouple measures the temperature, sending a signal to a PID controller. The controller then adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain the desired temperature accurately.
The Indirect Connection to Fluid Mechanics
While not a fluid dynamics tool, a muffle furnace is crucial in research and development that supports fluid mechanics applications. Its role is to prepare or test the solid materials that interact with fluids.
Preparing Materials for Fluid Systems
Engineers use muffle furnaces for the heat treatment of metal components like turbine blades, valve bodies, or sensor casings.
This process—such as annealing or hardening—alters the material's microstructure. The component is then tested to see how its new properties withstand the stresses of high-temperature or corrosive fluid flow.
Synthesizing Powders for Nanofluids
A critical application is in the creation of nanofluids. A muffle furnace is used for the calcination (high-temperature decomposition) of chemical precursors to synthesize oxide nanoparticles.
These engineered nanoparticles are then dispersed into a base fluid (like water or glycol). The resulting nanofluid has enhanced thermal properties, and its behavior is then studied using the principles of fluid mechanics and heat transfer.
Calibrating Instrumentation
To accurately measure temperature in a high-velocity fluid, sensors like thermocouples must be precisely calibrated. A muffle furnace provides the stable, uniform, high-temperature environment needed to perform this calibration before the sensor is installed in a fluid test rig.
Understanding the Limitations
Recognizing what a muffle furnace cannot do is as important as understanding its function. It is a specialized tool with clear boundaries.
Not for Direct Fluid Heating
A muffle furnace is designed to heat solid objects placed inside its chamber, typically in air. It is not designed to heat bulk liquids or flowing gases directly. For that, tools like immersion heaters, heat exchangers, or heated flow loops are required.
Static, Batch-Process Environment
The furnace provides a static heating environment. You place a sample inside, heat it for a period, and remove it. It is inherently a batch process and cannot be used to study phenomena related to continuous flow.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The key is to determine if your task involves preparing a material or studying the fluid itself.
- If your primary focus is preparing a material for a fluid environment: A muffle furnace is the correct tool for heat treatment, ashing, or material synthesis before you expose it to fluid flow.
- If your primary focus is creating enhanced thermal fluids: Use a muffle furnace to synthesize the nanoparticle powders that you will later disperse into a base fluid to create a nanofluid.
- If your primary focus is studying fluid flow dynamics: A muffle furnace is not the right tool; you need equipment like a wind tunnel, water tunnel, or a dedicated flow loop.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is a materials processing tool that prepares the actors, not a stage for the fluid dynamics performance itself.
Summary Table:
| Role of Muffle Furnace | Application in Fluid Mechanics Context |
|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing or hardening metal components (e.g., turbine blades) for fluid systems |
| Material Synthesis | Calcining precursors to create nanoparticles for nanofluids |
| Instrument Calibration | Providing stable high temperatures for sensor calibration in fluid test rigs |
Need precise high-temperature processing for your fluid mechanics projects? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable muffle furnaces for heat treatment, material synthesis, and calibration. Enhance your R&D efficiency with our tailored solutions—contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating
- How hot does a furnace get in Celsius? From 1100°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? Discover the Precision Engineering for Pure, Controlled Heating
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing



















