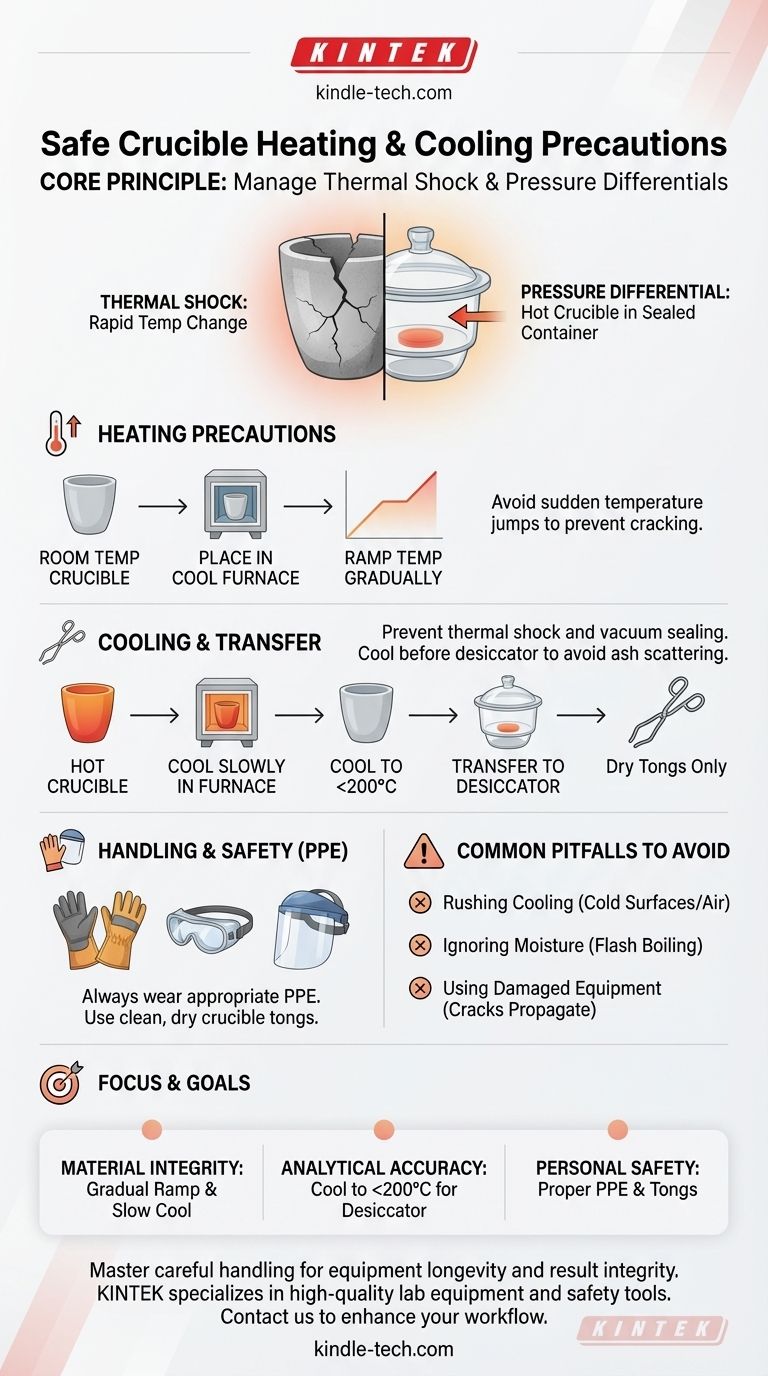
To safely heat and cool a crucible, the most critical precautions are to manage the rate of temperature change to prevent thermal shock and to handle it with the correct personal protective equipment. A crucial step is allowing the crucible to cool to below 200°C before moving it into a desiccator. This prevents hot air convection from scattering light samples, like ash, and avoids forming a strong vacuum that can seal the desiccator lid shut.
The core principle behind safe crucible handling is the management of two physical forces: thermal shock and pressure differentials. Abrupt temperature changes introduce stress that cracks the material, while transferring an extremely hot crucible to a sealed container creates a powerful and often problematic vacuum.

The Primary Risk: Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the single most common reason for crucible failure. It occurs when one part of the crucible expands or contracts faster than another, creating internal stress that results in cracks or complete fracture.
What Causes Thermal Shock?
All materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. If this temperature change happens too quickly, the temperature difference across the crucible body becomes extreme. The outside cools and shrinks while the inside is still hot and expanded, leading to catastrophic failure.
Precaution for Heating
Never place a room-temperature crucible directly into a red-hot furnace. The sudden temperature jump is a primary cause of cracking. Instead, place the crucible in a cool furnace and allow it to heat up gradually as the furnace's temperature is ramped up.
Precaution for Cooling
Never place a hot crucible on a cold surface, such as a granite countertop or steel bench. The rapid heat transfer will almost certainly crack it. The safest method is to allow the crucible to cool slowly inside the furnace itself, perhaps with the door slightly ajar once the temperature has dropped significantly.
Handling and Transfer Precautions
Proper handling ensures both personal safety and the integrity of your experiment. The moments of transfer—from furnace to bench, from bench to desiccator—are points of high risk.
Always Use Proper Tools
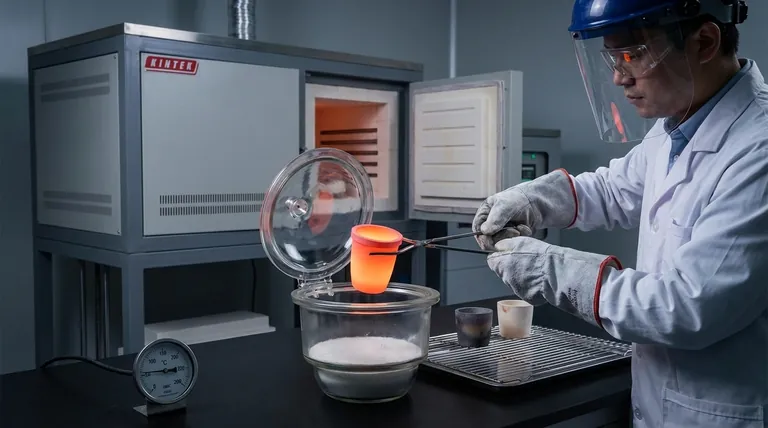
Use clean, dry crucible tongs for handling. Do not use standard pliers or grips. Ensure the tongs are free of any contaminants that could be transferred to your sample. Wet tongs can also introduce moisture, which can cause thermal shock.
The Desiccator Cooling Step
As noted, a crucible should be cooled to below 200°C before being placed in a desiccator. A very hot crucible will heat the air inside the sealed container. As this air cools, its pressure drops dramatically, creating a vacuum that can make the lid nearly impossible to remove without breaking the seal.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear appropriate safety gear. This is non-negotiable, especially when working with high temperatures or molten materials. Essential equipment includes thermal-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and often a full face shield to protect from splashes or unexpected reactions.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding common mistakes is key to developing a reliable and safe workflow.
Rushing the Process
The most frequent mistake is impatience. Attempting to cool a crucible quickly by placing it on a heat sink or using compressed air is a recipe for disaster. The time saved is not worth the cost of a ruined experiment or broken equipment.
Ignoring Moisture
Even microscopic amounts of moisture can be dangerous. If a crucible with residual moisture is heated rapidly, the water can turn to steam and flash boil, potentially cracking the crucible or ejecting its contents. Always ensure crucibles are completely dry before heating.
Using Damaged Equipment
Before every use, perform a quick visual inspection of your crucible. Do not use a crucible that has any existing cracks, no matter how small. The stress of heating will almost certainly cause a small crack to propagate and lead to failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific procedure should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material integrity (avoiding cracks): Always ramp heating and cooling temperatures gradually and avoid placing hot crucibles on cold surfaces.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy (e.g., ashing): Ensure the crucible cools sufficiently (below 200°C) before placing it in a desiccator to prevent sample loss from air currents.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always use clean, dry crucible tongs and wear thermal gloves and full-face protection, especially when working with molten materials.
Mastering the careful heating and cooling of a crucible is the definitive way to ensure the longevity of your equipment and the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Precautions | Key Actions | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Place in cool furnace, ramp temperature gradually | Prevent cracking from thermal shock |
| Cooling | Cool slowly inside furnace, avoid cold surfaces | Ensure material integrity and longevity |
| Transfer | Use clean, dry crucible tongs; cool below 200°C before desiccator | Maintain sample accuracy and prevent vacuum sealing |
| Safety | Wear thermal gloves, safety goggles, and face shield | Protect against burns and splashes |
Ensure your lab's crucible handling is safe and effective. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable crucibles and safety tools designed for precise thermal processes. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to prevent thermal shock and enhance your workflow's safety and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace? Achieve High-Purity Heating for Your Lab
- How do you clean a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Safety and Longevity
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between oven and muffle furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Equipment



















