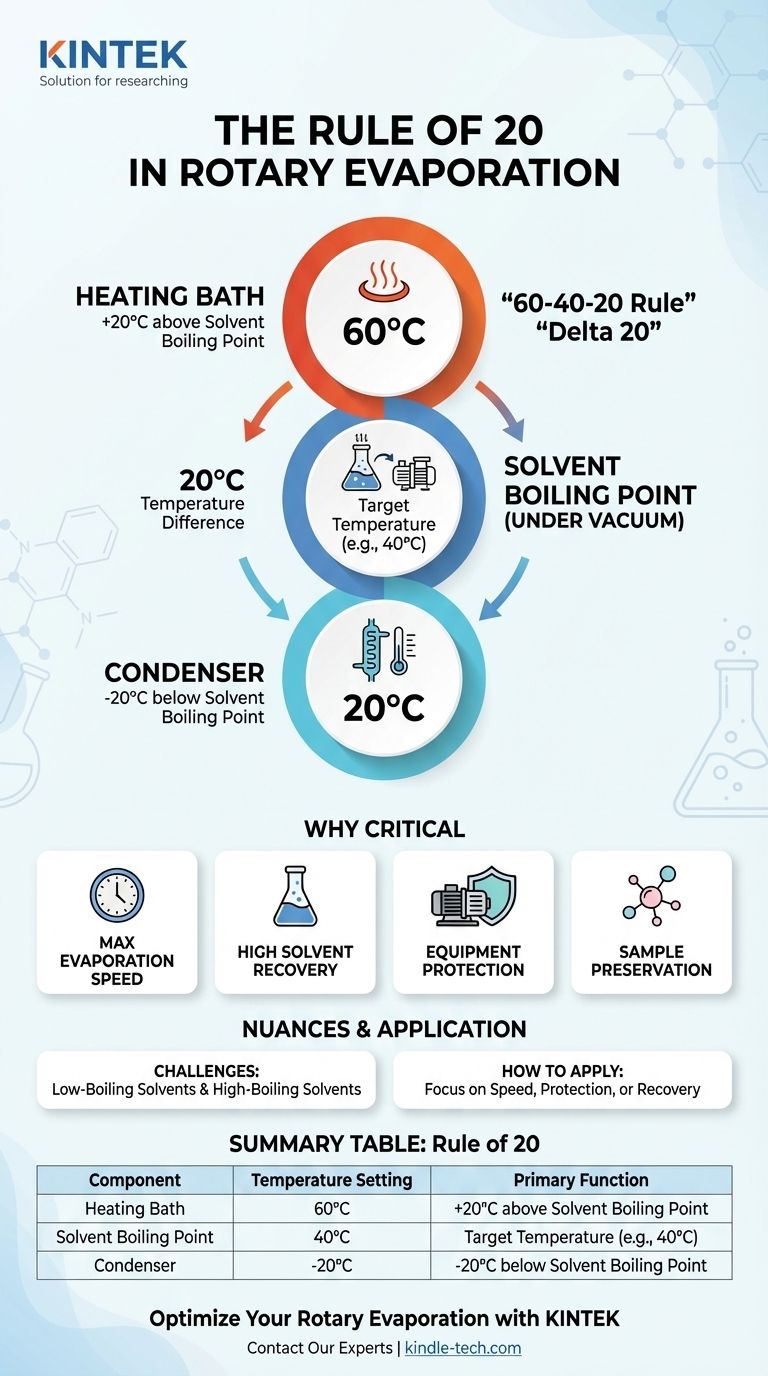
The "Rule of 20" is a foundational guideline for safely and efficiently operating a rotary evaporator (rotovap). It dictates that you should maintain a 20°C temperature difference between three critical points: the heating bath, the solvent's boiling point under vacuum, and the condenser. Adhering to this creates the optimal temperature gradients needed for rapid evaporation and near-complete solvent recovery.
At its core, the Rule of 20 isn't just a set of numbers; it's a framework for controlling energy flow. It ensures you are adding heat fast enough to vaporize your solvent while removing heat effectively enough to condense and recover it.
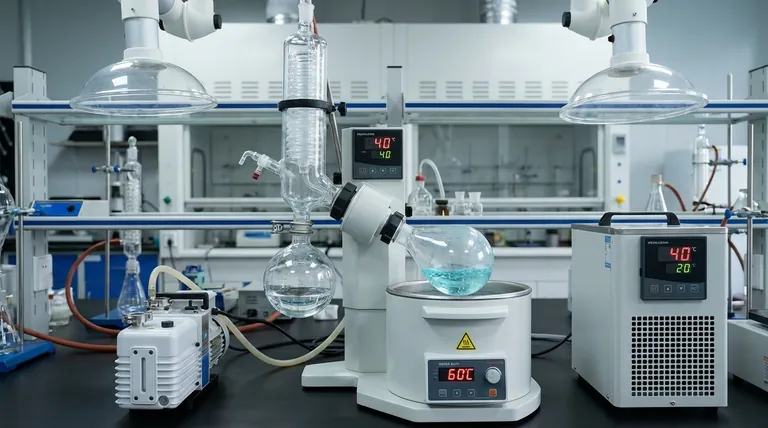

The Three Pillars of the Rule of 20
The rule is best understood as a sequence of three temperatures, each separated by 20°C. This is often called the "Delta 20" principle.
H3: The Heating Bath Temperature
The bath provides the energy (latent heat of vaporization) required to turn the liquid solvent into a gas.
The Rule: Set the bath temperature 20°C warmer than the desired boiling point of your solvent.
This 20°C gradient provides a strong driving force for rapid evaporation without applying excessive, uncontrolled heat that could lead to "bumping" or decomposition of your sample.
H3: The Solvent Boiling Point (Under Vacuum)
This is the central variable you control. The boiling point of a solvent drops significantly as you reduce the pressure with a vacuum pump.
The Rule: This is your target temperature. For many common organic solvents, a target boiling point of 40°C is a good starting point as it is gentle on most compounds.
To achieve this, you must adjust the vacuum level until the solvent begins to boil at your target temperature. This requires a vacuum controller or careful manual adjustment while observing the process.
H3: The Condenser Temperature
The condenser's job is to remove the heat from the solvent vapor, turning it back into a liquid so it can be collected.
The Rule: Set the condenser's coolant temperature 20°C colder than the solvent's boiling point.
If your solvent is boiling at 40°C, your condenser should be at 20°C or cooler. This ensures efficient condensation, maximizes solvent recovery, and prevents solvent vapor from escaping into the vacuum pump or the lab atmosphere.
A common application of this is the "60-40-20 Rule":
- Heating bath at 60°C
- Solvent boils at 40°C (by adjusting vacuum)
- Condenser at 20°C
Why This Rule Is Critical for Your Work
Following this guideline moves you from guessing to a controlled, reproducible process. It directly impacts your results, safety, and equipment longevity.
H3: Maximizing Evaporation Speed
The 20°C difference between the bath and the flask ensures a constant, high rate of energy transfer, leading to faster evaporation. A smaller difference would slow down the process significantly.
H3: Ensuring High Solvent Recovery
The 20°C difference between the vapor and the condenser is the most critical factor for solvent recovery. If the condenser is too warm, vapor will pass right through it, resulting in solvent loss.
H3: Protecting Your Equipment
Solvent vapor that bypasses the condenser will enter your vacuum pump. This can contaminate pump oil, corrode pump components, and significantly shorten the lifespan of an expensive piece of equipment.
H3: Preserving Heat-Sensitive Samples
The rule allows you to work at the lowest practical temperature. If your compound is unstable above 30°C, you can set that as your target boiling point and adjust the vacuum, bath, and condenser temperatures accordingly (e.g., Bath at 50°C, Condenser at 10°C).
Understanding the Nuances and Trade-offs
While the Rule of 20 is a powerful tool, it's a guideline, not an unbreakable law. Real-world chemistry requires you to understand its limits.
H3: Is It a "Rule" or a "Guideline"?
Think of it as an optimized starting point. You can deviate, but you must understand the consequences. Using a 30°C bath-to-solvent gradient may speed things up but increases the risk of bumping. Using only a 10°C solvent-to-condenser gradient will slow condensation and lower your recovery rate.
H3: The Challenge of Low-Boiling Solvents
For solvents like dichloromethane (DCM) or diethyl ether, their boiling points are very low even at modest vacuum. If you want DCM to boil at 20°C, the rule suggests a condenser at 0°C, which is achievable. If you need it to boil colder, you may need a powerful, costly chiller to maintain the 20°C differential.
H3: The Reality of High-Boiling Solvents
For solvents like water or DMSO, you need a very deep vacuum to achieve a reasonable boiling point (e.g., 50-60°C). While the rule still applies (e.g., bath at 70°C for a 50°C boil), the primary challenge becomes the quality of your vacuum pump, not the temperature settings.
H3: The "Bumping" Problem
Violent, uncontrolled boiling (bumping) can cause you to lose your valuable sample into the rest of the apparatus. This is often caused by too much heat being applied too quickly (a gradient > 20-25°C) or the flask being more than half full. The Rule of 20 helps provide a controlled rate of boiling, minimizing this risk.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Use the Rule of 20 as a strategic tool to meet your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed: Use the full +20°C differential for the bath and ensure your chiller is powerful enough to maintain the -20°C differential for the condenser.
- If your primary focus is protecting a fragile compound: Determine the maximum safe temperature for your sample first. Set this as your target boiling point and adjust the vacuum, bath, and condenser to match the Rule of 20.
- If your primary focus is solvent recovery (cost/environmental): Prioritize the -20°C solvent-to-condenser differential above all else. It is better to evaporate slightly slower than to lose solvent to the pump and atmosphere.
- If you are working with a challenging solvent: Recognize that you may need to compromise. With low-boiling solvents, you may need a more powerful chiller. With high-boiling solvents, you need a better vacuum pump.
By understanding these principles, you move from simply following a rule to strategically controlling the entire evaporation process.
Summary Table:
| Rule of 20 Component | Temperature Setting | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Bath | +20°C above solvent boiling point | Provides energy for vaporization |
| Solvent Boiling Point (Under Vacuum) | Target temperature (e.g., 40°C) | Controlled evaporation point |
| Condenser | -20°C below solvent boiling point | Condenses vapor back to liquid for recovery |
Optimize Your Rotary Evaporation Process with KINTEK
Mastering the Rule of 20 is just the beginning. Whether you're working with heat-sensitive compounds, prioritizing solvent recovery, or handling challenging solvents, having the right equipment is crucial for success.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables designed to meet the exacting demands of modern laboratories. Our rotary evaporators, vacuum controllers, and chilling systems are engineered to help you maintain the precise temperature gradients required for efficient and safe solvent removal.
Let us help you achieve:
- Faster evaporation rates with precise temperature control
- Near-complete solvent recovery to reduce costs and environmental impact
- Enhanced sample protection for delicate compounds
- Longer equipment lifespan by preventing solvent contamination
Ready to elevate your evaporation process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can deliver superior results for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a rotary vane mechanical vacuum pump necessary for sub-surface etching? Ensure Precision in ALD/ALE Experiments
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- How does a Rotary Vane Pump operate? Discover Efficient Vacuum Technology for Your Lab
- What are the limitations of rotary vane pumps? Understanding Oil Dependence and Gas Compatibility
- What is a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Efficiency and Performance for Laboratory Vacuum Systems



















