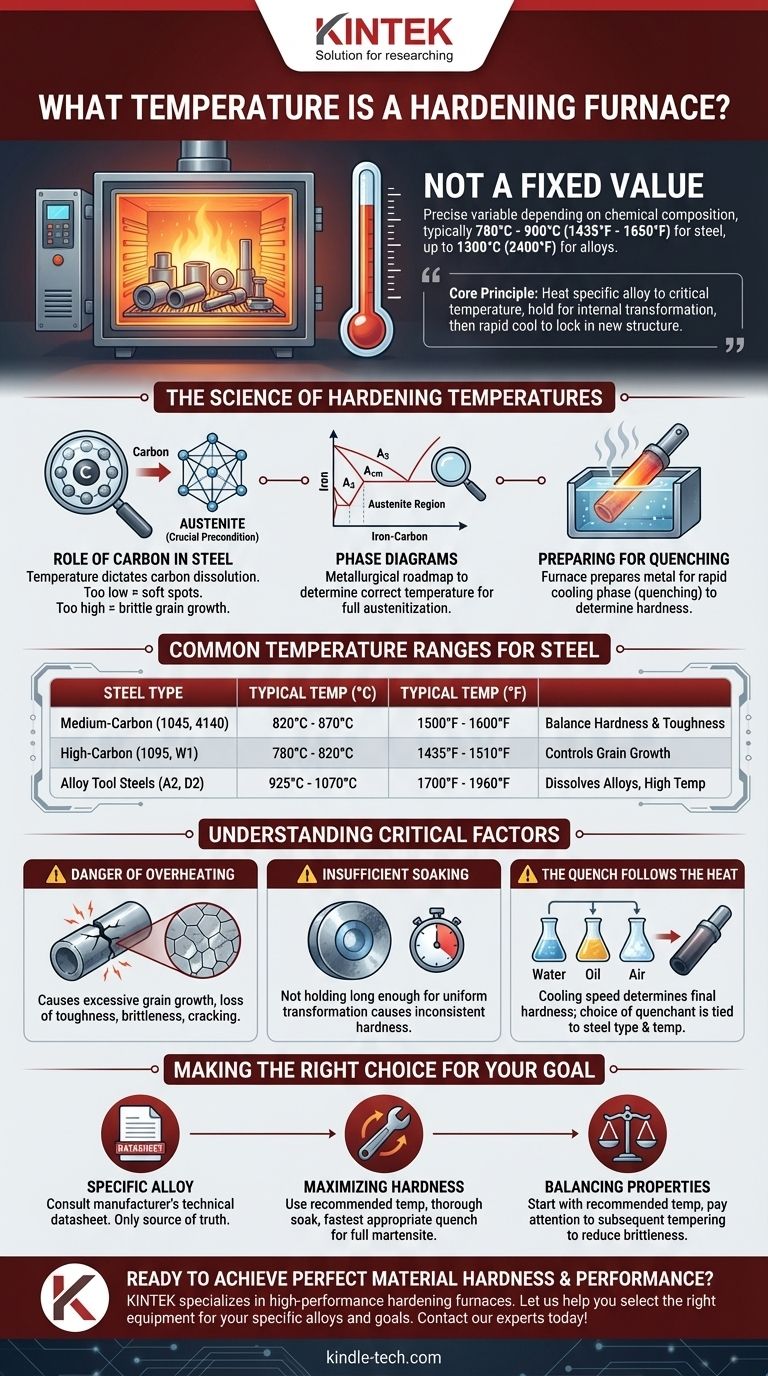
The temperature of a hardening furnace is not one specific value; it is a precise variable that depends entirely on the chemical composition of the metal being treated. For the most common application, steel, this temperature typically falls between 780°C and 900°C (1435°F and 1650°F), but for specialized tool steels and alloys, it can extend up to 1300°C (2400°F). The exact temperature is chosen to achieve a specific change in the metal's internal crystal structure before quenching.
The core principle of hardening is not about just getting metal hot. It's about heating a specific alloy to a precise critical temperature, holding it there to achieve a complete internal transformation, and then cooling it rapidly to lock in a new, harder structure.

The Science of Hardening Temperatures
To understand why there's no single answer, you must understand the goal of the heating process. The furnace's job is to prepare the metal for a rapid cooling phase, known as quenching.
The Role of Carbon in Steel
For steel, the hardening temperature is dictated primarily by its carbon content. The heat is used to dissolve carbon and other elements into a specific crystal structure known as austenite.
This austenitic state is the necessary precondition for hardening. If the temperature is too low, the transformation to austenite will be incomplete, resulting in soft spots. If it's too high, the steel's internal grains will grow too large, making it brittle.
The Metallurgical Roadmap: Phase Diagrams
Metallurgists use a tool called an iron-carbon phase diagram to determine the correct temperature. This diagram maps out the steel's internal structure at any given temperature and carbon content.
The key is to heat the steel just above its upper critical temperature (labeled A3 or Acm on the diagram). This is the point where the structure becomes fully austenitic and ready for quenching.
Common Temperature Ranges for Steel
While a datasheet for the specific alloy is always the definitive source, general ranges provide a good frame of reference:
- Medium-Carbon Steels (e.g., 1045, 4140): These are typically hardened between 820°C and 870°C (1500°F - 1600°F). They offer a good balance of hardness and toughness.
- High-Carbon Steels (e.g., 1095, W1): These steels require a slightly lower temperature, usually 780°C to 820°C (1435°F - 1510°F). The lower temperature helps control grain growth, which is critical in these more brittle alloys.
- Alloy Tool Steels (e.g., A2, D2): These complex alloys contain elements like chromium and molybdenum and require higher temperatures, often from 925°C to 1070°C (1700°F - 1960°F), to dissolve these elements properly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Achieving the correct temperature is only part of the process. Several other factors are equally critical to a successful hardening operation.
The Danger of Overheating
Heating a steel far above its critical temperature causes excessive grain growth. Large internal grains create planes of weakness within the metal, leading to a significant loss of toughness and making the final part brittle and prone to cracking.
The Problem of Insufficient Soaking
Soaking is the process of holding the metal at the target temperature. It is not enough to simply reach the temperature; the material must be held there long enough for the heat to penetrate completely and for the internal transformation to austenite to be uniform throughout the part's cross-section. Insufficient soaking is a primary cause of inconsistent hardness.
The Quench Follows the Heat
The entire purpose of heating is to prepare for the quench. The speed of this cooling process determines the final hardness. The choice of quenchant—be it water, oil, or air—is directly tied to the type of steel and the austenitizing temperature used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the correct hardening temperature, you must first define your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is a specific known alloy: Always consult the manufacturer's or supplier's technical datasheet. This is the only source of truth for that material's heat treatment protocol.
- If your primary focus is maximizing hardness for a tool: Use the recommended temperature from the datasheet and ensure a thorough soak, followed by the fastest appropriate quench to achieve a full martensitic transformation.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness and toughness for a component: Start with the recommended hardening temperature, but pay close attention to the subsequent tempering process, which is used to reduce brittleness at the cost of some hardness.
Ultimately, mastering hardening is about using precise temperature control to dictate the final performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Steel Type | Typical Hardening Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Hardening Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Medium-Carbon Steels (e.g., 1045, 4140) | 820°C - 870°C | 1500°F - 1600°F |
| High-Carbon Steels (e.g., 1095, W1) | 780°C - 820°C | 1435°F - 1510°F |
| Alloy Tool Steels (e.g., A2, D2) | 925°C - 1070°C | 1700°F - 1960°F |
Ready to achieve perfect material hardness and performance?
Precise temperature control is the foundation of successful heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance hardening furnaces and lab equipment designed for metallurgists, engineers, and manufacturing labs. Our solutions deliver the accuracy and reliability you need to master critical processes like austenitizing and quenching.
Let us help you select the right equipment for your specific alloys and hardening goals. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















