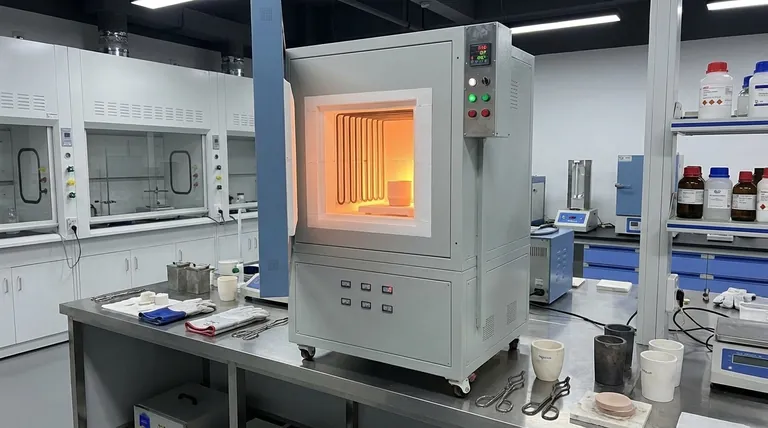
In a modern laboratory, a furnace is far more than a simple oven. It is a critical instrument used for high-temperature thermal processing, designed to fundamentally alter the physical or chemical properties of a material. From creating advanced ceramics and treating metals to preparing samples for analysis, furnaces enable a vast range of scientific and industrial applications by applying precise and controlled heat.
The central purpose of a laboratory furnace is not just to heat a sample, but to execute a specific thermal process. Understanding your end goal—whether it's removing moisture, hardening a metal, or synthesizing a new compound—is the key to selecting and using the right type of furnace.

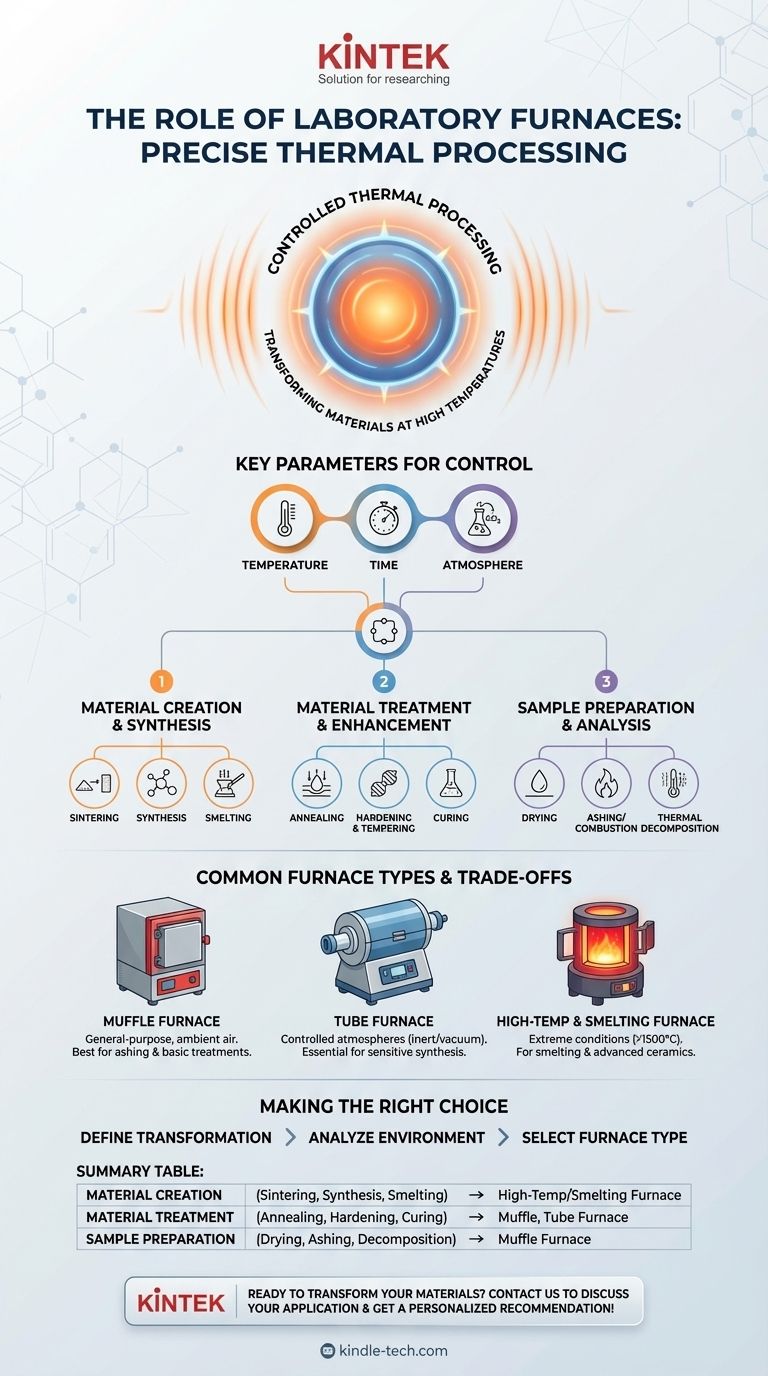
The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Processing
A furnace gives researchers and technicians precise control over a material's transformation. This is achieved by manipulating the key variables of any thermal process.
Changing a Material's Properties
Nearly every use of a laboratory furnace comes down to changing a material in a predictable way. This can mean making a metal harder, a ceramic denser, or breaking a compound down into its basic components.
Key Parameters: Temperature, Time, and Atmosphere
The outcome of a process is determined by temperature (how hot), time (how long), and atmosphere (the gases surrounding the sample). An open-air furnace behaves very differently from a vacuum or inert gas furnace, even at the same temperature.
Primary Applications Across Disciplines
The applications for laboratory furnaces are incredibly broad, spanning fields from metallurgy and materials science to chemistry and geology. They can be grouped into three main categories.
Material Creation and Synthesis
Many processes use heat to combine or compact raw ingredients into a finished material.
- Sintering: Fusing powders together to create a solid, dense object, such as producing technical ceramics or parts via powder metallurgy.
- Synthesis: Performing chemical reactions at high temperatures to create new inorganic or organic compounds.
- Smelting: Extracting a metal from its ore by heating it beyond its melting point.
Material Treatment and Enhancement
These processes modify the properties of an existing material to improve its performance.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material (usually metal or glass) to remove internal stresses and increase ductility.
- Hardening & Tempering: A two-step process to increase the hardness and toughness of metals.
- Curing: Using heat to trigger a chemical reaction that solidifies a material, such as an epoxy or polymer.
Sample Preparation and Analysis
Furnaces are also essential tools for preparing samples for further testing.
- Drying: Gently heating a sample to remove residual moisture without otherwise changing it.
- Ashing / Combustion: Burning off all organic material at a high temperature to determine the amount of inorganic residue.
- Thermal Decomposition: Breaking down a compound into simpler substances to analyze its composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Furnace Types
Different thermal processes require different types of furnaces. Choosing the wrong one can lead to failed experiments and damaged materials.
Muffle Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A muffle furnace is the most common type, featuring an insulated chamber that heats a sample in ambient air. It is ideal for general-purpose applications like ashing, basic heat treatments, and material testing where a controlled atmosphere is not needed.
Tube Furnaces: For Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace contains the sample within a cylindrical tube, which can be sealed and filled with a specific gas (like argon or nitrogen) or put under a vacuum. This is essential for preventing oxidation and for processes like the synthesis of air-sensitive compounds.
High-Temperature & Smelting Furnaces: For Extreme Conditions
These specialized units are built with advanced refractory materials and heating elements to safely reach extreme temperatures, often above 1500°C. They are primarily used for smelting metals, firing advanced ceramics, and conducting high-temperature materials research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct instrument, first define the transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is routine sample preparation and analysis: A general-purpose muffle furnace for ashing, drying, or basic heat treatment is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing materials or heat treating in a specific environment: A tube furnace is necessary for its ability to control the atmosphere with an inert gas or a vacuum.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy or creating advanced ceramics: A specialized high-temperature or smelting furnace designed to reach extreme temperatures safely is required.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about precisely matching the tool to the desired transformation of your material.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Material Creation | Sintering, Synthesis, Smelting | High-Temperature/Smelting Furnace |
| Material Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Curing | Muffle Furnace, Tube Furnace |
| Sample Preparation | Drying, Ashing, Thermal Decomposition | Muffle Furnace |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right laboratory furnace for your specific needs—whether it's a robust muffle furnace for routine ashing or a sophisticated tube furnace for sensitive synthesis under controlled atmospheres. Our experts will help you select the ideal equipment to achieve precise thermal processing, enhance your research outcomes, and boost lab efficiency.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the purpose of a laboratory furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a lab oven and a furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the annealing temperature of quartz? Achieve Optimal Thermal Stability for Your Components



















