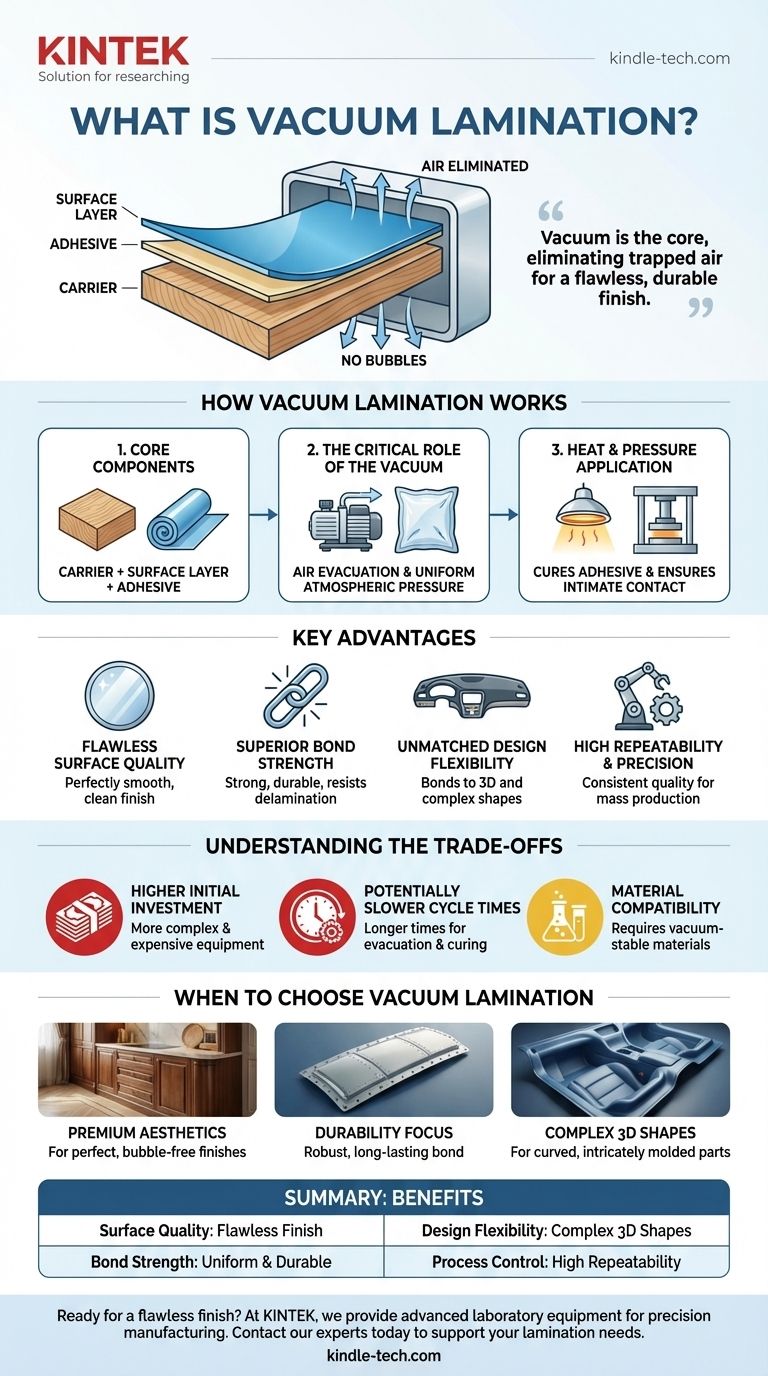
In essence, vacuum lamination is a high-precision manufacturing process used to bond a decorative or functional surface layer to a core material, known as a carrier. By performing this bonding process inside a vacuum, air is completely eliminated from between the layers, preventing bubbles and ensuring a flawless, durable, and seamless finish.
The critical insight is that using a vacuum is not just an incidental step; it is the core of the process. It solves the fundamental problem of trapped air and contaminants, enabling a level of surface quality and bond integrity that is difficult to achieve with conventional methods.

How Vacuum Lamination Works
To understand its value, it's important to grasp the fundamental mechanics. The process revolves around controlling the environment to create a perfect bond between two or more materials.
The Core Components
The process always involves a base material, or carrier, which provides the structure. This could be wood, MDF, metal, or a composite. A decorative or functional layer, such as a wood veneer, a colored film, or a protective coating, is then applied to this carrier, typically with an adhesive layer in between.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Once the materials are assembled, they are placed inside a press or a bag from which all the air is evacuated. This vacuum serves two purposes. First, it eliminates the risk of trapping air bubbles, which are a primary cause of defects and bond failure in lamination.
Second, it allows atmospheric pressure to apply a completely uniform force across the entire surface of the part. This ensures consistent bonding even on complex, curved, or intricately shaped surfaces.
The Application of Heat and Pressure
While the assembly is under vacuum, heat and pressure are often applied. The heat helps to cure the adhesive, creating a permanent chemical bond between the layers. The controlled pressure ensures the materials are held in intimate contact during this curing phase.
Key Advantages of the Vacuum Process
Choosing to laminate in a vacuum is a deliberate engineering decision driven by the need for superior results. This method offers distinct advantages over atmospheric pressure alternatives.
Flawless Surface Quality
By removing air and potential contaminants like dust, the process yields a perfectly smooth and clean surface. This is critical for high-end decorative applications where visual appearance is paramount.
Superior Bond Strength
The uniform pressure and absence of air pockets create an exceptionally strong and durable bond. This significantly reduces the risk of delamination over the product's lifespan, even under stress or environmental changes.
Unmatched Design Flexibility
Vacuum lamination excels at bonding flexible materials to three-dimensional and complex shapes. The atmospheric pressure naturally conforms the surface layer to every curve and contour of the carrier, something difficult for mechanical presses to achieve.
High Repeatability and Precision
Modern vacuum lamination systems are computer-controlled, ensuring that process parameters like temperature, pressure, and time are identical for every part. This leads to high repeatability and consistent quality in mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum lamination is not the solution for every scenario. It's essential to understand its limitations to make an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
The equipment required for vacuum lamination, such as a vacuum press, is more complex and more expensive than basic mechanical presses. This can be a barrier for smaller operations.
Potentially Slower Cycle Times
The process of evacuating the chamber, heating, and cooling can result in longer cycle times compared to some simpler lamination methods. This must be factored into production planning.
Material Compatibility
The materials and adhesives used must be suitable for the vacuum environment and the temperatures involved. Some materials may outgas (release trapped gasses) under vacuum, which can interfere with the bonding process if not properly managed.
When to Choose Vacuum Lamination
Your specific goal will determine if this process is the right fit for your application.
- If your primary focus is premium aesthetics: Choose vacuum lamination for products like high-end cabinetry, automotive dashboards, or architectural panels where a perfect, bubble-free finish is required.
- If your primary focus is durability: This method is ideal for components that require a robust, long-lasting bond that resists delamination, such as in aerospace or marine applications.
- If you are manufacturing complex 3D shapes: Vacuum lamination is the superior choice for applying a surface finish to curved or intricately molded parts.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum lamination is an investment in quality and reliability for demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit of Vacuum Lamination |
|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Eliminates air bubbles and contaminants for a flawless finish. |
| Bond Strength | Creates a uniform, durable bond that resists delamination. |
| Design Flexibility | Perfect for complex, curved, and 3D shapes. |
| Process Control | Ensures high repeatability and consistent quality in production. |
Ready to achieve a flawless, bubble-free finish on your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for precision manufacturing processes like vacuum lamination. Whether you're working on high-end cabinetry, automotive interiors, or aerospace components, our solutions can help you ensure superior bond strength and perfect surface quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific lamination needs and enhance your production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process



















