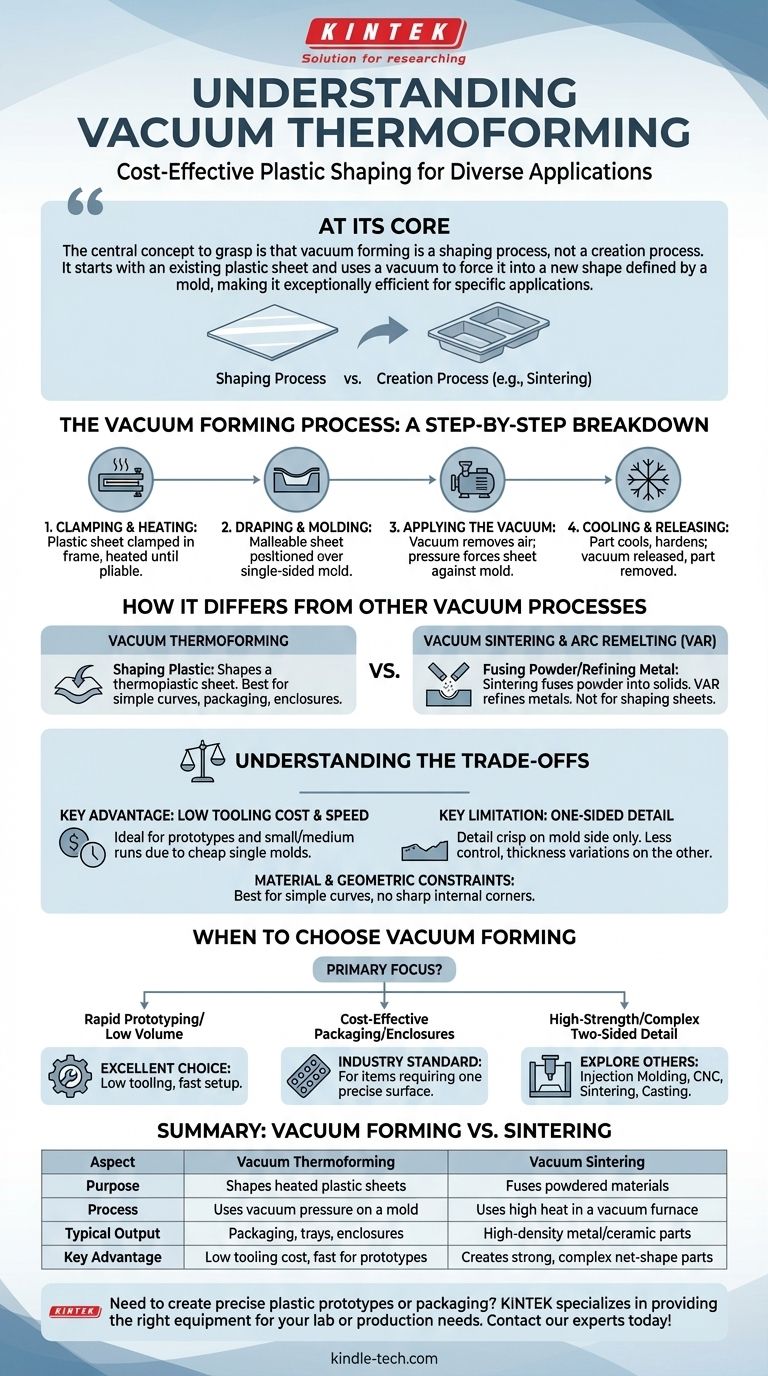
At its core, vacuum thermoforming is a simplified manufacturing process that uses vacuum pressure to shape a heated sheet of plastic over a single mold. It is one of the most common and cost-effective methods for creating plastic parts, especially those that only require precise detail on one side, such as contoured packaging, trays, and simple enclosures.
The central concept to grasp is that vacuum forming is a shaping process, not a creation process. It starts with an existing plastic sheet and uses a vacuum to force it into a new shape defined by a mold, making it exceptionally efficient for specific applications.

The Vacuum Forming Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand its applications, you must first understand its mechanics. The process is straightforward, which is a primary source of its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Clamping and Heating
A sheet of plastic is clamped into a frame. This sheet is then heated until it becomes soft, pliable, and reaches a formable temperature.
Step 2: Draping and Molding
Once malleable, the plastic sheet is positioned over a mold. This mold contains the desired final shape of the part.
Step 3: Applying the Vacuum
A vacuum is activated, removing the air between the plastic sheet and the mold. Atmospheric pressure then pushes the soft plastic down, forcing it to conform tightly against the surface of the mold.
Step 4: Cooling and Releasing
The plastic cools and hardens into its new shape. The vacuum is released, and the newly formed part is removed from the mold, ready for trimming and finishing.
How Vacuum Forming Differs from Other Vacuum Processes
The term "vacuum" is used in many industrial processes, leading to potential confusion. Vacuum forming is fundamentally different from processes that use a vacuum for material creation or refinement.
Thermoforming vs. Sintering
Vacuum forming shapes a thermoplastic sheet. In contrast, vacuum sintering fuses a powdered material (like metal or ceramic) into a solid, high-density object inside a furnace. Sintering relies on atomic diffusion at high temperatures to create a material, not just shape it.
Thermoforming vs. Arc Remelting (VAR)
Vacuum arc remelting is a metallurgical process used to refine and purify metals. It uses an electric arc to melt an impure electrode in a vacuum, with the purified molten metal solidifying in a water-cooled mold. This is a high-purity refinement process, entirely different from shaping plastic.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Vacuum Forming
Like any manufacturing method, vacuum forming has a distinct profile of advantages and limitations. Understanding these is critical to choosing the right process for your project.
Key Advantage: Low Tooling Cost and Speed
Because it only requires a single-sided mold, tooling is significantly cheaper and faster to produce compared to methods like injection molding. This makes it ideal for prototypes, small-to-medium production runs, and large parts where mold costs would otherwise be prohibitive.
Key Limitation: One-Sided Detail
The side of the plastic touching the mold will have crisp, defined detail. However, the side away from the mold is less controlled, often resulting in less-defined features and variations in wall thickness. This is the primary trade-off of the process.
Material and Geometric Constraints
The process is best suited for parts with simple curves and no sharp internal corners or undercuts. Deep draws can cause excessive material thinning at the corners.
When to Choose Vacuum Forming
Your project's specific goals will determine if vacuum forming is the correct technical choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or low-volume production: Vacuum forming is an excellent choice due to its low tooling cost and fast setup times.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective packaging or simple enclosures: It is the industry standard for producing items like blister packs, food trays, and equipment covers where only one surface requires precise definition.
- If your primary focus is high-strength parts or complex, two-sided detail: You should explore other methods like injection molding, CNC machining, or for metals, processes like sintering or casting.
Choosing the right manufacturing process begins with a clear understanding of your project's non-negotiable requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Thermoforming | Vacuum Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Shapes heated plastic sheets | Fuses powdered materials into solids |
| Process | Uses vacuum pressure on a mold | Uses high heat in a vacuum furnace |
| Typical Output | Packaging, trays, enclosures | High-density metal/ceramic parts |
| Key Advantage | Low tooling cost, fast for prototypes | Creates strong, complex net-shape parts |
Need to create precise plastic prototypes or packaging? KINTEK specializes in providing the right equipment for your lab or production needs. Whether you're exploring vacuum forming or advanced processes like sintering, our expertise ensures you get the optimal solution for material shaping and fabrication. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- How does the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process work? Enhance Material Density and Integrity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace for refractory alloys? Enhance Nb-W Performance
- What conditions are needed for Ti/Al2O3 fabrication? Master Vacuum Hot-Pressing for High-Density Composites
- What are the technical advantages of using a vacuum hot-pressing furnace? Enhance Graphene-Alumina Composites
- Why is a vacuum hot press furnace required for sintering copper-based diamond composites? Achieve Maximum Density
- What are the benefits of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Maximum Component Reliability and Performance
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Achieve Peak Density for TiB-Titanium
- What are the functions of a graphite mold during the vacuum hot-press sintering? Optimize Diamond/Copper Densification



















