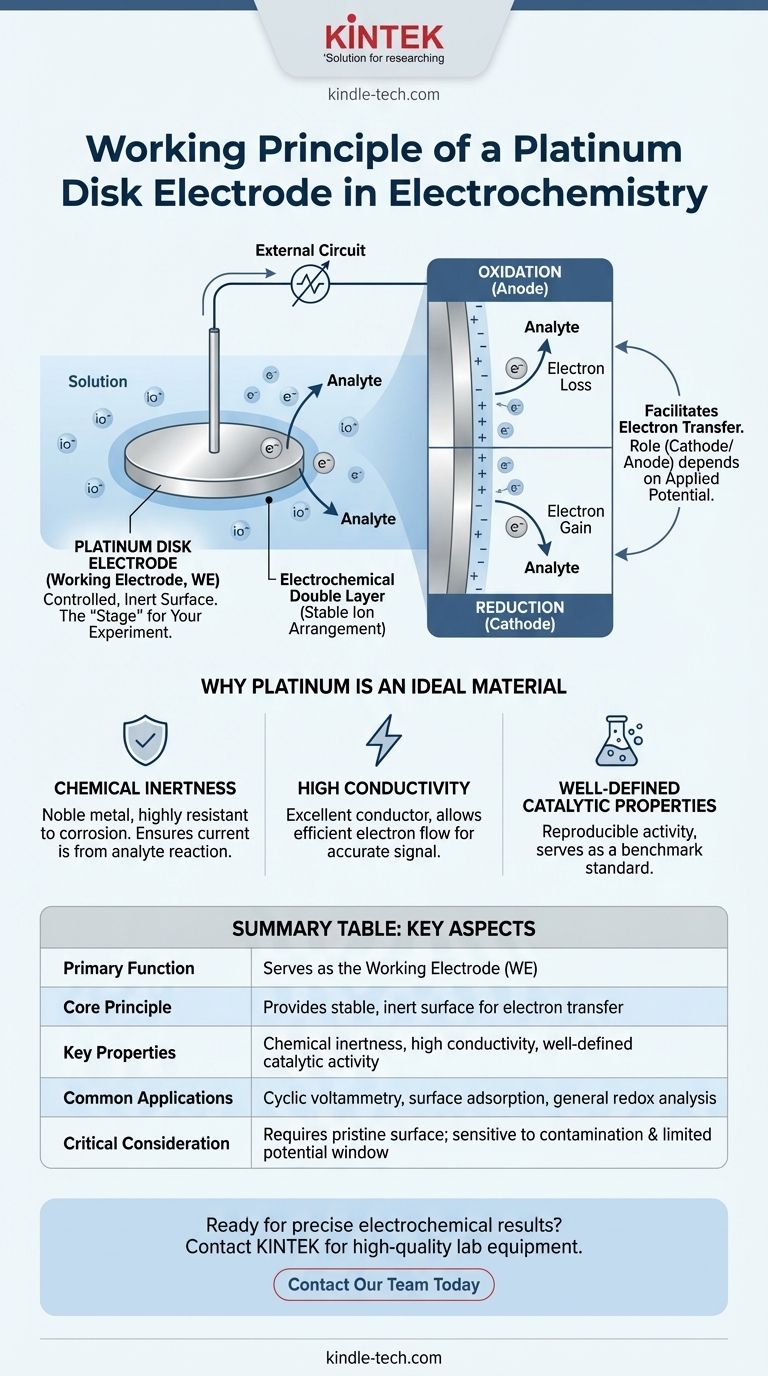
In an electrochemical process, a platinum disk electrode's primary role is to serve as a controlled, inert surface where the reaction of interest occurs. Connected to an external circuit, it facilitates the transfer of electrons between the electrode and the chemical species (analyte) in the solution. By precisely measuring the resulting current or potential changes, researchers can study the properties and mechanisms of the electrochemical system.
The platinum disk electrode is not just a conductor; it is the "stage" for your experiment. Its working principle is to provide a stable and non-reactive platform, allowing you to isolate and measure the specific oxidation or reduction reaction you intend to study, without the electrode itself interfering.

The Core Function: The Working Electrode
In a typical three-electrode electrochemical cell, the platinum disk is almost always used as the working electrode (WE). This is the most critical component for your analysis.
The Site of the Main Event
Think of the working electrode as a test coupon in a corrosion study. It is the specific location where the primary electrochemical reaction—the one you are investigating—takes place.
All measurements of current and potential are fundamentally related to the processes happening directly at this surface.
Facilitating Electron Transfer
The electrode's surface acts as an interface. Depending on the applied potential, it can either donate electrons to the analyte in the solution (reduction) or accept electrons from it (oxidation).
As the central hub for this electron exchange, the working electrode can function as either the cathode (site of reduction) or the anode (site of oxidation). This role is not fixed and changes based on the voltage you apply.
Forming the Electrochemical Double Layer
When the electrode is immersed in an electrolyte solution, ions in the solution arrange themselves at the electrode's surface. This creates a stable structure known as the electrochemical double layer.
This organized layer is essential for facilitating predictable and efficient electron transfer, which is the basis for generating a measurable current.
Why Platinum is an Ideal Material
The choice of platinum is deliberate. Its physical and chemical properties make it exceptionally well-suited for serving as a reliable working electrode.
Chemical Inertness
Platinum is a noble metal, meaning it is highly resistant to corrosion and reaction in most electrolytes. This ensures that the current you measure is from your analyte's reaction, not from the electrode itself dissolving or reacting.
High Conductivity
Platinum is an excellent electrical conductor. It allows electrons to move with minimal resistance between the analyte and the external measurement circuit (the potentiostat), ensuring an accurate signal.
Well-Defined Catalytic Properties
For certain reactions, like the hydrogen evolution reaction, platinum has known and highly reproducible catalytic activity. This makes it a benchmark standard against which other materials are often compared.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Realities
While powerful, the platinum disk electrode is not without its limitations and practical considerations. Understanding these is key to generating reliable data.
Surface Contamination Is a Constant Concern
The working principle relies on a pristine surface. Any impurities, adsorbed molecules from previous experiments, or even oxides formed on the platinum can block or interfere with electron transfer.
This is why rigorous cleaning procedures, such as polishing with alumina powder and rinsing with distilled water, are not optional—they are essential for reproducible results.
Limited Potential Window
Even platinum is not perfectly inert under all conditions. At extreme positive or negative potentials, the electrode can begin to oxidize its own surface or participate in the breakdown of the solvent (e.g., splitting water into oxygen or hydrogen).
This reality defines the "potential window," or the usable voltage range within which the electrode remains passive and your measurements are valid.
Disk vs. Other Geometries
It is crucial to distinguish between electrode geometries. While a platinum disk is typically the working electrode due to its well-defined surface area, platinum sheets or wires are commonly used as the counter electrode (also called the auxiliary electrode).
The counter electrode's job is simply to balance the current from the working electrode, completing the circuit without influencing the reaction being studied.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying this knowledge correctly depends entirely on your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is general analysis: For standard techniques like cyclic voltammetry, the platinum disk electrode is a robust, reliable, and often default choice for studying a wide range of redox reactions.
- If your primary focus is studying surface adsorption: The disk's smooth, uniform surface and well-defined geometric area are critical for obtaining reproducible data on processes that involve molecules binding to the electrode.
- If your primary focus involves cost-sensitivity or known interference: In cases where platinum is too expensive or catalytically interferes with your reaction, you should consider alternatives like glassy carbon or gold electrodes.
Ultimately, understanding that the working electrode is the heart of your experiment empowers you to design more meaningful and accurate electrochemical studies.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role of Platinum Disk Electrode |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Serves as the Working Electrode (WE) for the reaction of interest |
| Core Principle | Provides a stable, inert surface for controlled electron transfer (oxidation/reduction) |
| Key Properties | Chemical inertness, high conductivity, well-defined catalytic activity |
| Common Applications | Cyclic voltammetry, studying surface adsorption, general redox analysis |
| Critical Consideration | Requires pristine surface; sensitive to contamination and has a limited potential window |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable results in your electrochemical research?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable platinum electrodes and electrochemical cells. Our products are designed to provide the stable, inert surfaces you need for accurate redox studies, surface adsorption analysis, and more.
Let our experts help you select the right electrode for your specific application, whether you're focused on general analysis, cost-sensitive projects, or require alternatives like glassy carbon.
Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your electrochemical experiments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- Why is platinum wire selected as the auxiliary electrode? Achieve High-Precision Corrosion Data with Inert Electrodes
- What is the function of a platinum electrode as an auxiliary electrode? Ensure Precise Nickel Coating Corrosion Testing
- What are the technical advantages of using a spiral platinum wire? Optimize Your Electrochemical Precision
- Why is platinum a good counter electrode? For Superior Chemical Inertness and Electron Transfer
- Why is a platinum electrode typically selected as the auxiliary or counter electrode? Unlock Precise Data Accuracy



















