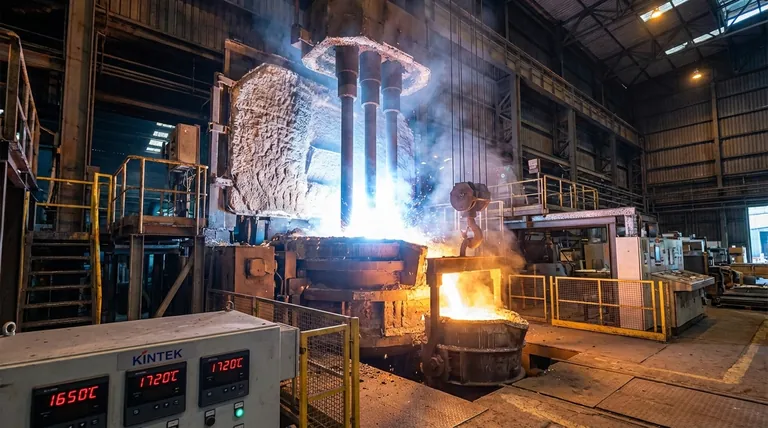
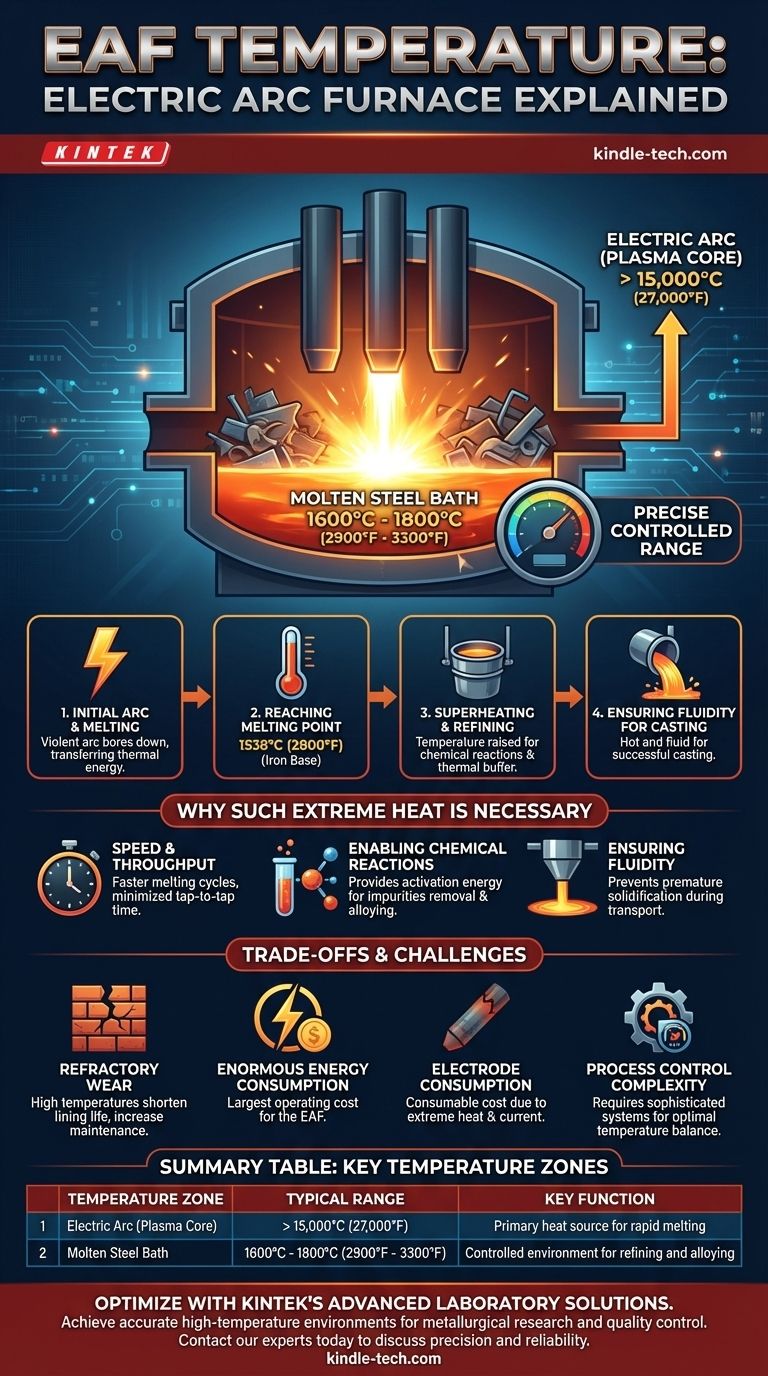
In an electric arc furnace (EAF), the temperature of the molten steel bath is precisely controlled to operate in a range of 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3300°F). This is significantly above the melting point of steel, allowing for critical refining and alloying processes to occur. The electric arc itself, which generates this heat, is far hotter, reaching temperatures in its plasma core that can exceed 15,000°C (27,000°F).
Understanding the temperature in an EAF is not about a single number. It's about recognizing the difference between the immense, localized heat of the electric arc and the carefully managed temperature of the molten steel bath, which is the key variable for producing quality steel efficiently.

The Journey to Molten Steel
The process inside an EAF is a carefully controlled sequence of intense heating and metallurgical refinement. The temperature is the primary tool used to drive each stage.
The Initial Arc and Melting
The process begins when three massive graphite electrodes are lowered into a furnace filled with scrap metal. A powerful electric current is passed through them, creating a brilliant and violent electric arc between the electrodes and the scrap. This arc, like a contained bolt of lightning, instantly begins to bore down, transferring enormous thermal energy and melting the metal.
Reaching the Melting Point
The base melting point of pure iron is approximately 1538°C (2800°F). The EAF must not only reach this temperature but significantly surpass it to ensure all the scrap becomes fully liquid and to prepare the steel for the next steps.
Superheating and Refining the Bath
Once a molten pool, or bath, has formed, the goal shifts from simple melting to refining. The temperature is deliberately raised further, a process known as superheating. This higher temperature is essential for two reasons: it accelerates the chemical reactions needed to remove impurities like phosphorus and sulfur, and it provides the thermal buffer needed to keep the steel molten during subsequent transport and casting.
Why Such Extreme Heat is Necessary
Operating well above steel's melting point is a deliberate strategy driven by the demands of modern steelmaking. The high temperature is not just a byproduct; it is a fundamental requirement for the process.
Speed and Throughput
Higher temperatures translate directly to faster melting cycles. In a high-production environment, minimizing the "tap-to-tap" time—the total duration of one steelmaking cycle—is critical for economic viability. Intense heat gets the job done quickly.
Enabling Chemical Reactions
Many essential refining reactions are endothermic, meaning they require energy input to proceed. The high temperatures within the EAF provide the necessary activation energy to remove unwanted elements and dissolve alloys into the molten bath, ensuring the final product meets precise chemical specifications.
Ensuring Fluidity for Casting
The finished molten steel must be tapped from the furnace and transported in a ladle to a continuous caster. During this time, it will naturally lose heat. The initial superheat ensures that the steel remains sufficiently hot and fluid to be cast successfully without premature solidification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Managing these extreme temperatures creates a series of significant operational challenges and economic trade-offs.
Refractory Wear
The inner lining of the furnace, made of heat-resistant refractory bricks, is under constant assault from the intense heat and chemical reactions. Higher operating temperatures drastically shorten the life of this lining, representing a major maintenance cost and source of downtime.
Enormous Energy Consumption
Creating and sustaining an electric arc of this magnitude requires a vast amount of electrical power. Energy is often the single largest operating cost for an EAF, making temperature control and efficient heating strategies paramount.
Electrode Consumption
The graphite electrodes are not permanent. They are slowly consumed during the process due to the extreme temperatures and high electrical current. This consumption is a direct operational cost that must be carefully managed.
Process Control Complexity
The goal is not simply maximum heat but optimal heat. Overheating wastes electricity and damages the furnace, while underheating can lead to a failed batch of steel with the wrong composition or casting problems. This requires sophisticated sensor systems and automated process controls to maintain the bath within a precise temperature window.
What the Temperature Tells Us
Choosing the right lens for viewing EAF temperature is key to understanding its function in the steelmaking process.
- If your primary focus is on the physics: The key is the plasma arc itself, which can exceed 15,000°C and acts as the incredibly efficient, localized heat source.
- If your primary focus is on metallurgy: The crucial temperature is that of the molten steel bath, typically controlled between 1600°C and 1800°C to enable refining and achieve final chemistry.
- If your primary focus is on operational efficiency: The central challenge is balancing the need for high superheat (for speed and quality) against the direct costs of energy consumption and refractory wear.
Ultimately, temperature is the primary lever that an EAF operator uses to control the speed, quality, and cost of making steel.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Zone | Typical Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc (Plasma Core) | > 15,000°C (27,000°F) | Primary heat source for rapid melting |
| Molten Steel Bath | 1600°C - 1800°C (2900°F - 3300°F) | Controlled environment for refining and alloying |
Optimize your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced laboratory solutions.
Understanding precise temperature control is fundamental to efficient steel production and material testing. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and temperature control systems, designed to meet the rigorous demands of metallurgical research and quality control.
Our products help you:
- Achieve accurate and consistent high-temperature environments
- Enhance process efficiency and repeatability
- Reduce operational costs through reliable performance
Whether you're involved in steel production, materials development, or industrial research, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can bring precision and reliability to your high-temperature applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating
- What is the muffle furnace used for in metallurgy? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- Can a muffle furnace be used for pyrolysis? How to adapt it for oxygen-free thermal decomposition
- How is the sintering temperature related to the melting temperature? A Guide to Solid-State Bonding



















