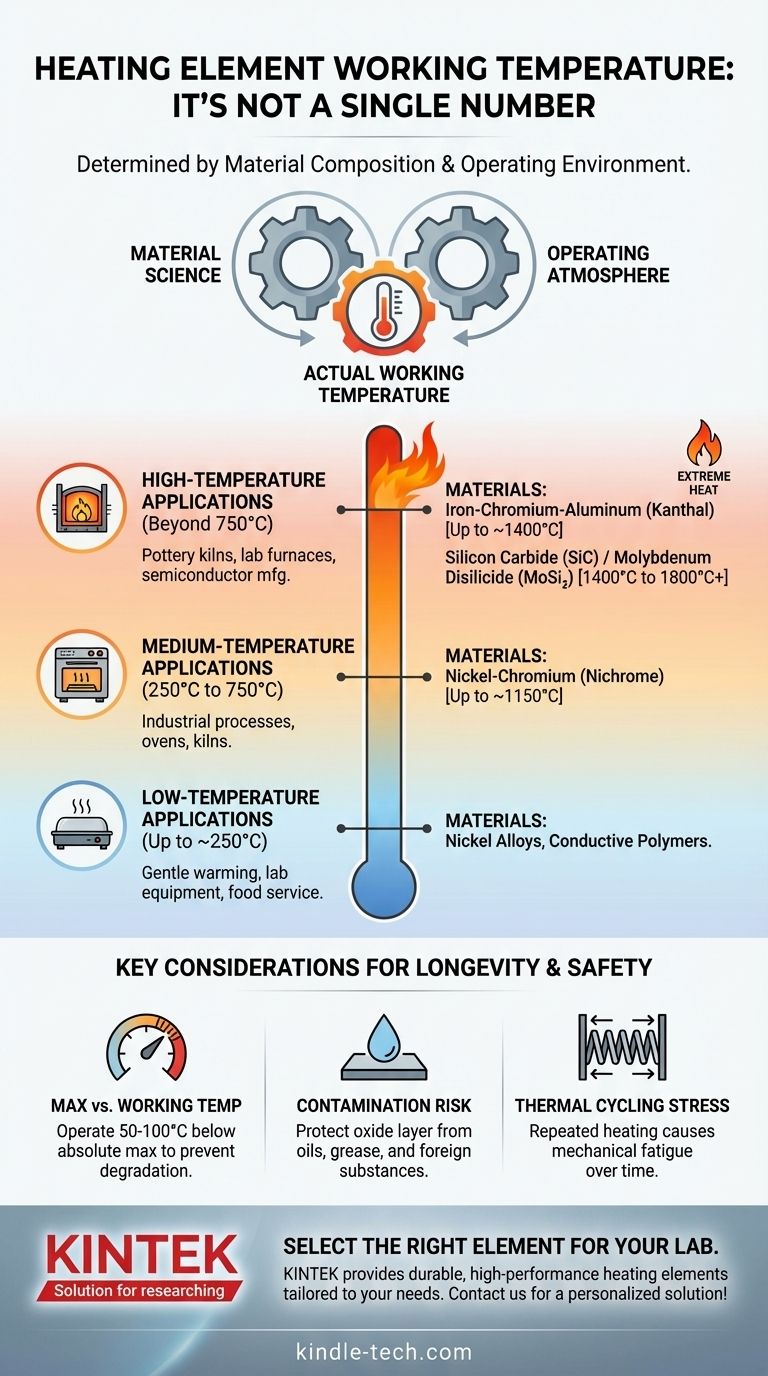
The working temperature of a heating element is not a single value but is determined entirely by its material composition and operating environment. While industrial heating processes are often categorized into low (under 250°C), medium (250°C - 750°C), and high-temperature (over 750°C) ranges, the elements themselves can operate anywhere from gentle warming to over 1800°C (3272°F) depending on the specific alloy or ceramic used.
The core issue is not finding a universal "working temperature," but matching the element's material capabilities to your specific temperature range and operating atmosphere to ensure efficiency, reliability, and a long service life.

What Truly Defines a Heating Element's Temperature?
An element's ability to generate heat without destroying itself is a function of its fundamental material science. Two factors are paramount: the material itself and the atmosphere in which it operates.
The Critical Role of Material Composition
The maximum operating temperature of a heating element is dictated by the alloy or ceramic it is made from. Different materials have vastly different thermal limits.
For example, a common Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) wire found in a household toaster operates effectively around 1150°C, while an industrial furnace may use a Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) element that can reach over 1800°C.
Oxidation and the Protective Layer
Metallic heating elements don't simply melt; they fail when they can no longer resist oxidation. At high temperatures, the metal reacts with oxygen in the air.
Successful heating alloys, like Nichrome or Kanthal (FeCrAl), are designed to form a thin, stable, and protective layer of oxide on their surface. This layer prevents oxygen from reaching the core metal, dramatically slowing further oxidation and allowing the element to survive at extreme temperatures.
The Impact of the Operating Atmosphere
The environment surrounding the element can drastically alter its performance and maximum temperature.
An element rated for 1200°C in open air might have a completely different limit in a vacuum, an inert gas like argon, or a chemically reactive atmosphere. Certain atmospheres can strip away the protective oxide layer, leading to rapid failure at temperatures far below the element's nominal rating.
Matching Element Materials to Temperature Ranges
Using the broad categories of industrial heating, we can map common element materials to their typical applications.
Low-Temperature Applications (Up to ~250°C)
This range is for gentle warming, such as in laboratory equipment or food service. Elements are often flexible pads or simple wires made of materials like nickel alloys or even specialized conductive polymers. The primary goal is controlled, low-intensity heat.
Medium-Temperature Applications (250°C to 750°C)
This is the domain of many industrial processes, ovens, and kilns. Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) alloys are a workhorse in this category and slightly above it, valued for their durability and stability.
High-Temperature Applications (Beyond 750°C)
This is where material selection becomes critical.
- Up to ~1400°C: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, often known by the trade name Kanthal, are superior to Nichrome at these temperatures. They form a more resilient aluminum oxide layer, giving them a longer lifespan in high-heat applications like pottery kilns and lab furnaces.
- Beyond ~1400°C: Metallic alloys reach their limits. Advanced ceramic elements are required for the most extreme temperatures. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are used in semiconductor manufacturing, glass melting, and advanced materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
Simply choosing an element with a high temperature rating is not enough. Understanding the practical limitations is key to preventing failure.
Maximum Temperature vs. Working Temperature
An element's "maximum temperature" is the absolute limit it can withstand before rapid degradation occurs. The ideal "working temperature" should be at least 50°C-100°C lower than this maximum.
Operating an element at its absolute limit will drastically shorten its service life.
The Risk of Contamination
The protective oxide layer is chemically vulnerable. Foreign substances like oils, grease, or even contact with certain types of insulation or ceramics at high temperatures can attack this layer, causing localized "hot spots" and rapid burnout.
Mechanical Stress and Thermal Cycling
Every time an element heats up, it expands; when it cools, it contracts. This thermal cycling induces mechanical stress. Over thousands of cycles, this stress can lead to cracks and failure, a phenomenon known as material fatigue.
How to Select the Right Element for Your Application
To ensure reliability and efficiency, you must match the element's material capabilities to your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating below 1100°C: Nichrome alloys offer a cost-effective and reliable solution for applications like commercial ovens, dryers, and heat treat furnaces.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature furnaces up to 1400°C: FeCrAl (Kanthal) alloys provide superior performance and longevity due to their more stable protective oxide layer.
- If your primary focus is extreme-temperature processing above 1400°C: You must use specialized ceramic elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) to handle the heat and environment.
Always select an element with a maximum temperature rating significantly above your intended operating point to guarantee a long and stable service life.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Alloys/Ceramics | Typical Max Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temp | Nickel Alloys, Polymers | Up to ~250°C | Lab equipment, food warming |
| Medium-Temp | Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) | Up to ~1150°C | Industrial ovens, kilns |
| High-Temp (Metallic) | Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Kanthal) | Up to ~1400°C | Pottery kilns, lab furnaces |
| High-Temp (Ceramic) | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1400°C to 1800°C+ | Semiconductor, glass melting, research |
Selecting the right heating element is critical for your lab's efficiency and safety. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing durable, high-performance heating elements tailored to your specific temperature range and atmosphere. Our experts can help you choose the ideal material—from Nichrome for medium-heat applications to advanced SiC for extreme temperatures—ensuring reliability and a long service life. Contact us today to discuss your heating needs and get a personalized solution that maximizes your lab's performance. Reach out via our contact form for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs











