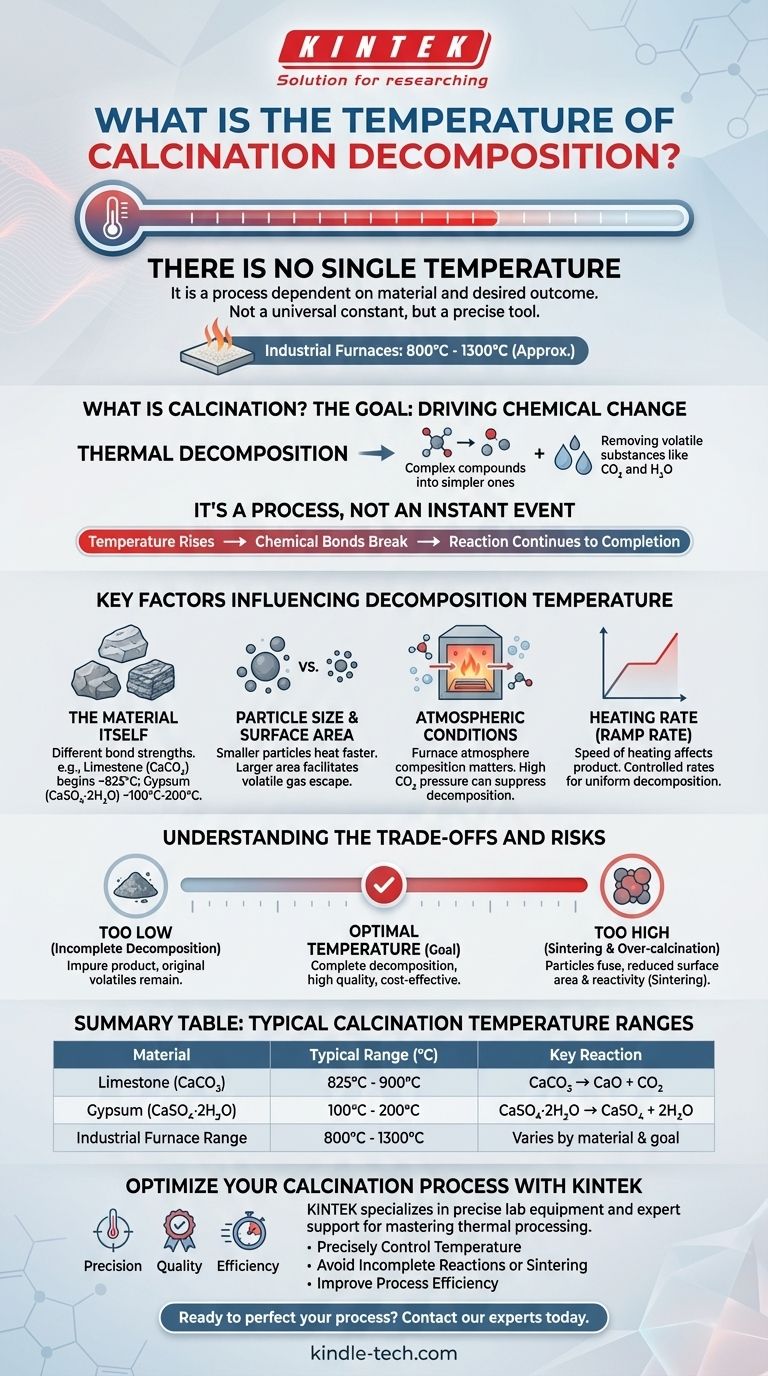
There is no single temperature for calcination decomposition. It is a process that occurs over a range of temperatures, entirely dependent on the specific material being heated and the desired outcome. While industrial calcination furnaces often operate between 800°C and 1300°C, the actual decomposition temperature for any given substance is a unique physical property.
Calcination temperature is not a universal constant but a variable that must be precisely controlled. The correct temperature is dictated by the chemical bonds within a specific material and the energy required to break them.

What is Calcination? A Deeper Look
To understand the temperature, you must first understand the purpose of the process. Calcination is a thermochemical treatment used to induce a chemical change in a material.
The Goal: Driving Chemical Change
The primary goal is thermal decomposition, which involves breaking down a complex compound into simpler ones by heating it.
This process is most often used to remove volatile substances that are chemically bound within the material's crystal structure, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) or water (H₂O).
It's a Process, Not an Instant Event
Decomposition does not happen instantly at a specific degree. As the material's temperature rises, it reaches a point where certain chemical bonds become unstable and begin to break.
This process continues as long as the temperature is maintained, until the reaction is complete. The commonly cited "calcination temperature" is the temperature required to drive this reaction to completion at a practical rate.
Key Factors Influencing Decomposition Temperature
The required temperature is a function of several variables. Understanding these factors is critical for controlling any calcination process.
The Material Itself
This is the most significant factor. Every material has a different decomposition point based on the strength of its chemical bonds.
For example, the decomposition of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) into lime (CaO) and CO₂ begins around 825°C. In contrast, removing chemically bound water from gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) occurs at much lower temperatures, typically between 100°C and 200°C.
Particle Size and Surface Area
Smaller particles heat more uniformly and quickly. A larger surface area allows volatile gases like CO₂ to escape more easily, which can facilitate a more efficient decomposition process at a slightly lower temperature or in less time.
Atmospheric Conditions
The composition of the furnace atmosphere plays a crucial role. For instance, the presence of high partial pressure of CO₂ in the furnace will suppress the decomposition of calcium carbonate, requiring a higher temperature to drive the reaction forward.
Heating Rate (Ramp Rate)
How quickly the material is heated to the target temperature can influence the final product's characteristics. A slow, controlled heating rate often allows for a more complete and uniform decomposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing the wrong temperature can lead to process failure, wasted energy, or a low-quality final product.
Incomplete Decomposition
If the temperature is too low or the heating time is too short, the material will not fully decompose. This results in an impure product that still contains the original volatile components, defeating the purpose of the process.
Sintering and Over-calcination
If the temperature is too high, the material's particles can begin to fuse together, a process known as sintering. This reduces the surface area and reactivity of the final product, which is often highly undesirable. For example, over-calcined lime is less reactive and of lower quality.
Energy and Cost
Higher temperatures require significantly more energy, leading to higher operational costs. Optimizing the process to use the lowest effective temperature is a key goal in any industrial application.
Determining the Right Temperature for Your Application
The ideal temperature is the one that achieves complete decomposition without causing undesirable side effects like sintering, all within an economically viable framework.
- If your primary focus is producing a highly reactive material (like quicklime): You must find the precise temperature that drives off all CO₂ without exceeding the point where sintering begins to reduce surface area.
- If your primary focus is simply removing bound water (dehydration): Your temperature can likely be much lower, targeted only at breaking the specific bonds holding the water molecules.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and cost-efficiency: You will need to balance temperature, heating time, and particle size to achieve the minimum acceptable product quality in the shortest possible time.
Ultimately, successful calcination comes from treating temperature not as a fixed number, but as a precise tool to achieve a specific material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Calcination Temperature Range (°C) | Key Decomposition Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone (CaCO₃) | 825°C - 900°C | CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ |
| Gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) | 100°C - 200°C | CaSO₄·2H₂O → CaSO₄ + 2H₂O |
| Industrial Furnace Range | 800°C - 1300°C | Varies by material and goal |
Optimize Your Calcination Process with KINTEK
Choosing the correct calcination temperature is critical for achieving complete decomposition, preventing sintering, and controlling energy costs. The precise temperature depends entirely on your specific material and desired outcome.
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and expert support you need to master your thermal processing. Whether you are decomposing carbonates, dehydrating gypsum, or developing a new material, our high-temperature furnaces and consumables are designed for exact control and repeatability.
We help you:
- Precisely Control Temperature: Achieve the exact thermal profile required for your specific material decomposition.
- Avoid Incomplete Reactions or Sintering: Ensure a high-quality, reactive final product.
- Improve Process Efficiency: Optimize your energy usage and throughput.
Ready to perfect your calcination process? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the characteristics of the slipping, slumping, and rolling modes of bed motion? Optimize Your Rotary Process



















