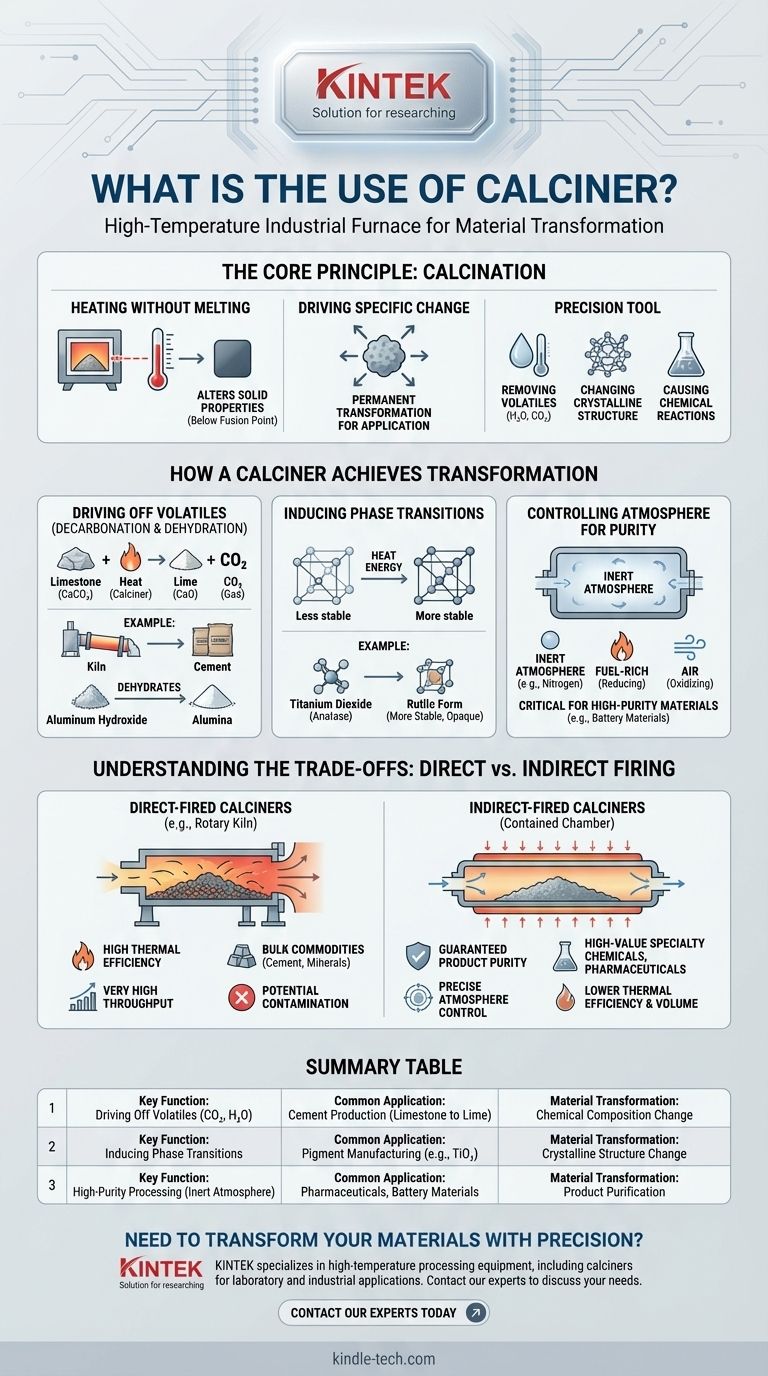
At its core, a calciner is a high-temperature industrial furnace used to heat solid materials to induce a chemical reaction or physical transformation. The defining characteristic of calcination is that this heating occurs at a temperature below the material’s melting point, fundamentally altering its properties without turning it into a liquid.
The primary purpose of a calciner is not just to heat a material, but to transform it. It is a precision tool for removing volatile substances like water and CO₂, changing a material's crystalline structure, or causing a specific chemical reaction to occur.

What is Calcination? The Core Principle
Calcination is one of the most fundamental thermal processing techniques used across heavy industry, from cement plants to specialty chemical manufacturing. Understanding the principle is key to understanding the machine.
Heating Without Melting
The process intentionally keeps temperatures below the material's fusion point. This is crucial because the goal is to alter the solid itself, not to cast it into a new shape from a liquid state.
This controlled heating allows for precise changes at a molecular or crystalline level.
The Goal: Driving Specific Change
The reason for calcining a material is to achieve a specific, desirable outcome. This isn't just about drying; it's about forcing a permanent transformation that makes the material suitable for its next application.
How a Calciner Achieves This Transformation
A calciner uses a combination of high temperature, controlled residence time, and a specific atmospheric environment to force the desired change. The most common transformations fall into a few key categories.
Driving Off Volatiles (Decarbonation & Dehydration)
This is the most common use of calcination. The heat provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds and drive off components as gas.
A classic example is in cement production, where limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is heated in a calciner to drive off carbon dioxide (CO₂). This transforms it into lime (calcium oxide, CaO), a primary ingredient in cement.
Similarly, calcination is used to remove chemically bound water (dehydration) from materials like aluminum hydroxide to produce high-purity alumina.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Some materials can exist in different crystalline structures, known as polymorphs. Calcination provides the energy to rearrange the atoms from a less stable form to a more stable or desirable one.
For example, this is used in pigment manufacturing to convert titanium dioxide from its anatase crystal form to the more opaque and stable rutile form, which is critical for paints and coatings.
Controlling the Atmosphere for Purity
The gas environment inside the calciner is often as important as the temperature. The process can be done in air, in a fuel-rich (reducing) environment, or in an inert atmosphere like nitrogen.
Using an inert atmosphere is critical when any oxidation of the product would be detrimental, ensuring the production of a high-purity material free from unwanted side reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
Calciners are broadly categorized by how heat is transferred to the material. This design choice represents a fundamental trade-off between efficiency and product purity.
Direct-Fired Calciners: For Speed and Scale
In a direct-fired calciner, the material comes into direct contact with the hot gases from combustion. The most common example is a rotary kiln.
This method is highly thermally efficient and allows for very high throughput, making it ideal for bulk commodities like cement and minerals. The main drawback is the potential for the product to be contaminated by the byproducts of combustion.
Indirect-Fired Calciners: For Purity and Precision
In an indirect-fired calciner, the material is contained within a chamber or tube that is heated from the outside. The material never touches the combustion gases.
This design guarantees product purity and allows for precise control over the processing atmosphere. It is the required choice for high-value specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, battery materials, and catalysts where even trace contamination is unacceptable. However, it is less thermally efficient and generally handles lower volumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a calciner, and which type, is dictated entirely by the final properties your material needs to possess.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing where minor contamination is acceptable: A direct-fired rotary kiln is the industry standard due to its unmatched efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-purity product or requiring precise atmospheric control: An indirect-fired calciner is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and manage reactions.
- If your process requires extremely uniform heating and excellent gas-solid contact: A fluidized bed calciner, where the material is suspended on a bed of hot gas, may be the optimal choice.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational tool for engineering materials with the exact chemical and physical properties required for their intended use.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Common Application | Material Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Off Volatiles (e.g., CO₂, H₂O) | Cement Production (Limestone to Lime) | Chemical Composition Change |
| Inducing Phase Transitions | Pigment Manufacturing (e.g., TiO₂) | Crystalline Structure Change |
| High-Purity Processing (Inert Atmosphere) | Pharmaceuticals, Battery Materials | Product Purification |
Need to transform your materials with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature processing equipment, including calciners for laboratory and industrial applications. Whether you require high-volume processing or ultra-pure product development, our expertise in lab equipment can help you achieve your material science goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific calcination needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which type of furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Heat Treating Solution
- How does a laboratory vacuum oven facilitate the gel content testing of UV-cured silicone rubber films?
- What are the different types of pyrolysis furnace? Choose the Right Reactor for Bio-Oil or Biochar
- What is a drop bottom furnace? Achieve Superior Uniform Heating for Heavy & Delicate Parts
- What is the temperature of debinding? A Guide to Mastering the Thermal Profile for MIM/CIM
- How are high-performance vacuum furnaces used in helium implantation annealing? Master Material Defect Visualization
- What is meant by annealing process? Transform Brittle Metals into Workable Materials
- What are the requirements for a heat treatment furnace? A Guide to Precise Temperature and Atmosphere Control



















