At its core, vacuum annealing is a high-precision heat treatment process where a material, typically metal, is heated to a specific temperature and then slowly cooled inside a vacuum chamber. Unlike standard annealing, conducting the process in a vacuum prevents surface oxidation and other atmospheric reactions, resulting in a cleaner, more pristine final product with enhanced ductility and reduced internal stress.
The fundamental purpose of annealing is to soften a material and relieve internal stresses. Using a vacuum elevates this process by creating a controlled, contamination-free environment, which is critical for protecting the material's surface integrity and achieving superior, predictable results.

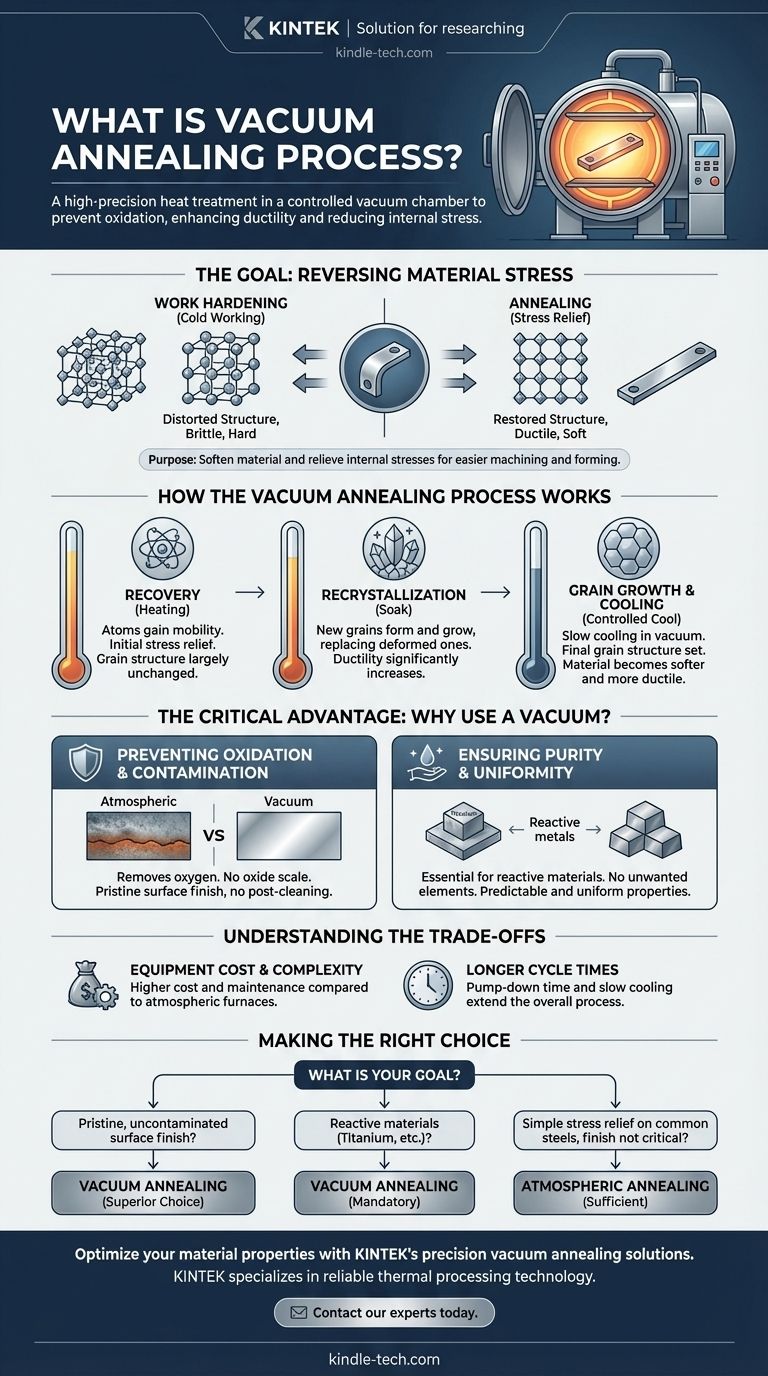
The Goal of Annealing: Reversing Material Stress
What is Work Hardening?
When metals are bent, stamped, or machined—a process known as cold working—their internal crystalline structure becomes distorted and strained. This effect, called work hardening or strain hardening, makes the material harder and more brittle.
While increased hardness can be desirable, it also reduces the material's ductility (its ability to deform without fracturing). A severely work-hardened part may crack or fail if subjected to further processing or operational stress.
The Purpose of the Anneal
Annealing is a thermal process designed to reverse the effects of work hardening. By carefully heating and cooling the material, the process relieves these internal stresses and restores its original ductility.
This makes the material easier to machine, form, or shape in subsequent manufacturing steps without the risk of failure. It essentially "resets" the material's internal structure to a more uniform and stable state.
How the Vacuum Annealing Process Works
The process can be broken down into three distinct stages that occur as the material is heated and cooled within the vacuum furnace.
Stage 1: Recovery
As the temperature inside the furnace rises, the material enters the recovery stage. During this phase, the atoms within the metal's crystal lattice gain enough thermal energy to begin moving.
This initial movement allows the material to relieve some of its internal stresses that were induced during cold working. However, the core grain structure of the metal remains largely unchanged.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
As the temperature continues to increase to the target level, the material enters recrystallization. At this point, new, strain-free crystals (or "grains") begin to form and grow, gradually replacing the old, deformed ones.
The material is held at this temperature—known as the "soak" period—long enough for this process to complete. This stage is what truly erases the effects of work hardening, dramatically reducing hardness and increasing ductility.
Stage 3: Grain Growth and Cooling
After the soak period, the material is cooled at a very slow, controlled rate, often by simply turning the furnace off and letting it cool naturally. This slow cooling prevents new stresses from being introduced.
During this phase, the newly formed grains may continue to grow. The final grain size is a critical factor that influences the material's mechanical properties; slower cooling typically results in larger grains and a softer, more ductile material.
The Critical Advantage: Why Use a Vacuum?
While the thermal cycle is similar to standard annealing, performing it in a vacuum offers distinct and crucial advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The primary benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen and other reactive gases. At high temperatures, metals like steel, titanium, and copper react readily with oxygen, forming a layer of oxide scale on the surface.
This scale is undesirable, often requiring costly and abrasive post-processing steps like sandblasting or acid pickling to remove. Vacuum annealing produces parts with a bright, clean surface finish straight out of the furnace.
Ensuring Purity and Uniformity
For high-performance or reactive materials (like titanium or certain specialty alloys), even trace amounts of atmospheric gases can contaminate the material and degrade its mechanical properties.
A vacuum environment ensures that no unintended elements are introduced into the metal during the heat treatment. This guarantees the material's purity and results in highly predictable and uniform properties across the entire workpiece.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. The systems required to create and maintain a high vacuum add layers of complexity and maintenance.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to the beginning of every cycle. Furthermore, the slow, controlled cooling that often occurs within the insulated vacuum chamber can extend the overall process time compared to other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding on a heat treatment process, your choice should be driven by the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is a pristine, uncontaminated surface finish: Vacuum annealing is the superior choice, as it eliminates the need for post-process cleaning.
- If you are working with reactive materials like titanium, refractory metals, or certain stainless steels: Vacuum annealing is often mandatory to prevent surface oxidation and material degradation.
- If your goal is simple stress relief on common steels and surface finish is not critical: A less expensive atmospheric annealing process may be sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, specifying the correct annealing process is a critical step in guaranteeing the performance, reliability, and manufacturability of your component.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery | Heating begins; atoms gain mobility | Initial stress relief |
| Recrystallization | Held at target temperature; new grains form | Work hardening reversed; ductility restored |
| Grain Growth & Cooling | Slow, controlled cooling in vacuum | Final grain structure set; material softened |
Optimize your material properties with KINTEK's precision vacuum annealing solutions.
Are you working with reactive metals like titanium or require a flawless, scale-free surface finish? Our advanced vacuum furnaces provide the contamination-free environment necessary to protect your materials and achieve predictable, superior results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable thermal processing technology.
Contact our experts today to discuss how vacuum annealing can enhance your manufacturing process and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















