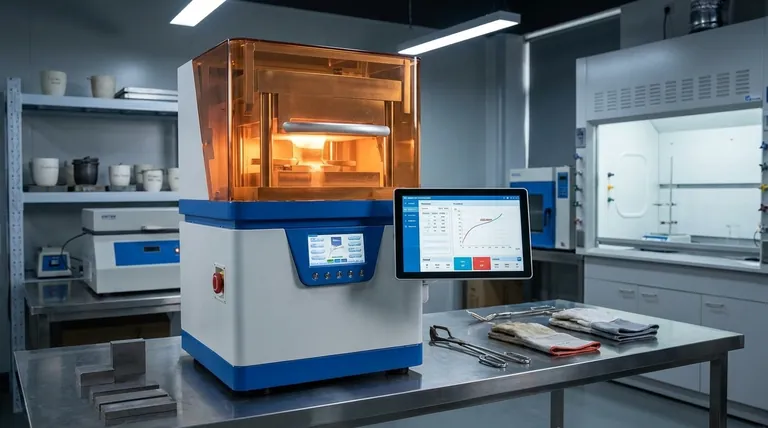
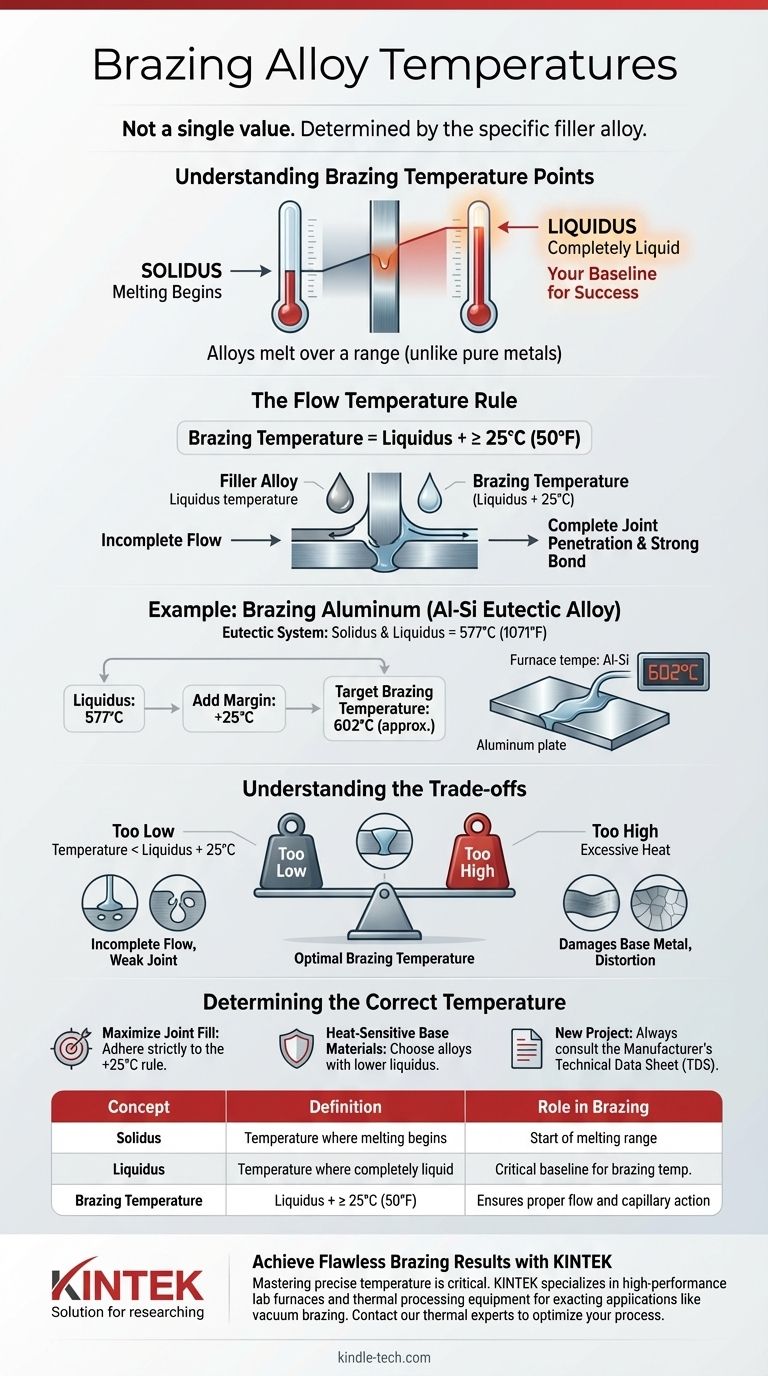
Brazing temperature is not a single value but is determined by the specific filler alloy being used. The correct brazing temperature is always set slightly above the alloy's liquidus temperature—the point at which it becomes completely liquid. As a rule, the target temperature should be at least 25°C (50°F) higher than the alloy's specified liquidus point to ensure it flows properly.
The core principle of brazing temperature is not to hit a universal number, but to precisely control heat based on the specific melting properties of your chosen filler alloy. Success depends on being hot enough for the alloy to flow freely without being so hot that you damage the base metals being joined.

What Defines a Brazing Temperature?
To properly control the brazing process, you must understand the two critical temperature points of any brazing alloy: the solidus and the liquidus.
The Role of Solidus and Liquidus
Unlike pure metals that melt at a single temperature, brazing alloys melt over a range. The solidus is the temperature at which the alloy begins to melt. The liquidus is the temperature at which the alloy becomes completely liquid.
The "Liquidus" Temperature: Your Baseline
The liquidus temperature is the most critical piece of information. This is the point where the filler metal has fully transitioned to a liquid state and can flow into the joint via capillary action.
The Flow Temperature Rule
To guarantee complete melting and promote good flow, the industry standard is to heat the assembly to a temperature at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus of the filler alloy. This buffer ensures the entire filler charge melts and has enough thermal energy to penetrate the joint completely.
A Practical Example: Brazing Aluminum
The principles of brazing temperature are best understood with a real-world example, such as vacuum brazing aluminum components.
The Al-Si Eutectic Alloy
A common filler for brazing aluminum is an aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloy. An alloy with 11.7% silicon is a eutectic system, which means its solidus and liquidus temperatures are the same: 577°C (1071°F).
Calculating the Brazing Temperature
Using our rule, we can determine the proper brazing temperature for this specific alloy. We take the liquidus temperature and add our safety margin.
- 577°C (Liquidus) + 25°C = 602°C (Brazing Temperature)
Therefore, the furnace or torch should be set to bring the entire assembly to approximately 602°C to ensure a successful joint with this particular filler.
Why This Alloy Works
This Al-Si alloy is chosen because its melting point (577°C) is significantly lower than that of the aluminum base metals being joined. This allows the filler to become fully liquid while the parent materials remain solid, which is the fundamental requirement of any brazing operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving the correct temperature is a balancing act. Deviating in either direction introduces significant risks to the quality and integrity of the joint.
Too Low: Incomplete Flow
If the brazing temperature does not sufficiently exceed the liquidus point, the filler metal will be sluggish. This results in incomplete capillary action, leaving voids and creating a weak, unreliable joint that will likely fail under stress.
Too High: Damaging the Base Metal
Excessive heat is equally dangerous. Overheating can lead to warping, distortion, or grain growth in the base metals, compromising their structural integrity. In a worst-case scenario, you can inadvertently melt the base metals, destroying the parts.
Determining the Correct Temperature for Your Project
Selecting the right temperature is a function of your materials and your goal. Use these principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum joint fill: Strictly adhere to the rule of setting your process temperature at least 25°C (50°F) above the alloy's liquidus to promote strong capillary flow.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive base materials: Choose a filler alloy with a lower liquidus temperature to minimize the thermal stress on the components being joined.
- If you are selecting a new alloy for a project: Always consult the manufacturer's Technical Data Sheet (TDS). It will provide the exact solidus and liquidus temperatures, which are the foundation for all your calculations.
Mastering these temperature relationships is the key to creating consistently strong and reliable brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Concept | Definition | Role in Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Solidus | Temperature where alloy begins to melt. | Marks the start of the melting range. |
| Liquidus | Temperature where alloy is completely liquid. | Critical baseline for setting brazing temperature. |
| Brazing Temperature | Liquidus + at least 25°C (50°F). | Ensures proper flow and capillary action for a strong joint. |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK
Mastering the precise temperature for your brazing alloy is critical for creating strong, reliable joints. Whether you're working with aluminum, high-temperature alloys, or other materials, the right equipment ensures consistent and accurate heat control.
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for exacting applications like vacuum brazing. Our solutions help you precisely reach and maintain the target temperature—safely above the liquidus point—to guarantee complete filler metal flow and perfect joints every time, while protecting your base materials from thermal damage.
Let us help you optimize your brazing process. Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect KINTEK solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification






