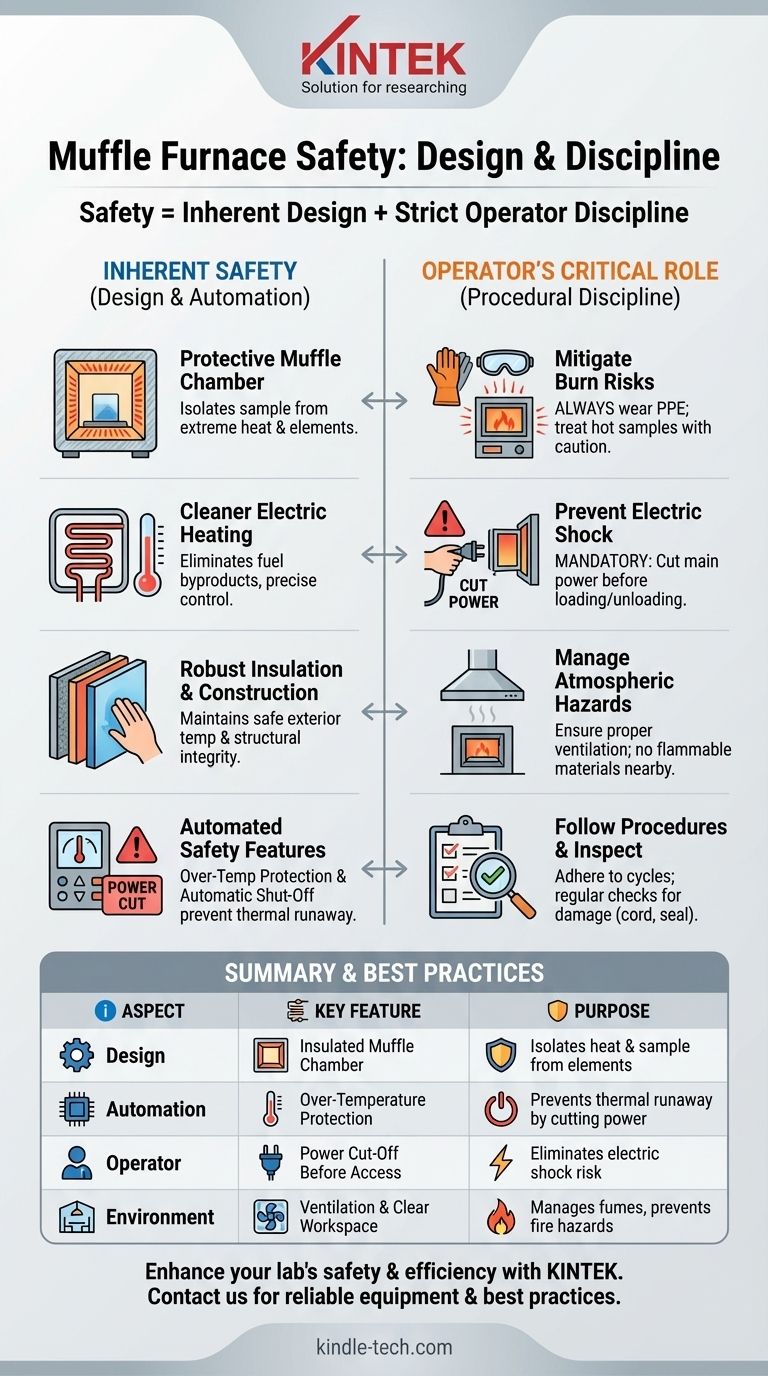
Fundamentally, a modern muffle furnace is designed to be safe, but this safety is entirely conditional on proper use. Its engineering incorporates multiple protective layers and automated controls to contain extreme heat. However, the high temperatures involved mean that operator error or negligence can lead to severe accidents, making procedural discipline absolutely critical.
A muffle furnace's safety relies on two pillars: its inherent design that isolates extreme heat and its automated controls. However, ultimate safety is only achieved when operators adhere to strict procedural discipline, treating the equipment with the respect its high-temperature capabilities demand.
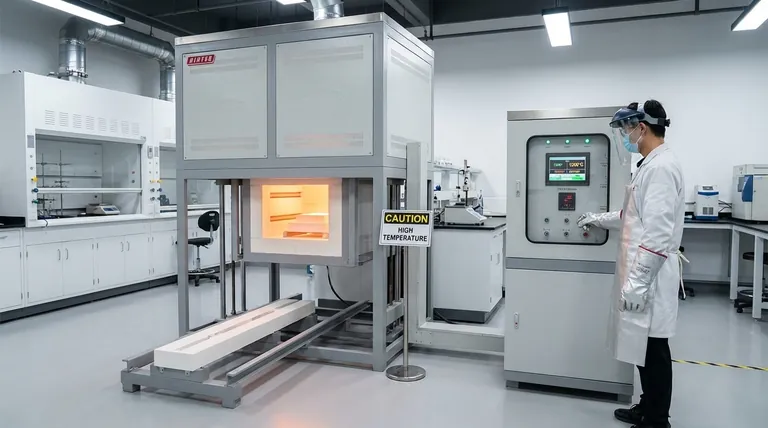

How Design Creates an Inherently Safe Environment
A furnace's safety begins with its core architecture. The design is intended to contain extreme energy and provide a stable, predictable environment for both the sample and the operator.
The Protective 'Muffle' Chamber
The key feature is the "muffle" itself—an insulated, airtight chamber where the sample is placed. This design isolates the sample from the raw heating elements.
This separation prevents direct contact with electrical components and, in older fuel-fired models, keeps combustion byproducts from contaminating the sample.
Electric Heating for a Cleaner Process
Modern electric furnaces use high-resistance heating elements. This design is inherently safer than combustion because it eliminates fuel sources and their associated byproducts from the lab environment.
It also allows for exceptionally precise temperature control, reducing the risk of unexpected temperature spikes.
Robust Construction and Insulation
The furnace is built with a heavy-duty outer casing, typically steel, and layers of high-quality refractory insulation.
This multi-layer construction serves a primary safety function: to keep the outer surfaces of the furnace at a safe temperature and ensure structural integrity even when the interior is over 1000°C.
Built-in Automated Safety Features
Beyond its physical construction, a muffle furnace relies on automated systems to prevent common failure scenarios.
Over-Temperature Protection
This is arguably the most critical automated safety feature. A thermocouple constantly measures the internal temperature.
If the controller detects a temperature that exceeds a preset safety limit, it will automatically cut power to the heating elements, preventing a thermal runaway event.
Automatic Shut-Off Mechanisms
Many furnaces include additional safety interlocks. For example, a system may be designed to shut off power if the door is opened during a heating cycle.
These features are designed to protect the operator from immediate exposure to extreme heat and electrical hazards.
Simple Controls to Minimize Error
Ease of operation is a subtle but important safety feature. Clear digital displays, intuitive controls, and simple programming reduce the likelihood of user error.
When operators can set and monitor a heating program with confidence, the risk of accidental misconfiguration drops significantly.
Understanding the Primary Risks
To operate a furnace safely, you must have a clear understanding of the primary hazards involved.
The Risk of Severe Burns
The most obvious danger is the extreme heat. Temperatures inside can easily exceed 1000°C (1832°F). Any direct contact with the interior or improper handling of hot samples will cause immediate and severe burns.
Always wear appropriate heat-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and other personal protective equipment (PPE).
The Hazard of Electric Shock
A muffle furnace is a high-power electrical device. A critical and non-negotiable safety rule is to always cut the main power supply before loading or unloading samples.
Relying solely on the door being open is not sufficient. This prevents any risk of accidental contact with live electrical components.
Atmospheric and Material Hazards
The furnace itself may not produce fumes, but the sample you are heating might. Always ensure the furnace is used in a well-ventilated area or under an exhaust system to safely vent any gases or fumes produced by the sample.
Never place flammable, combustible, or explosive materials inside or near the furnace. The interior temperature will ignite them, and heat radiating from the furnace can ignite nearby items.
The Operator's Critical Role in Safety
A safe design is only half of the equation. The operator is responsible for following strict procedures to mitigate risk during every stage of use.
Before Operation: Preparation is Key
Before turning the furnace on, inspect the equipment for any visible damage, particularly to the power cord and door seal.
Ensure the furnace is on a stable, level surface and that the area around it is completely clear of combustible materials. Confirm that the electrical connection is properly grounded.
During Operation: Procedural Discipline
Adhere strictly to the programmed heating and cooling cycles. Avoid overloading the chamber, as this can lead to uneven heating and potential damage.
Never attempt to open the door to check on a sample while the furnace is at high temperature unless it is part of a specific, approved procedure.
After Operation: Safe Shutdown and Maintenance
After a cycle is complete, turn off the main power. Allow the furnace to cool down naturally; attempting to cool it rapidly can cause thermal shock and damage the insulating chamber.
Keep the furnace clean and perform regular checks as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure all components, especially safety features, are functioning correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to safety will depend on whether you are buying, using, or maintaining a furnace.
- If your primary focus is routine use and operator training: Prioritize strict adherence to procedure, especially the use of PPE and the rule to cut all power before accessing the chamber.
- If your primary focus is purchasing a new furnace: Look for models with certified over-temperature protection, robust door seals, and high-quality insulation.
- If your primary focus is maintaining existing equipment: Establish a schedule for regularly inspecting the thermocouple, door gaskets, and electrical wiring for wear and tear.
By respecting the furnace's power and adhering to disciplined procedures, you can ensure a safe and effective operational environment.
Summary Table:
| Safety Aspect | Key Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Insulated Muffle Chamber | Isolates extreme heat and sample from elements |
| Automation | Over-Temperature Protection | Prevents thermal runaway by cutting power |
| Operator Role | Power Cut-Off Before Access | Eliminates risk of electric shock during loading/unloading |
| Environment | Ventilation & Clear Workspace | Manages sample fumes and prevents fire hazards |
Ensure your lab operates with maximum safety and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable muffle furnaces with advanced safety features tailored to laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and establish best practices for secure operation. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your lab's safety protocol!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is ash content determined using muffle furnace? Achieve Accurate Mineral Analysis
- In which industry is the muffle furnace used? Discover Its Role in Science and Industry
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What is the theory of calcination? Master Precise Thermal Decomposition for Your Materials
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? How to adapt it for oxygen-free thermal decomposition



















