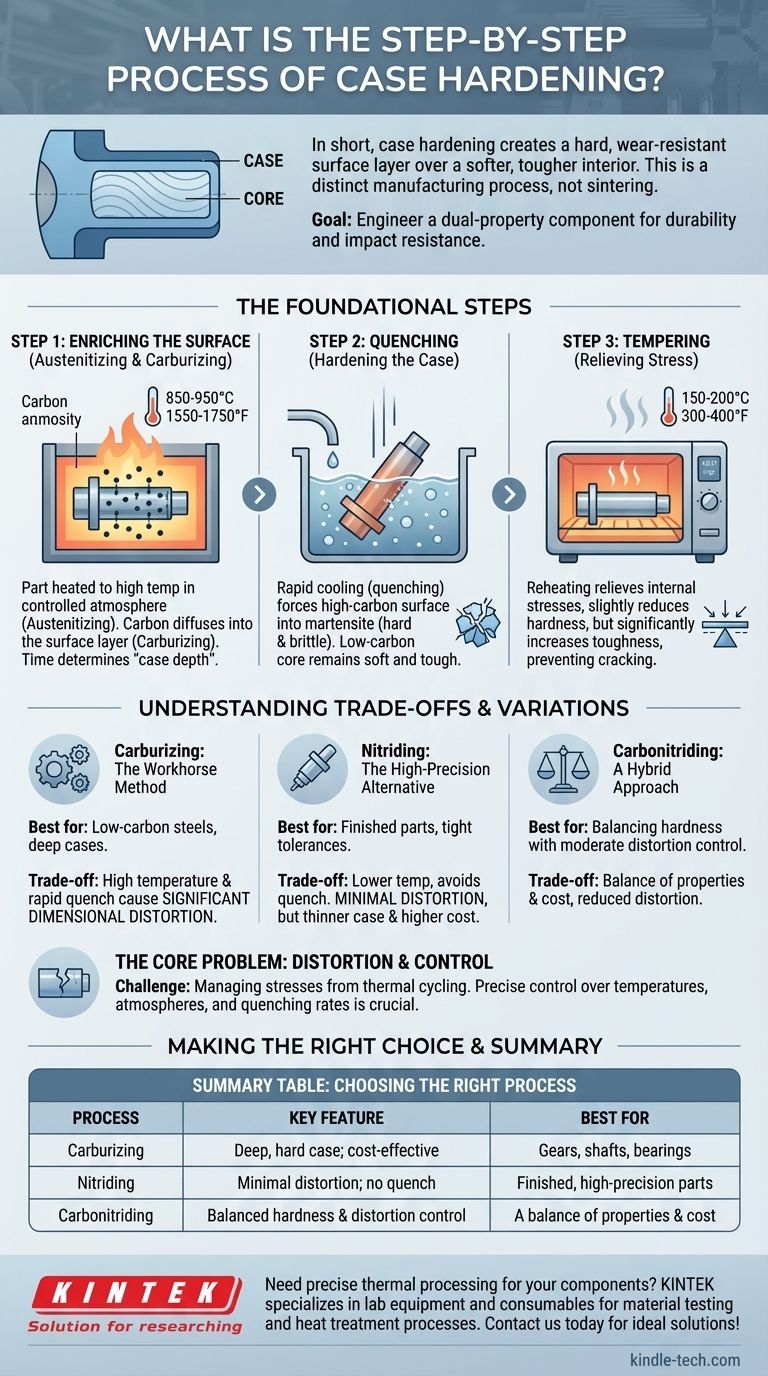
In short, case hardening is a heat treatment process that creates a hard, wear-resistant surface layer (the "case") over a softer, tougher interior (the "core"). This is a distinct manufacturing process and should not be confused with metal sintering—the subject of the provided references—which involves fusing metal powders together to form a solid part.
The fundamental goal of case hardening is to engineer a dual-property component. It imbues a metal part with a highly durable surface to resist wear and abrasion, while preserving a ductile, shock-absorbent core to prevent catastrophic failure under impact.
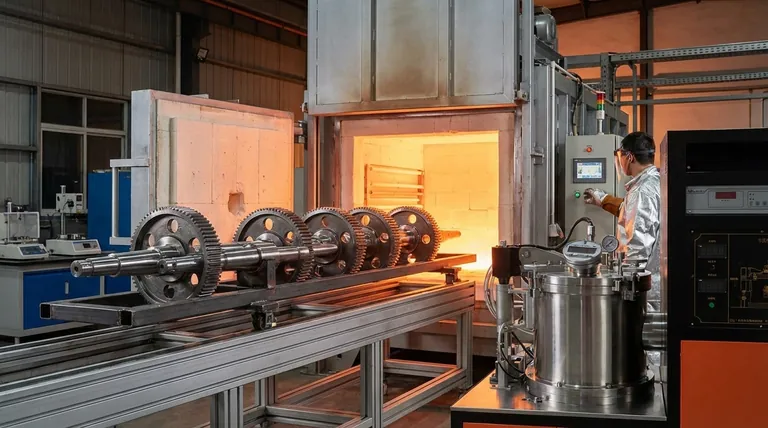

The Foundational Steps of Case Hardening
Case hardening is not a single action but a sequence of controlled thermal and chemical processes. The most common method, especially for low-carbon steels, involves three critical stages.
Step 1: Enriching the Surface (Austenitizing & Carburizing)
The first step is to change the chemical composition of the part's surface. The metal, typically a low-carbon steel, is heated to a high temperature (around 850-950°C or 1550-1750°F) in a controlled atmosphere.
At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure changes to austenite, which can readily absorb more carbon. The part is held at this temperature in an environment rich in carbon. This process, called carburizing, allows carbon atoms to diffuse into the surface layer of the steel. The longer the part is held, the deeper the carbon penetrates, determining the "case depth."
Step 2: Quenching (Hardening the Case)
Once the surface has absorbed enough carbon, the part is rapidly cooled, or quenched, by submerging it in a medium like oil, water, or brine.
This rapid cooling forces the high-carbon surface layer (the austenite) to transform into martensite, an extremely hard and brittle crystal structure. The low-carbon core, however, does not harden as dramatically, remaining relatively soft and tough.
Step 3: Tempering (Relieving Stress)
The quenching process leaves the hardened case in a state of high internal stress, making it very brittle. To counteract this, the part is tempered.
Tempering involves reheating the component to a much lower temperature (typically 150-200°C or 300-400°F) and holding it for a set time. This process relieves the internal stresses and slightly reduces the hardness of the case, but significantly increases its toughness, preventing it from chipping or cracking in service.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While carburizing is the most common method, several variations and alternatives exist, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Carburizing: The Workhorse Method
Carburizing is highly effective for low-carbon steels and is relatively cost-efficient for creating deep, hard cases. However, the high temperatures and subsequent rapid quench can introduce significant dimensional distortion, which may require final grinding or machining.
Nitriding: The High-Precision Alternative
Nitriding achieves a similar result by diffusing nitrogen—not carbon—into the surface. A key advantage is its lower process temperature, which completely avoids the quenching step. This results in minimal distortion, making it ideal for finished parts with tight tolerances. The trade-off is often a thinner case and potentially higher cost.
Carbonitriding: A Hybrid Approach
This process diffuses both carbon and nitrogen into the surface. It offers a balance of properties, often providing a harder case than carburizing at a lower temperature, which helps reduce but not eliminate distortion.
The Core Problem: Distortion and Control
The primary challenge in all case hardening is managing the stresses from thermal cycling. Uneven heating or cooling can cause parts to warp, bend, or even crack. Success depends on precise control over furnace atmospheres, temperatures, and quenching rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires understanding the final application of the component. Your decision should be guided by the part's operational demands.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and impact strength: Standard carburizing followed by quenching and tempering provides a deep, durable case with a tough core, ideal for gears, shafts, and bearings.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight dimensional tolerances: Gas nitriding is the superior choice, as the lack of a quench step results in minimal part distortion.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness with cost and moderate distortion control: Carbonitriding offers a compromise, delivering excellent surface hardness with less distortion than traditional carburizing.
By understanding these distinct processes, you can specify the precise treatment needed to achieve a component with the ideal balance of surface durability and core strength.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Carburizing | Deep, hard case; cost-effective | Gears, shafts, bearings |
| Nitriding | Minimal distortion; no quench | Finished, high-precision parts |
| Carbonitriding | Balanced hardness & distortion control | A balance of properties & cost |
Need precise thermal processing for your components? The right case hardening method is critical for part performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and heat treatment processes. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution to achieve the perfect balance of surface hardness and core toughness for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish



















