In essence, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a compact of powdered material into a solid, dense object using heat and pressure. Crucially, this is achieved without melting the primary material, allowing for the creation of parts from metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points.
The core principle of sintering is to heat a shaped powder compact to a high temperature, just below its melting point. This heat energizes the atoms, causing them to diffuse across the surfaces of the particles, fusing them together and dramatically reducing the internal porosity of the material.

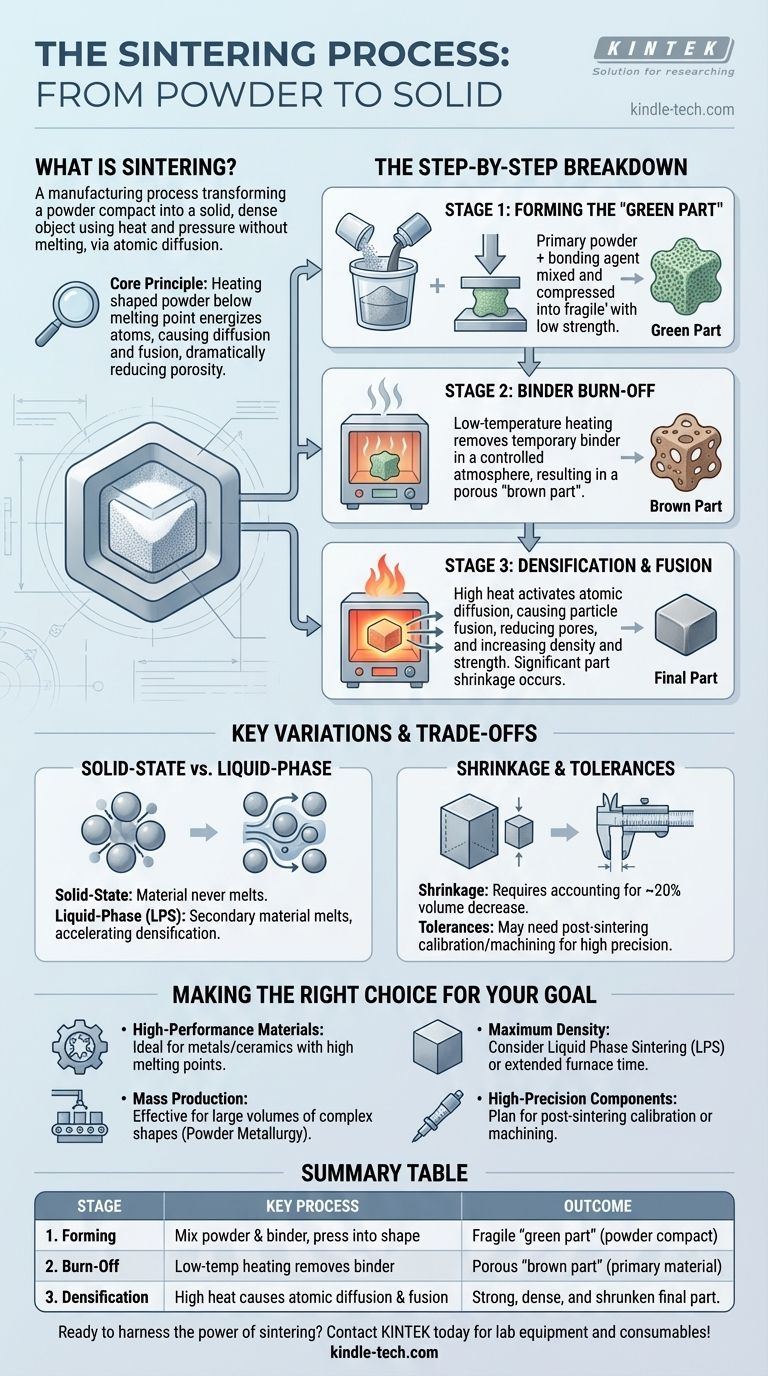
The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Sintering is not a single action but a sequence of carefully controlled stages. Each step is critical to transforming loose powder into a strong, functional component.
Stage 1: Forming the "Green Part"
The process begins by creating an initial, fragile version of the final component, often called a "green part" or "powder compact."
A primary powder, which is the base material of the final part, is mixed with a temporary bonding agent. This binder can be wax, a polymer, or another substance that temporarily holds the powder particles together.
This mixture is then compressed into the desired shape using methods like pressing tools, molds, or even 3D printing techniques. The resulting green part is solid enough to be handled but has low strength and high porosity.
Stage 2: Binder Burn-Off
Once the green part is formed, it enters a furnace with a controlled atmosphere for the heating cycle.
The initial phase of heating occurs at a relatively low temperature. The primary goal here is to carefully burn away or evaporate the temporary bonding agent that was used to form the green part.
After the binder is eliminated, the part is often referred to as a "brown part." It remains porous and fragile, consisting only of the primary material powder.
Stage 3: Densification and Fusion
This is the core of the sintering process where the material gains its final strength and density.
The temperature in the furnace is raised significantly, approaching but not reaching the melting point of the primary material. This high heat activates a process called atomic diffusion.
Atoms migrate across the surfaces of the individual powder particles, causing the contact points between them to grow and eventually fuse. This fusion pulls the particle centers closer together, systematically eliminating the pores between them.
The result is a single, unified mass with significantly higher density and strength. The part shrinks in size as this densification occurs.
Understanding the Key Variations and Trade-offs
While the principle remains the same, understanding the nuances of sintering is key to controlling the final properties of the part. This process inherently involves trade-offs between cost, precision, and material performance.
Solid-State vs. Liquid-Phase Sintering
The primary method described is solid-state sintering, where the main material never melts.
A common variation is Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS). In this technique, a secondary material with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. During heating, this secondary material melts and flows into the gaps between the solid primary particles, acting as a powerful bonding agent that accelerates densification.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
A fundamental consequence of sintering is part shrinkage. As the pores are eliminated and the material densifies, the overall volume of the component decreases.
This shrinkage can be substantial, often around 20%, and must be accounted for during the initial design of the green part's mold or shape.
Achieving Tight Tolerances
Because of the inherent shrinkage, achieving precise final dimensions directly from the furnace can be difficult.
If a part requires very tight tolerances, a post-sintering calibration step is often necessary. This may involve re-pressing the cooled part in a highly accurate die to fine-tune its final dimensions or performing secondary machining operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying sintering effectively requires aligning the process with your specific manufacturing objectives.
- If your primary focus is working with high-performance materials: Sintering is the ideal choice for metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points (like tungsten or carbides) that are difficult or impossible to process with traditional casting.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex shapes: Powder metallurgy, which relies on sintering, is highly effective for creating large volumes of small, intricate metal parts with good dimensional consistency.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum part density: Consider using Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) or extending the time and temperature in the furnace to minimize residual porosity and create a stronger final component.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components: You must plan for secondary operations like calibration or machining after the sintering stage to meet tight dimensional tolerances.
Ultimately, sintering is a powerful manufacturing tool that enables the creation of robust components from powdered materials by fundamentally altering their internal structure.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Forming | Powder is mixed with a binder and pressed into a "green part." | A fragile, shaped powder compact. |
| 2. Burn-Off | Low-temperature heating removes the temporary binder. | A porous "brown part" of primary material. |
| 3. Densification | High heat causes atomic diffusion, fusing particles together. | A strong, dense, and shrunken final part. |
Ready to harness the power of sintering for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables that make advanced processes like sintering possible. Whether you are developing new materials or mass-producing complex components, our expertise and high-quality solutions are designed to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with reliable equipment and consumables, ensuring you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What causes hydraulic pressure spikes? Prevent System Damage from Hydraulic Shock
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- How is the pressure and temperature process used to make a synthetic diamond? Replicate Earth's Diamond Formation in a Lab
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating



















