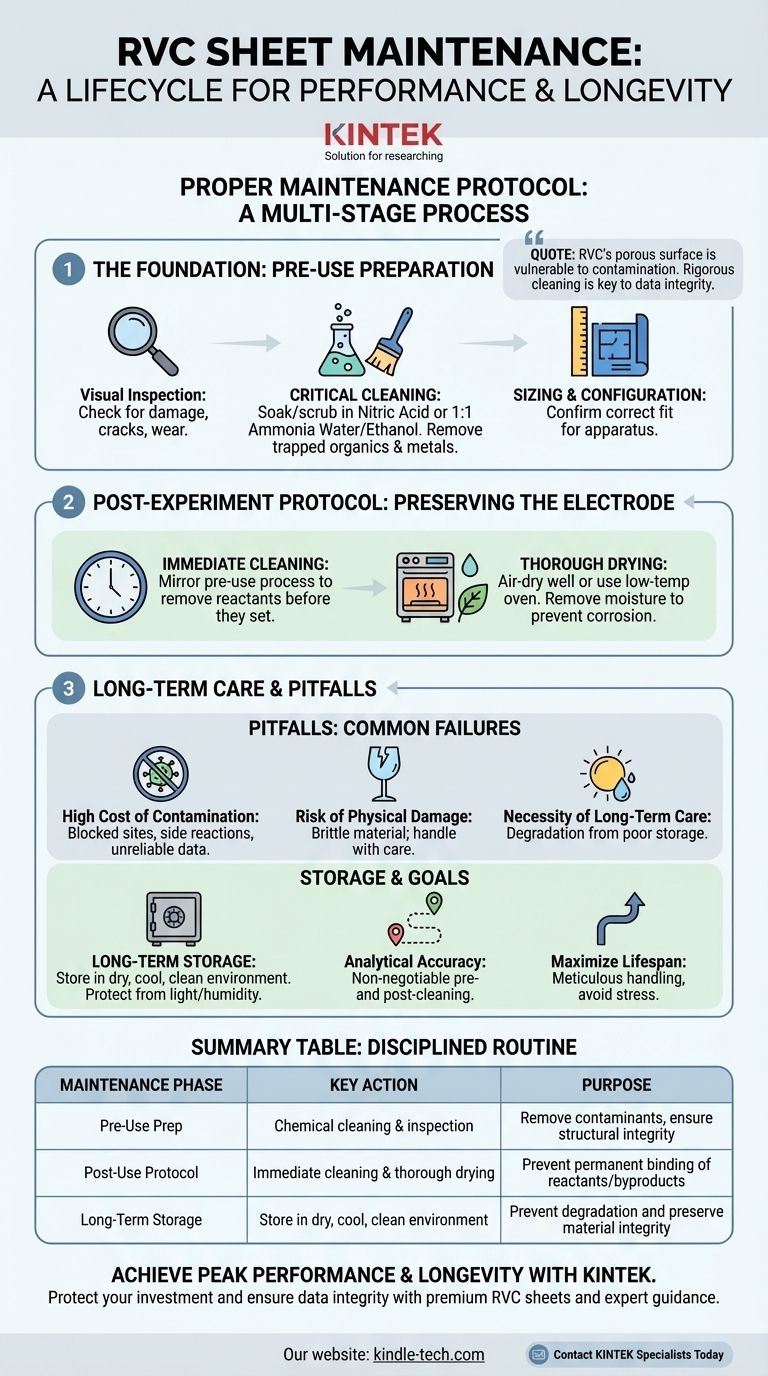
Proper maintenance of an RVC sheet is a multi-stage process that extends beyond simple periodic checks. It encompasses a disciplined protocol for preparation before use, immediate cleaning after an experiment, and correct long-term storage. The goal is to remove contaminants and preserve the material's unique porous structure to ensure consistent and reliable performance.
Reticulated Vitreous Carbon's (RVC) greatest strength—its vast, porous surface area—is also its greatest vulnerability to contamination. Therefore, effective maintenance is not about occasional check-ups but a rigorous cleaning protocol executed before and after every single use to guarantee the integrity of your experimental data.

The Foundation: Pre-Use Preparation
Before an RVC sheet can be used in any experiment, it must be properly prepared. This is the most critical phase for ensuring a clean, electrochemically active surface.
Visual Inspection for Physical Integrity
First, always inspect the sheet for any physical damage. Look for cracks, significant wear, or structural defects that could compromise its performance or the integrity of your electrochemical cell. A damaged sheet should be replaced.
The Critical Cleaning Step
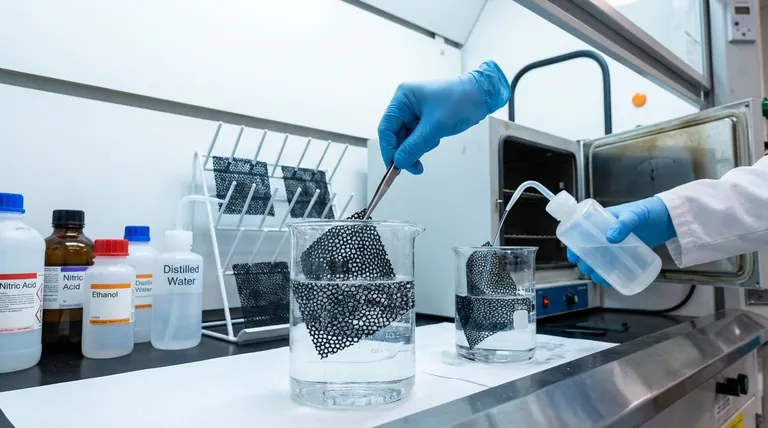
The high surface area of RVC can easily trap organic matter and metal compounds from previous use or even from the air. To remove these, a chemical cleaning is required.
Common methods involve soaking and gently scrubbing the sheet in a solution like nitric acid or a 1:1 mixture of ammonia water and anhydrous ethanol or ethyl acetate. This process removes contaminants that would otherwise interfere with your results.
Sizing and Configuration
Finally, confirm that the sheet's size and shape are appropriate for your specific experimental apparatus. An improper fit can lead to inconsistent current distribution and unreliable data.
Post-Experiment Protocol: Preserving the Electrode
What you do immediately after an experiment is just as important as what you do before. The goal is to prevent reactants and byproducts from permanently binding to the electrode surface.
Immediate Cleaning to Remove Contaminants
The RVC sheet must be cleaned immediately after the experiment concludes. This procedure should mirror the pre-use cleaning process to effectively remove all residual reactants and impurities before they have a chance to set.
Thorough Drying to Prevent Degradation
After cleaning, the sheet must be completely dried. You can either let it air-dry in a well-ventilated area or use a drying oven at a low temperature. Removing all moisture is crucial for preventing corrosion or unwanted side reactions during storage.
Understanding the Pitfalls
While RVC is robust, improper handling and a misunderstanding of its nature are the most common sources of failure. Recognizing these challenges is key to effective maintenance.
The High Cost of Contamination
A contaminated RVC electrode will not produce reliable data. Trapped impurities can block electrochemically active sites, introduce unwanted side reactions, and cause significant, non-reproducible shifts in measured potentials. Rigorous cleaning is your primary defense against this.
The Risk of Physical Damage
RVC is a form of glassy carbon and can be brittle. Aggressive scrubbing or careless handling can easily cause fractures. Always handle the material with care, especially during the cleaning and drying stages.
The Necessity of Long-Term Care
Even when not in use, an RVC sheet requires proper care. Cleaned and dried sheets must be stored in a dry, cool, and clean environment. Keep them protected from direct sunlight and high humidity, which can degrade their integrity over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific maintenance focus may shift slightly depending on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy and reproducibility: The non-negotiable pre- and post-experiment cleaning protocol is the most critical factor for success.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the lifespan of the RVC sheet: Meticulous handling, proper storage, and avoiding unnecessary physical stress during cleaning are your top priorities.
Ultimately, a disciplined maintenance routine is the foundation for achieving trustworthy and repeatable results with your RVC electrodes.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Phase | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Use Preparation | Chemical cleaning (e.g., nitric acid) & visual inspection | Remove contaminants, ensure structural integrity |
| Post-Use Protocol | Immediate cleaning & thorough drying | Prevent permanent binding of reactants/byproducts |
| Long-Term Storage | Store in a dry, cool, clean environment | Prevent degradation and preserve material integrity |
Achieve peak performance and longevity for your RVC electrodes with KINTEK.
Our high-quality RVC sheets are engineered for reliability, but their performance depends on proper care. The meticulous maintenance routine outlined above is essential for protecting your investment and ensuring the integrity of your electrochemical data.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of research and quality control laboratories. Whether you are setting up a new lab or optimizing an existing one, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success.
Let us support your research with reliable products and expert guidance.
Contact our lab equipment specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- What is the difference between RDE and RRDE? Unlock Advanced Electrochemical Reaction Analysis
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode
- What is the application of RRDE? Unlock Quantitative Catalyst and Reaction Insights



















