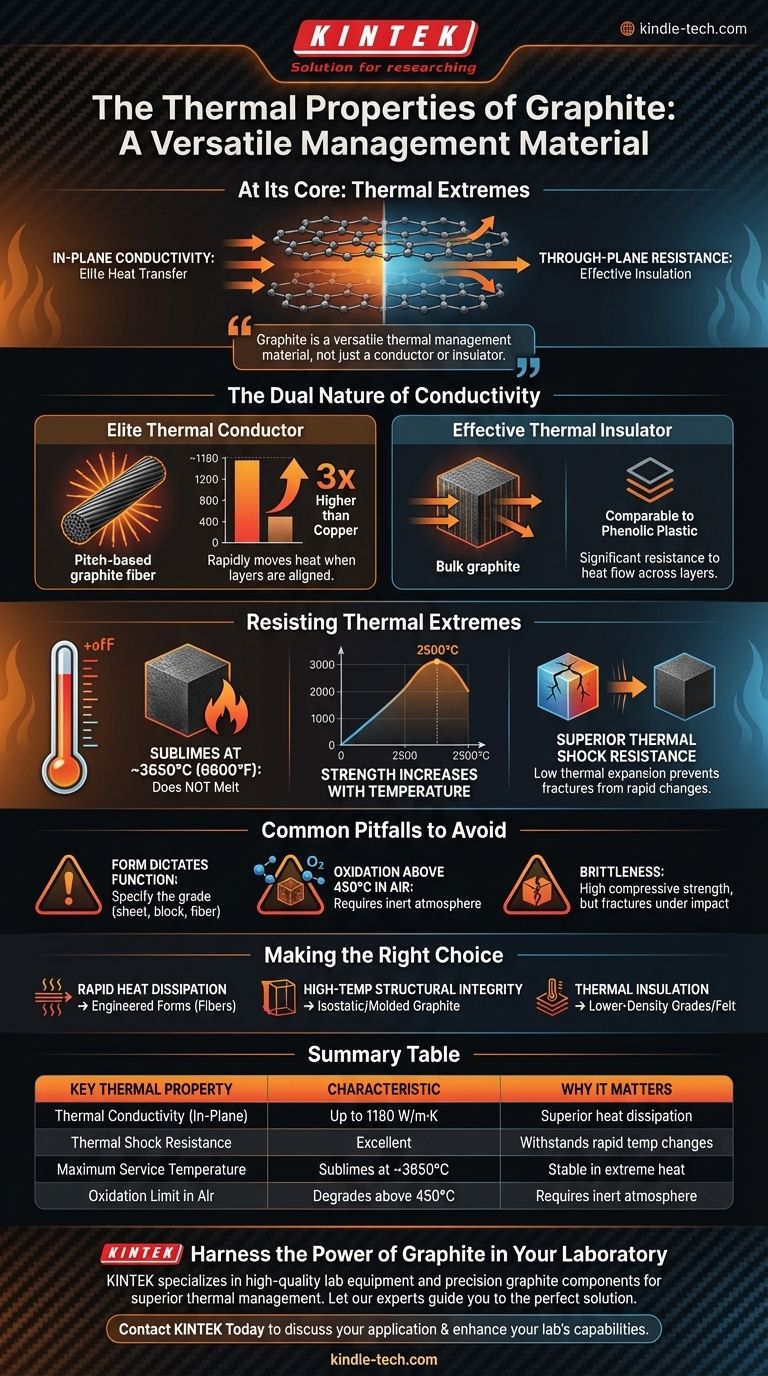
At its core, graphite is a material of thermal extremes. Its most notable thermal property is an exceptionally high thermal conductivity in specific forms, capable of transferring heat more efficiently than copper. However, this is combined with an outstanding ability to resist thermal shock and maintain its structural integrity at temperatures that would melt most metals.
Graphite should not be viewed as simply a conductor or an insulator, but as a versatile thermal management material. Its true value lies in the combination of high heat conductivity, unparalleled resistance to thermal shock, and stability at extreme temperatures.

The Dual Nature of Graphite's Thermal Conductivity
The most common point of confusion regarding graphite is that it can act as both an excellent thermal conductor and an effective insulator. This apparent contradiction is resolved by understanding its unique internal structure.
Anisotropic Conductivity: The Key to Understanding
Graphite's properties are anisotropic, meaning they differ depending on the direction of measurement. Its crystal structure consists of strongly bonded layers of carbon atoms (graphene sheets).
Heat travels with extreme efficiency along these layers (in-plane direction) but struggles to travel across the layers (through-plane direction). This fundamental characteristic is the source of its dual thermal nature.
An Elite Thermal Conductor
When engineered to align its layers, as in certain graphite fibers, the thermal conductivity is maximized.
Pitch-based graphite fibers can exhibit a thermal conductivity of up to 1180 W/m·K. For perspective, this is nearly three times higher than copper (~400 W/m·K), one of the best metallic conductors. This makes it a superior material for rapidly moving heat away from a source.
An Effective Thermal Insulator
Conversely, if heat must travel across the atomic layers, the thermal conductivity drops dramatically.
In bulk forms or applications where the orientation is not controlled, the "through-plane" resistance to heat flow is significant. In these contexts, graphite's performance can be more comparable to an insulator like phenolic plastic.
Beyond Conductivity: Resisting Thermal Extremes
While its conductivity is remarkable, graphite's value in high-performance applications comes from its ability to survive extreme thermal environments.
Exceptional High-Temperature Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimes at approximately 3650°C (6600°F), allowing it to function in environments far hotter than most materials can withstand.
Uniquely, the mechanical strength of isostatic graphite increases with temperature, reaching a peak at around 2500°C. This is the opposite of metals, which weaken as they get hotter.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress and potential fracture caused by rapid changes in temperature.
Graphite has excellent resistance to thermal shock. This is a direct result of its high thermal conductivity (which prevents large temperature gradients from forming) and its very low coefficient of thermal expansion (it doesn't expand or contract much when heated or cooled).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding graphite's properties requires acknowledging its limitations and the importance of selecting the correct grade.
Form Dictates Function
The term "graphite" is very broad. The thermal properties of a flexible graphite sheet, a rigid block of isostatic graphite, and a composite graphite fiber are vastly different. You must specify the form of graphite that matches your application's needs.
Oxidation in Air
While graphite is stable at very high temperatures, this is primarily true in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere. In the presence of oxygen, it will begin to oxidize and degrade at temperatures above 450°C. Protective coatings or use in controlled environments are necessary for high-temperature air applications.
Brittleness
Like other ceramics, graphite is a brittle material. It has high compressive strength but can fracture without warning under sharp impact or high tensile stress. It is not a suitable replacement for metals in applications requiring ductility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right graphite depends entirely on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat dissipation: Choose engineered forms like pyrolytic graphite sheets or pitch-based graphite fibers that maximize in-plane thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity: Use high-density isostatic or molded graphite for its uniform strength and exceptional thermal shock resistance in furnaces or crucibles.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation: Utilize lower-density graphite grades or graphite felt, where the structure and orientation reduce overall thermal transport.
Ultimately, graphite is a uniquely capable material for managing thermal energy in the most demanding conditions.
Summary Table:
| Key Thermal Property | Characteristic | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (In-Plane) | Up to 1180 W/m·K (higher than copper) | Superior heat dissipation |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Sublimes at ~3650°C | Stable in extreme heat environments |
| Oxidation Limit in Air | Degrades above 450°C | Requires inert atmosphere for high-temp air use |
Harness the Power of Graphite in Your Laboratory
Understanding graphite's unique thermal properties is key to selecting the right material for your high-temperature applications, whether you need extreme heat dissipation, structural integrity in a furnace, or superior thermal insulation.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision graphite components designed for superior thermal management. We help laboratories like yours achieve peak performance and reliability in the most demanding thermal environments.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect graphite solution for your specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover how our materials can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and limitations for heat treatment process? Mastering Material Strength and Surface Integrity
- Can a diamond tester be wrong? Yes, and here’s why you need more than one test
- What refrigeration technologies are used in modern ULT freezers? Cascade vs. Stirling Cycle Explained
- What is an alternative to a rotary vacuum evaporator? Find the Right Evaporation Technology for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of handheld XRF? Achieve Instant, On-Site Elemental Analysis
- What is difference between sinter and pellet? Optimize Your Blast Furnace with the Right Agglomeration Choice
- What are the challenges associated with increasing the use of bioenergy? Navigating the Land, Carbon, and Economic Trade-offs
- What are the different types of biomass pellets? A Guide to Wood vs. Agricultural Pellets



















