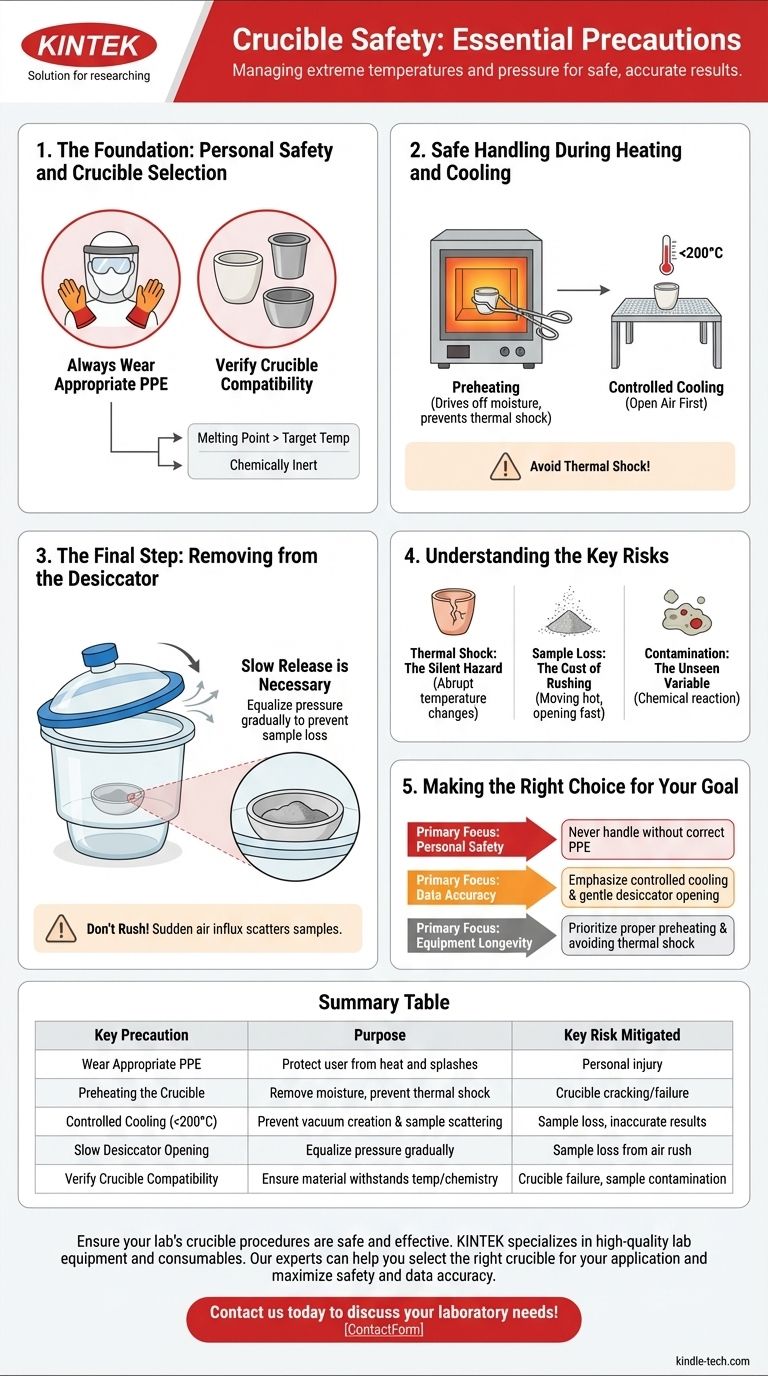
The most critical precautions for using a crucible involve managing extreme temperatures and pressure changes with deliberate, controlled actions. You must always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), ensure the crucible is preheated before use, allow it to cool properly before placing it in a desiccator, and open the desiccator slowly to prevent sample loss.
The core principle behind all crucible safety is avoiding sudden changes. Whether it's a rapid temperature shift causing thermal shock or a quick pressure change scattering your sample, methodical and patient handling is essential for both safety and accurate results.
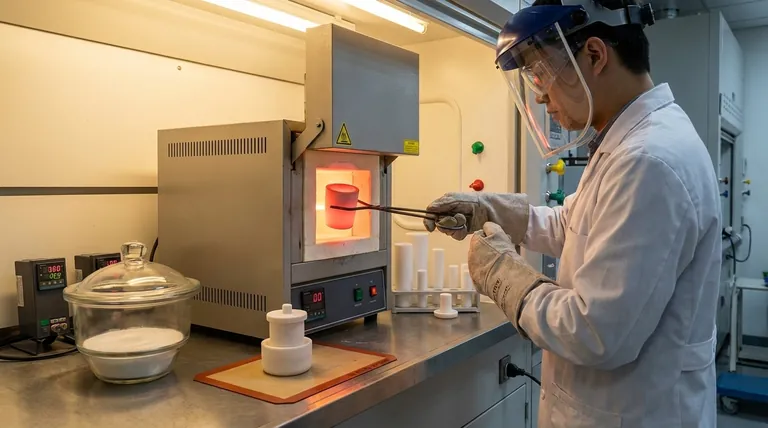

The Foundation: Personal Safety and Crucible Selection
Before you begin any work, you must prepare both yourself and your equipment. Neglecting this foundational stage introduces unnecessary risk.
Always Wear Appropriate PPE
Personal Protective Equipment is your first line of defense. When handling crucibles, especially those containing molten materials, proper PPE is non-negotiable.
This includes heat-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and often a full face shield to protect against splashes and intense heat.
Verify Crucible Compatibility
Using the wrong type of crucible can lead to catastrophic failure. Before heating, confirm that your crucible's material is appropriate for the task.
It must have a melting point higher than your target temperature and be chemically inert with the substances you are heating. This prevents the crucible from deteriorating, breaking, or contaminating your sample.
Safe Handling During Heating and Cooling
The heating and cooling phases are where crucibles are most vulnerable to damage. The primary danger is thermal shock—stress caused by a rapid change in temperature.
The Importance of Preheating
A crucible must be properly prepared for high temperatures. Use crucible tongs to place the empty crucible in a muffle or electric furnace to preheat it.
This process serves two purposes: it drives off any residual moisture that could interfere with your results and prevents thermal shock when the sample is introduced. Similarly, slightly warming your tongs before handling a very hot crucible helps prevent the temperature difference from cracking the ceramic.
Controlled Cooling is Critical
Never move a crucible directly from a hot furnace into a sealed desiccator. It must be allowed to cool in the open air first.
The crucible's temperature should be below 200℃ before being transferred. Placing a hotter crucible into a desiccator creates a strong vacuum as the air inside cools, which can make the lid nearly impossible to open. It also causes strong air convection that can scatter fine, lightweight samples like ash.
The Final Step: Removing from the Desiccator
A desiccator is used to keep a sample in a dry, low-humidity environment while it cools to room temperature. Because the crucible was placed in it while still warm, the air inside has cooled and contracted, creating a partial vacuum.
Why a Slow Release is Necessary
The vacuum inside the desiccator is the primary hazard at this stage. If the lid is opened quickly, atmospheric air will rush in violently.
This sudden influx of air can easily blow your sample out of the crucible, ruining the experiment and invalidating your results. This is especially critical when working with fine powders or ash.
The Correct Unsealing Technique
To prevent sample loss, you must equalize the pressure gradually. Slide the desiccator lid open very slowly and gently.
Opening it just a crack allows air to hiss in over several seconds. Once the pressure has equalized, you can remove the lid completely and safely access your crucible.
Understanding the Key Risks
Every precaution is designed to mitigate a specific risk. Understanding these risks helps reinforce the importance of proper procedure.
Thermal Shock: The Silent Hazard
The single greatest threat to a crucible's integrity is thermal shock. Abrupt temperature changes create internal stress that can cause microscopic fractures to form and spread, leading to a complete failure. Preheating crucibles and tongs, and allowing for controlled cooling, are the primary defenses against this.
Sample Loss: The Cost of Rushing
Two procedural mistakes directly lead to sample loss: moving a hot crucible into a desiccator too soon (scattering ash via convection) and opening the desiccator too quickly (scattering ash via air pressure). Both are caused by impatience and can render an entire analysis useless.
Contamination: The Unseen Variable
This risk is managed before the heating even begins. If the crucible material reacts with the melt, it will not only damage the crucible over time but also introduce impurities into your sample. Always verify chemical compatibility as a non-negotiable first step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which precautions are most critical to your success.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Never handle a crucible without the correct heat-resistant gloves, goggles, and face shield.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Emphasize controlled cooling and extremely gentle desiccator opening to prevent any loss of your final sample.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Prioritize proper preheating and avoiding thermal shock to prevent cracks and extend the life of your crucibles.
Ultimately, safe and effective crucible use is defined by deliberate, methodical work that respects the material's physical limits.
Summary Table:
| Key Precaution | Purpose | Key Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Appropriate PPE (gloves, goggles) | Protect user from heat and splashes | Personal injury |
| Preheating the Crucible | Remove moisture, prevent thermal shock | Crucible cracking/failure |
| Controlled Cooling (<200°C before desiccator) | Prevent vacuum creation and sample scattering | Sample loss, inaccurate results |
| Slow Desiccator Opening | Equalize pressure gradually | Sample loss from air rush |
| Verify Crucible Compatibility | Ensure material withstands temperature/chemistry | Crucible failure, sample contamination |
Ensure your lab's crucible procedures are safe and effective. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles designed for durability and precise thermal performance. Our experts can help you select the right crucible for your application and provide guidance on best practices to maximize safety and data accuracy. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and enhance your crucible handling protocols!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Boron Nitride (BN) Crucible for Phosphorous Powder Sintered
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety



















