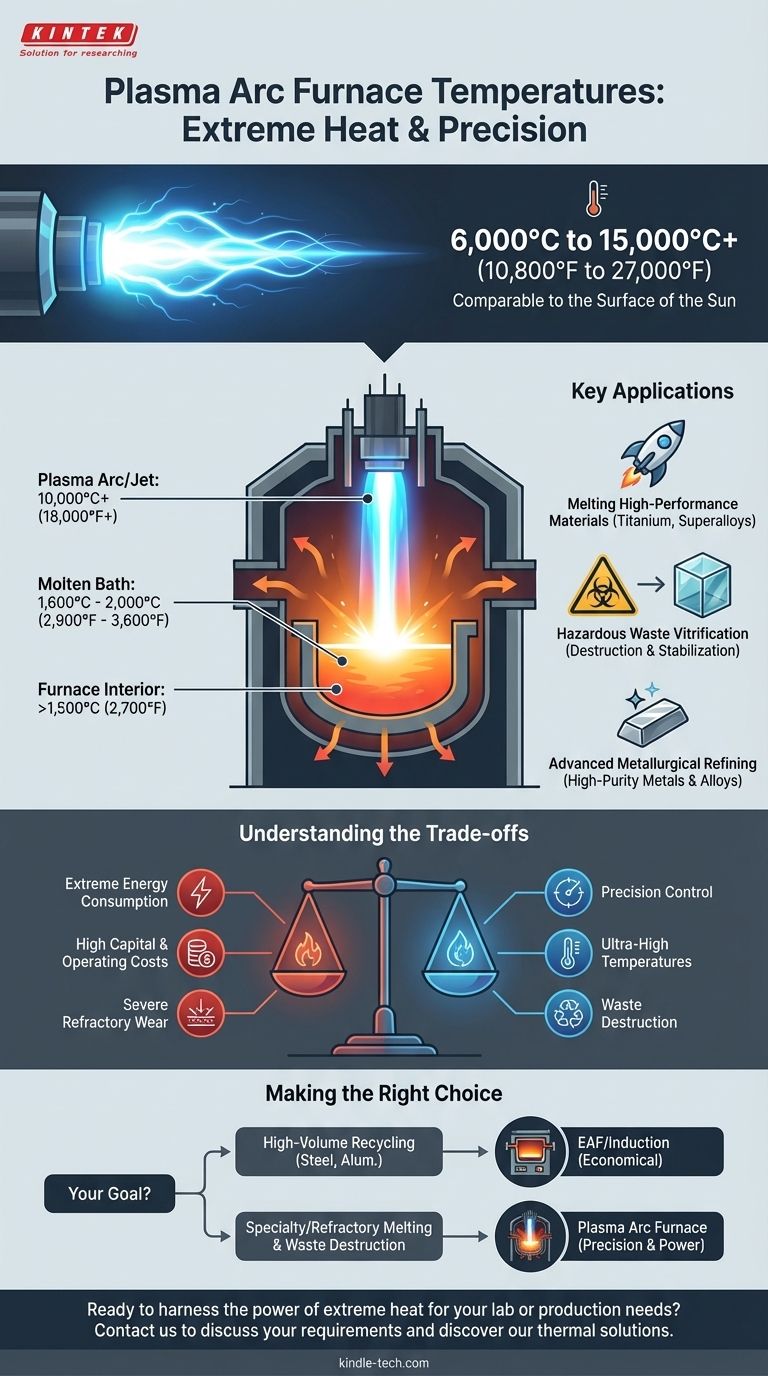
At its core, a plasma arc furnace operates at temperatures that defy conventional heating methods, with the plasma jet itself reaching from 6,000°C to over 15,000°C (10,800°F to 27,000°F). This is comparable to the surface temperature of the sun. However, this extreme heat is highly localized to the arc, while the molten material and furnace interior operate at different, lower temperatures.
The defining feature of a plasma arc furnace is not just its extreme heat, but its ability to deliver that heat with precision and control. This transforms it from a simple melting device into a sophisticated tool for advanced material processing and waste destruction.

How a Plasma Arc Achieves Extreme Temperatures
To understand the furnace, you must first understand the plasma. Plasma is the fourth state of matter, created when a gas is energized to the point where its electrons are stripped from their atoms, forming an ionized, electrically conductive gas.
The Principle of Plasma Generation
A plasma torch generates a high-voltage electric arc, similar to a lightning bolt, within a flow of gas (such as argon, nitrogen, or even air). This intense electrical energy superheats the gas, ionizing it and creating a focused plasma jet. The stability and temperature of this jet are precisely controlled by the power supply and gas flow rate.
Transferred vs. Non-Transferred Arcs
There are two primary configurations. A transferred arc is formed between the torch's electrode and the conductive material being heated (the "charge"). This method is incredibly efficient at delivering energy directly to the target, making it ideal for melting metals.
A non-transferred arc is contained entirely within the torch itself. The plasma is then expelled as a high-velocity jet of superheated gas. This is often used for applications like thermal spraying or destroying waste that is not electrically conductive.
The Anatomy of Heat in the Furnace
It is critical to understand that a plasma furnace does not have one single temperature. It has distinct thermal zones.
- The Plasma Arc/Jet: The core of the arc is the hottest point, reaching 10,000°C+. This is where the physics of ionization occurs.
- The Molten Bath: The material being melted, such as steel or titanium, typically resides at a temperature needed for its liquid state, often between 1,600°C and 2,000°C. The plasma arc acts as the heat source that maintains this temperature.
- The Furnace Interior (Freeboard): The space above the molten bath is significantly cooler than the arc but still incredibly hot, often holding temperatures well above 1,500°C.
Why This Level of Heat Matters: Key Applications
The unique capabilities of plasma arc heating enable processes that are difficult or impossible with conventional furnaces like electric arc (EAF) or induction furnaces.
Melting High-Performance Materials
The primary advantage is melting metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points. This includes titanium, nickel-based superalloys, and refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, which are essential for aerospace, defense, and medical applications.
Hazardous Waste Vitrification
Plasma heating is a definitive solution for destroying hazardous materials. The intense heat breaks down complex organic compounds, asbestos, and medical waste into their elemental components. These elements are then cooled and fused into a stable, non-leaching, glass-like solid called slag.
Advanced Metallurgical Refining
The combination of extreme heat and a controlled atmosphere allows for superior metallurgical refining. It enables the efficient removal of impurities and the production of high-purity metals and alloys with precisely controlled compositions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The exceptional capabilities of plasma technology come with significant operational considerations. It is not the right tool for every job.
Extreme Energy Consumption
Generating and sustaining a stable plasma arc requires a massive amount of electrical energy. This makes the process significantly more energy-intensive and costly per ton than a conventional Electric Arc Furnace used for standard steel recycling.
High Capital and Operating Costs
Plasma torches, their specialized power supplies, and the gas delivery systems are complex and expensive. Furthermore, the cost of plasma gases like argon can be a major operational expense, although some systems are designed to operate on air.
Severe Refractory Wear
The intense, focused heat of the plasma arc is extremely destructive to the refractory materials that line the furnace. This "refractory wear" is a primary operational challenge, leading to higher maintenance costs and downtime compared to other furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal technology depends entirely on your specific material and processing objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume recycling of standard metals like steel or aluminum: A conventional Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) or an induction furnace is almost always the more economical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is melting specialty alloys, titanium, or refractory metals: A plasma arc furnace provides the necessary temperature, control, and clean environment that other technologies cannot match.
- If your primary focus is the complete destruction of hazardous waste or creating ultra-pure materials: A plasma arc furnace is the definitive tool, offering a level of thermal decomposition and refining that is unparalleled.
Ultimately, a plasma arc furnace is best viewed not as a brute-force heater, but as a precision instrument for manipulating matter at its most fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Temperature Range | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Arc/Jet | 10,000°C+ (18,000°F+) | Ionization, extreme heating |
| Molten Material | 1,600°C - 2,000°C (2,900°F - 3,600°F) | Melting metals, alloys |
| Furnace Interior | >1,500°C (2,700°F) | Controlled atmosphere processing |
Ready to harness the power of extreme heat for your lab or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal solutions, including plasma arc furnaces designed for precision melting of high-performance alloys, refractory metals, and hazardous waste vitrification. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for superior material processing and control.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our lab equipment can elevate your research or production capabilities. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















