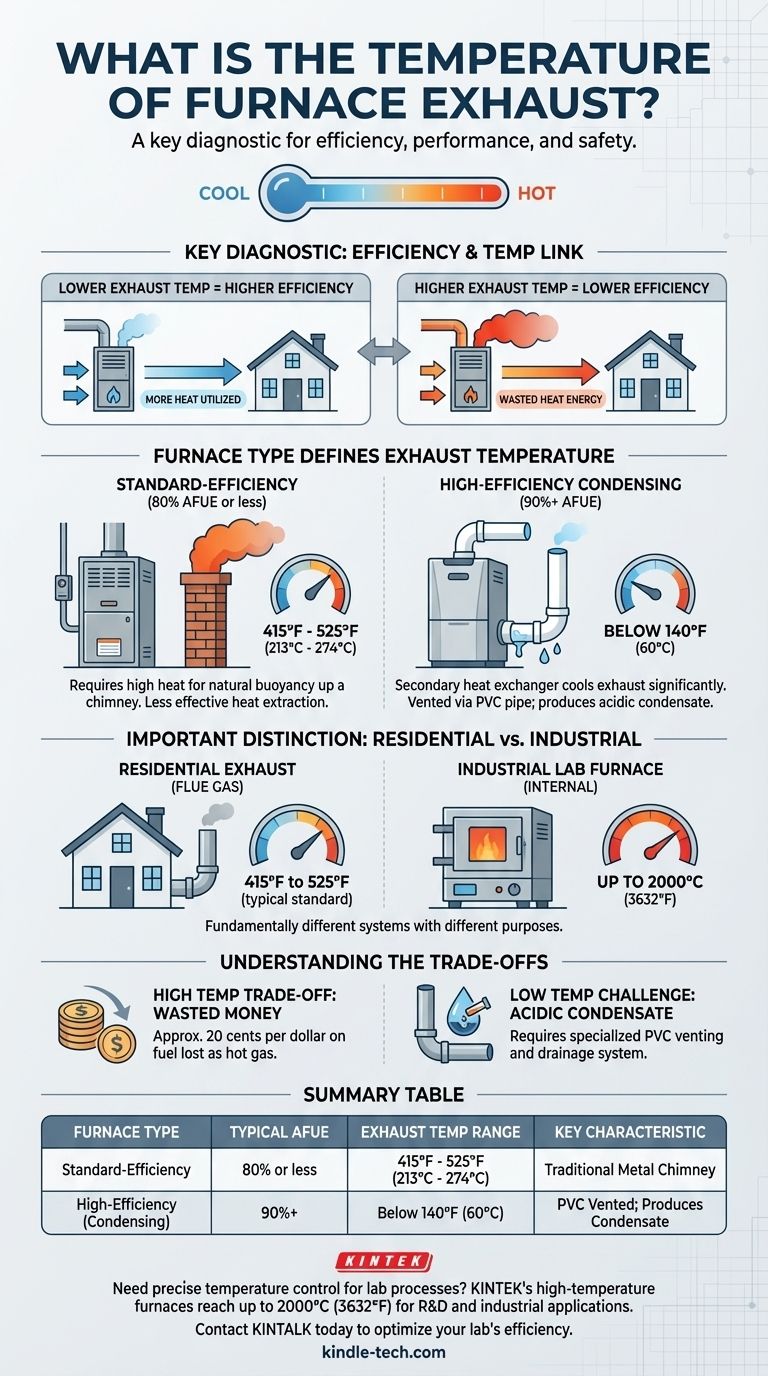
For a typical residential gas furnace, the exhaust gas temperature in the flue is consistently between 415°F and 525°F (213°C to 274°C). This temperature, however, varies significantly based on the furnace's design and efficiency rating, and it is a critical indicator of the system's performance and safety.
Furnace exhaust temperature is not a single number but a direct reflection of the unit's efficiency. A higher exhaust temperature indicates lower efficiency, as more heat is being wasted up the chimney instead of being used to heat your home.

Why Exhaust Temperature Is a Key Diagnostic
Furnace exhaust, or flue gas, temperature is one of the most important measurements a technician can take. It reveals how effectively the furnace is transferring heat from the combustion process into your home's air.
The Link Between Temperature and Efficiency
A furnace is designed to extract as much heat as possible from burning fuel. Any heat that leaves through the exhaust vent is essentially wasted energy.
Therefore, a lower exhaust temperature generally signals a more efficient furnace that is successfully capturing and distributing heat.
Safety and System Health
An exhaust temperature that is too high can be a symptom of a problem, such as improper airflow over the heat exchanger. Conversely, a temperature that is too low in the wrong type of system can lead to condensation and corrosion issues.
Furnace Type Defines Exhaust Temperature
The single biggest factor determining exhaust temperature is the type of furnace. Modern systems are engineered to have much cooler exhaust than their older counterparts.
Standard-Efficiency Furnaces (80% AFUE or less)
These are often older, "atmospheric" furnaces. They are less effective at extracting heat, so a significant amount of heat is lost through the exhaust.
Their flue gas temperatures are typically in the 415°F to 525°F range. This high heat is necessary to ensure the exhaust has enough buoyancy to rise naturally up a traditional chimney.
High-Efficiency Condensing Furnaces (90%+ AFUE)
These units are designed for maximum heat extraction. They have a secondary heat exchanger that captures additional heat from the exhaust gases.
This process cools the exhaust so much—often to below 140°F (60°C)—that the water vapor in it condenses into liquid. This is why these furnaces can be vented through PVC plastic pipes; the exhaust is not hot enough to melt them.
Distinguishing Exhaust vs. Internal Furnace Temperature
It is critical not to confuse residential flue gas temperatures with the internal operating temperatures of the furnace itself, especially in industrial or laboratory settings.
While a home furnace's exhaust might be 500°F, specialized high-temperature furnaces can reach internal temperatures of 1800°C (3272°F) or even 2000°C (3632°F) for scientific and manufacturing processes. These are fundamentally different systems with different purposes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The pursuit of efficiency by lowering exhaust temperatures creates new engineering challenges that must be managed.
The Cost of High Temperatures
The primary trade-off of a high exhaust temperature is wasted money. For a standard-efficiency furnace, for every dollar you spend on fuel, 20 cents or more is effectively sent outdoors as hot gas.
The Challenge of Low Temperatures
The condensate produced by high-efficiency furnaces is acidic. This corrosive liquid would quickly destroy a traditional masonry or metal chimney.
This is why condensing furnaces require specialized venting materials like PVC and a drainage system to safely dispose of the acidic liquid. An older furnace retrofitted incorrectly could cause severe damage if its flue gases start to condense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding your furnace's exhaust temperature helps you gauge its performance and intended operation.
- If your primary focus is diagnosing a standard-efficiency furnace: A flue temperature between 415°F and 525°F is a good sign that the system is operating within its designed parameters.
- If your primary focus is understanding a high-efficiency furnace: The cool exhaust, often vented through a plastic pipe, is a key feature, indicating that the unit is successfully extracting maximum heat from the fuel.
- If your primary focus is choosing a new furnace: The difference in exhaust temperature is a direct proxy for the long-term difference in your heating bills between a standard and a high-efficiency model.
Knowing what your furnace's exhaust temperature should be empowers you to better understand its health, safety, and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical AFUE Rating | Exhaust Temperature Range | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard-Efficiency | 80% or less | 415°F to 525°F (213°C to 274°C) | Requires a traditional metal chimney |
| High-Efficiency (Condensing) | 90%+ | Below 140°F (60°C) | Vented through PVC pipe; produces condensate |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK's high-temperature furnaces are engineered for reliability and accuracy, reaching up to 2000°C (3632°F) for demanding R&D and industrial applications. Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your specific thermal processing needs. Contact KINTALK today to optimize your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is the importance of melting process? Master the Foundation of Metal Production
- What controls melting point? The Hierarchy of Forces from Ionic Bonds to Intermolecular Attractions
- What precautions you will take while handling the muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- How do the properties of materials change with the heat treatment? Tailor Hardness, Strength, and Ductility



















