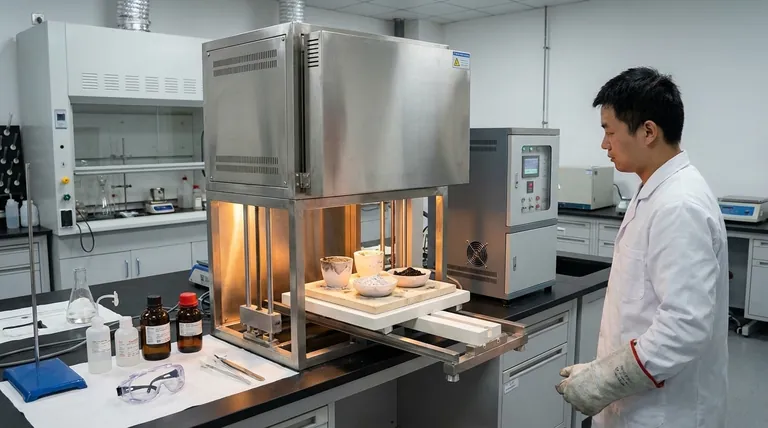
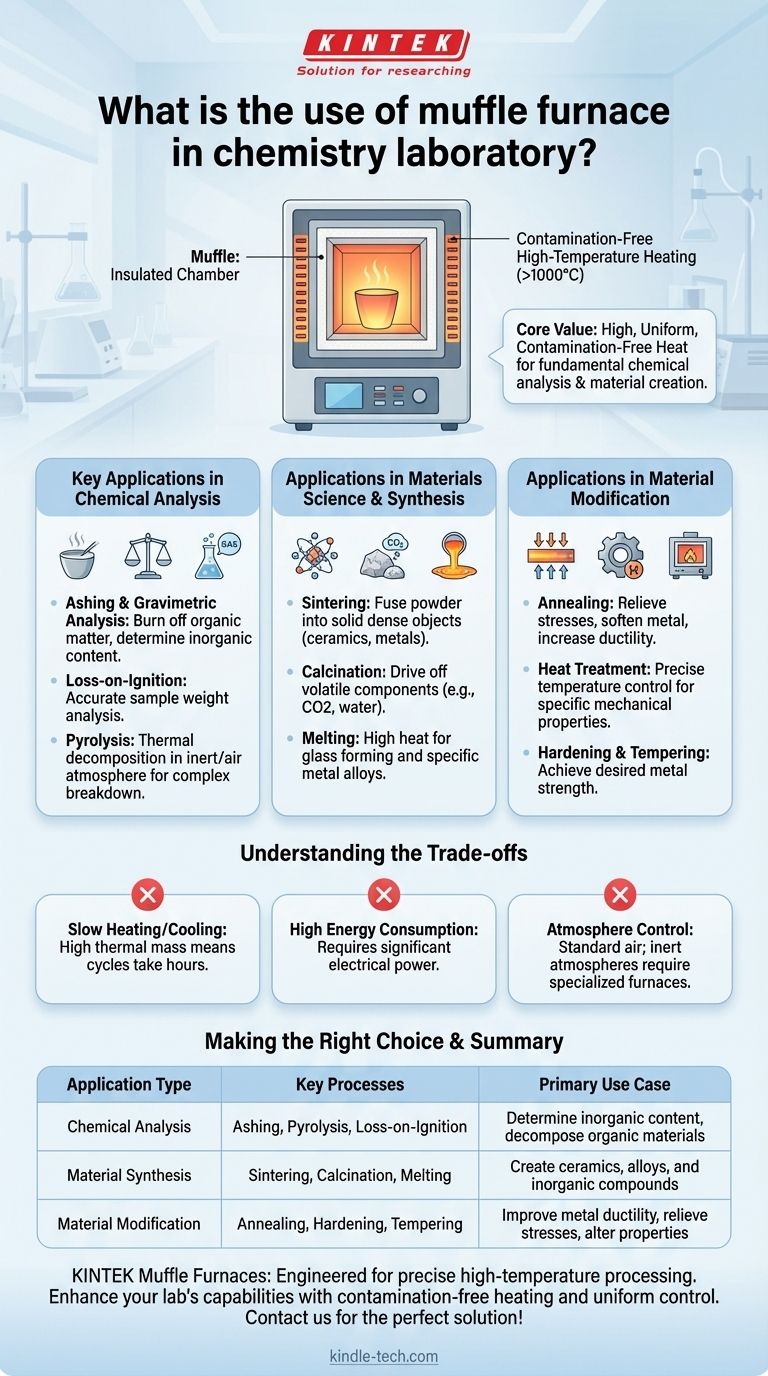
In a chemistry laboratory, a muffle furnace is a specialized oven used for high-temperature applications that require thermal processing. Its primary functions include transforming materials through processes like ashing, sintering, and annealing, where samples must be heated to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C in a controlled environment.
The core value of a muffle furnace is its ability to provide extremely high, uniform, and contamination-free heat. Unlike a standard oven, it isolates the sample from the heating elements, making it essential for analyzing or creating materials at a fundamental chemical level.

The Core Principle: Contamination-Free High-Temperature Heating
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace stem from its design, which is optimized for purity and extreme heat. Understanding this principle is key to knowing when to use it.
What "Muffle" Means
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that contains the sample. This chamber acts as a barrier, separating the material being heated from the actual heating elements and any potential contaminants from combustion.
This separation is critical for applications where chemical purity is paramount.
Achieving Uniform and Precise Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are engineered with heavy insulation and high-power heating elements (like Kanthal or silicon carbide) to reach and maintain precise temperatures.
This design ensures that the entire sample experiences a uniform temperature, which is essential for consistent results in both material synthesis and analysis.
Key Applications in Chemical Analysis
Many analytical chemistry procedures rely on a muffle furnace to determine a sample's composition by breaking it down with heat.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is the most common analytical use. The furnace heats a sample to a temperature high enough to burn off all organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue (ash).
By weighing the sample before and after ashing, chemists can accurately determine its inorganic content. This is also known as loss-on-ignition and is standard practice in fields like food science, mining, and environmental testing.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis involves thermally decomposing materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere (though often performed in air in simpler applications). A muffle furnace provides the necessary heat to break down complex organic materials into simpler substances for analysis.
Applications in Materials Science and Synthesis
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are workhorses for creating and modifying materials. The high heat enables fundamental changes to a substance's physical and chemical structure.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering is a process where powdered material (like ceramic or metal dust) is heated to just below its melting point. The heat causes the particles to fuse into a solid, dense object.
Calcination involves heating a material to drive off volatile components, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone to produce lime, or water from a chemical hydrate.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, annealing uses a muffle furnace to heat a metal and then cool it slowly. This process relieves internal stresses, softens the metal, and makes it more ductile and easier to work with.
Related processes like hardening and tempering also use the furnace's precise temperature control to achieve specific mechanical properties in metals and alloys.
Glass and Metal Melting
For small-scale lab work, muffle furnaces can reach temperatures high enough to melt certain types of glass for forming or to create specific metal alloys for research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not always the right tool. Its specialized nature comes with practical limitations.
Slow Heating and Cooling Cycles
Due to their heavy insulation and high thermal mass, muffle furnaces heat up and cool down very slowly. A cycle can take several hours, making them unsuitable for processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures of 1000°C or more requires a significant amount of electrical energy. This makes them one of the more energy-intensive pieces of equipment in a lab.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert (like nitrogen or argon) or reactive atmosphere, a more specialized and expensive tube furnace or vacuum furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select the furnace based on the specific transformation or analysis you need to perform on your material.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Use the furnace for ashing to determine the inorganic content of a sample or for loss-on-ignition testing.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials: Use the furnace for sintering ceramic powders, calcining chemical precursors, or synthesizing high-temperature inorganic compounds.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties: Use the furnace for annealing metals to improve their workability or for other heat treatments to achieve desired hardness and strength.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace empowers chemists to fundamentally alter and precisely analyze materials under extreme thermal conditions.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Processes | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Analysis | Ashing, Pyrolysis, Loss-on-Ignition | Determine inorganic content, decompose organic materials |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Calcination, Melting | Create ceramics, alloys, and inorganic compounds |
| Material Modification | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Improve metal ductility, relieve stresses, alter properties |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise high-temperature processing? KINTEK's muffle furnaces are engineered for chemists and material scientists who demand contamination-free heating, uniform temperature control, and reliable performance for applications like ashing, sintering, and annealing. Whether you're analyzing sample composition or synthesizing new materials, our equipment ensures accuracy and repeatability. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is maintenance and how can you maintain the laboratory? Boost Lab Reliability & Data Integrity
- How hot can metal get? From Melting Points to Plasma Temperatures
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What are the uses of furnace in chemistry laboratory? Unlock High-Temperature Material Synthesis and Analysis
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction



















