Technically, molten steel is already in its liquid state. The question you are likely asking is, "At what temperature does solid steel begin to melt?" While a common approximation is around 1370°C (2500°F), the reality is that there is no single melting point for steel. The exact temperature varies significantly based on the steel's specific composition.
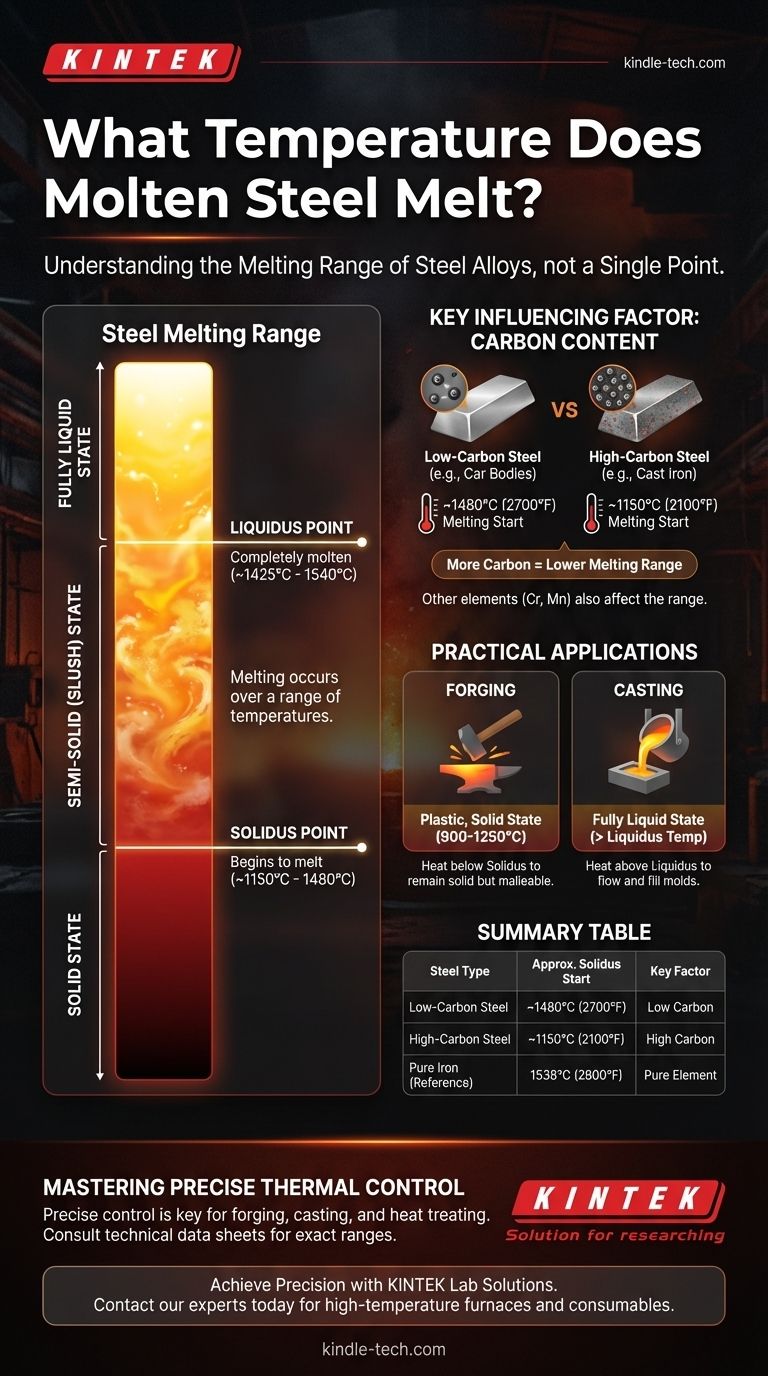
The most critical concept to understand is that steel, as an alloy, does not have a single melting point. Instead, it has a melting range defined by two different temperatures: the point where it begins to melt and the point where it becomes fully liquid.

Why a Single Temperature is an Inaccurate Answer
Many professionals are surprised to learn that a material as common as steel doesn't have one fixed melting temperature. This variability stems from its fundamental nature as an alloy.
Pure Metals vs. Alloys
A pure element, like iron, has a precise melting point. At standard pressure, pure iron melts and freezes at exactly 1538°C (2800°F). There is no in-between state.
Steel, however, is not a pure element. It is an alloy of iron and carbon, often with other elements mixed in. This mixture of atoms disrupts the neat, orderly crystal structure of pure iron, fundamentally changing its melting behavior.
Introducing the Melting Range
Because it's an alloy, steel melts over a range of temperatures. This range is defined by two key points:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the steel first begins to melt. Below this temperature, the steel is 100% solid.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the steel becomes completely molten. Above this temperature, the steel is 100% liquid.
Between the solidus and liquidus temperatures, the steel exists in a semi-solid, slushy state.
The Key Factors Influencing Steel's Melting Range
The width and position of this melting range are determined entirely by the steel's chemical recipe. Even a tiny change in composition can have a significant impact.
The Critical Role of Carbon
Carbon is the most influential element affecting steel's melting point. As you increase the carbon content, you generally lower the melting range.
A low-carbon steel (like those used for car bodies) might have a melting range starting around 1480°C (2700°F). In contrast, a very high-carbon steel (like cast iron) can begin to melt at temperatures as low as 1150°C (2100°F).
The Impact of Other Alloying Elements
Other elements are added to create specific properties, and they also affect the melting range.
Elements like chromium (for stainless steel) and manganese are often added. Each has a unique effect on the solidus and liquidus temperatures, which is why every specific grade of steel has its own documented melting characteristics.
Practical Implications for Steel Processing
Understanding this melting range is not just an academic exercise; it is essential for any industrial process involving steel. Using an incorrect temperature can lead to wasted energy, defective parts, and equipment failure.
Forging vs. Casting
Forging requires steel to be heated until it is soft and plastic, but it must remain fully solid. This is typically done well below the solidus temperature.
Casting, on the other hand, requires the steel to be completely liquid so it can flow and fill a mold. For this, the steel must be heated well above its liquidus temperature to ensure no solid particles remain.
Ensuring Quality and Consistency
In processes like welding or heat treating, precise temperature control is paramount. Knowing the exact solidus and liquidus points for a specific steel grade allows engineers to prevent unintended melting, which can ruin a component's structural integrity.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
The right temperature depends entirely on the specific steel alloy you are working with and your intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is casting: You must heat the material above its specific liquidus temperature, which can range from 1425-1540°C (2600-2800°F), to ensure it is fully molten.
- If your primary focus is forging: You must keep the material in its solid state, heating it to a plastic forming temperature that is safely below its solidus point, often between 900-1250°C (1650-2280°F).
- If you are performing any precise engineering: You must abandon general estimates and consult the technical data sheet provided by the material supplier for the exact melting range of that specific steel grade.
Understanding that steel has a melting range, not a fixed point, is the first step toward mastering its behavior in any application.
Summary Table:
| Steel Type | Approximate Melting Range Start (Solidus) | Key Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Carbon Steel | ~1480°C (2700°F) | Low Carbon Content |
| High-Carbon Steel (e.g., Cast Iron) | ~1150°C (2100°F) | High Carbon Content |
| Pure Iron | 1538°C (2800°F) | Pure Element (Reference Point) |
Mastering precise thermal control is key to successful steel processing. Whether you are casting, forging, or heat treating, having the right lab equipment ensures you work within the correct melting range for your specific alloy. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces and consumables, providing the reliable tools you need for consistent, high-quality results.
Let us help you achieve precision and efficiency in your lab. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your steel analysis and processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can two different materials have the same value of specific heat capacity? Unlocking the Science of Thermal Behavior
- What is the specific heat capacity for melting? Clarifying Latent Heat vs. Specific Heat
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- What are the factors that affect melting? Master Temperature, Pressure & Chemistry for High-Quality Results



















