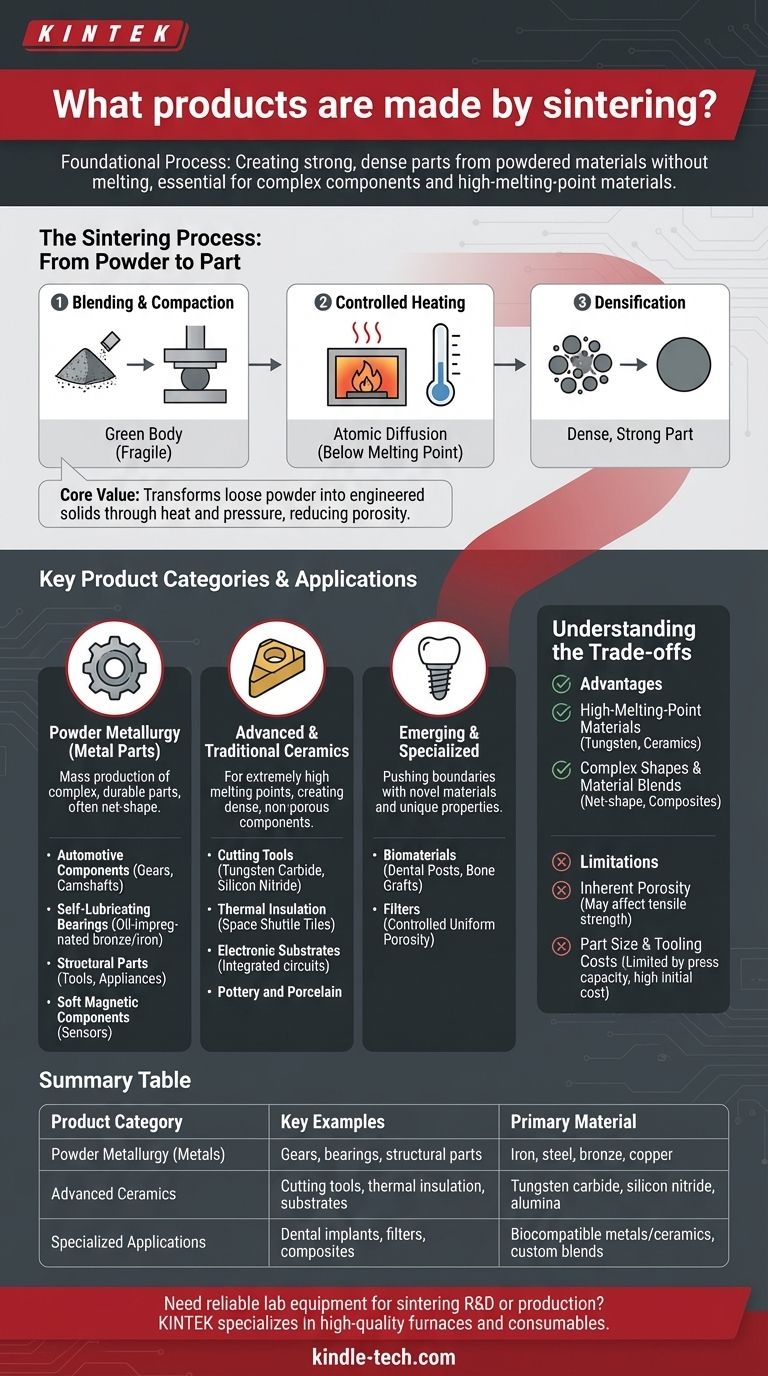
Sintering is the foundational process for creating a vast array of strong, dense parts from powdered materials without melting them. Key products include complex metal components like automotive gears and self-lubricating bearings, high-performance ceramics used for cutting tools and thermal insulation, and advanced medical products like dental implants. This method is essential for materials that are difficult or impossible to shape using traditional melting and casting.
The core value of sintering lies in its unique ability to create solid, high-performance components from materials with extremely high melting points or from specialized powder blends. It transforms loose powder into a dense, engineered solid through heat and pressure, enabling the manufacture of parts that would otherwise be impractical to produce.
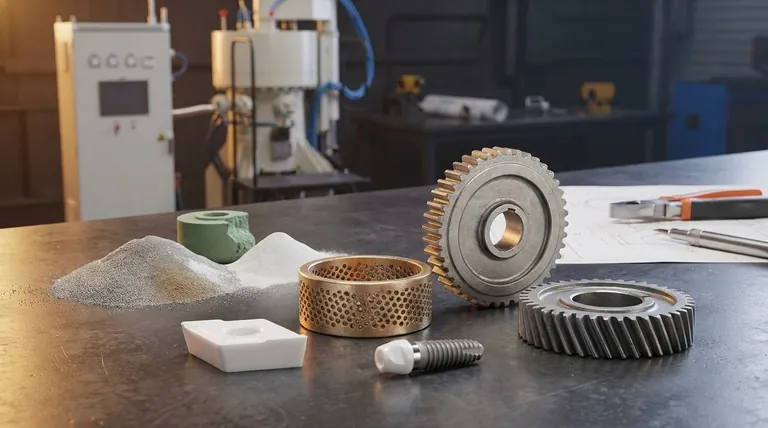

The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
To understand the products made by sintering, you must first understand how the process works. It's a method of atomic consolidation, not melting.
Stage 1: Blending and Compaction
The process begins with a fine powder, which can be a metal, ceramic, or a blend of different materials. This powder is precisely blended and then pressed into a mold under high pressure. The result is a fragile, lightly compressed part known as a "green body," which has the desired shape but lacks strength.
Stage 2: Controlled Heating
The green body is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The temperature is raised significantly, but critically, it is kept below the material's melting point. Any residual binding agents used during compaction are burned off at lower temperatures.
Stage 3: Atomic Diffusion and Densification
As the temperature rises, the atoms at the contact points between powder particles begin to diffuse across the boundaries. This atomic movement forms "necks" between particles, which grow and pull the particles closer together. This process systematically reduces the empty space (porosity) in the material, causing the part to shrink and become significantly more dense and strong.
Key Product Categories and Applications
Sintering is not a niche process; it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing across several critical industries.
Powder Metallurgy (Metal Parts)
This is the most common application of sintering for metals. It is used to mass-produce small, complex, and durable metal parts with high precision, often eliminating the need for further machining.
Common examples include:
- Automotive Components: Gears, camshaft lobes, sprockets, and engine connecting rods.
- Self-Lubricating Bearings: Created by sintering bronze or iron powders, leaving controlled porosity that is then impregnated with oil.
- Structural Parts: Components for power tools, appliances, and industrial machinery.
- Soft Magnetic Components: Used in sensors and actuators.
Advanced and Traditional Ceramics
Ceramics have extremely high melting points, making them impossible to cast like metals. Sintering is the primary method for producing dense, non-porous ceramic components.
Common examples include:
- Cutting Tools: Inserts for machining made from materials like tungsten carbide or silicon nitride.
- Thermal Insulation: The ceramic tiles on the Space Shuttle were a famous example, designed to withstand re-entry temperatures.
- Electronic Substrates: The base for integrated circuits.
- Pottery and Porcelain: Traditional ceramics are also produced through a form of sintering.
Emerging and Specialized Applications
Modern sintering techniques are pushing the boundaries of material science, enabling the creation of novel materials with unique properties.
- Biomaterials: Advanced methods like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) are used to create medical implants, such as dental posts and synthetic bone grafts, from biocompatible materials.
- Filters: By controlling the sintering process, parts can be made with a specific, uniform porosity, ideal for creating metal or ceramic filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is chosen for specific reasons, and it's important to understand both its advantages and its inherent limitations.
Advantage: High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is often the only practical way to form parts from materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and most technical ceramics. Their melting points are so high that melting and casting them is commercially or technically unfeasible.
Advantage: Complex Shapes and Material Blends
The process excels at creating net-shape or near-net-shape parts, drastically reducing waste and costly machining operations. It also allows for the creation of unique composites (like cermets—ceramic and metal) by blending powders that could not be combined via melting.
Limitation: Inherent Porosity
While the goal is densification, achieving 100% density is difficult. Most sintered parts retain a small amount of residual porosity, which can affect mechanical properties like tensile strength compared to a fully wrought or cast equivalent.
Limitation: Part Size and Tooling Costs
The size of sintered parts is limited by the capacity of the presses used for compaction. Furthermore, the initial cost of creating the molds and dies can be high, making the process most economical for medium-to-high volume production runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your material, geometry, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal parts: Powder metallurgy via sintering is an industry-standard, cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating components from high-temperature ceramics or refractory metals: Sintering is often the only viable manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced composites or biomedical devices: Modern sintering techniques provide a powerful tool for material innovation.
Ultimately, sintering is a versatile and powerful manufacturing process that enables the creation of high-performance parts that would otherwise be impossible to make.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Key Examples | Primary Material |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy (Metals) | Gears, bearings, structural parts | Iron, steel, bronze, copper |
| Advanced Ceramics | Cutting tools, thermal insulation, substrates | Tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, alumina |
| Specialized Applications | Dental implants, filters, composites | Biocompatible metals/ceramics, custom blends |
Need to source reliable lab equipment for your sintering R&D or production? KINTEK specializes in high-quality furnaces and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials or manufacturing complex parts, our solutions ensure consistent results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How heat is transferred differently for each type? Understand Conduction, Convection & Radiation
- How are advancements in compressor technology and refrigerant fluids improving ULT freezers? Boost Efficiency & Cut Costs
- What types of ultra low temperature freezer models are available for space-limited labs? Optimize Your Lab's Layout and Storage
- What materials should be heat treated? Enhancing Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the heat treatment process failures? A Guide to Preventing Cracking, Warping & Degradation
- What is the future potential for biomass? Unlocking a Sustainable Bioeconomy
- What are the requirements for polymer foam templates for reticulated MAX phase ceramics? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What is the process of plasma sputtering? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















