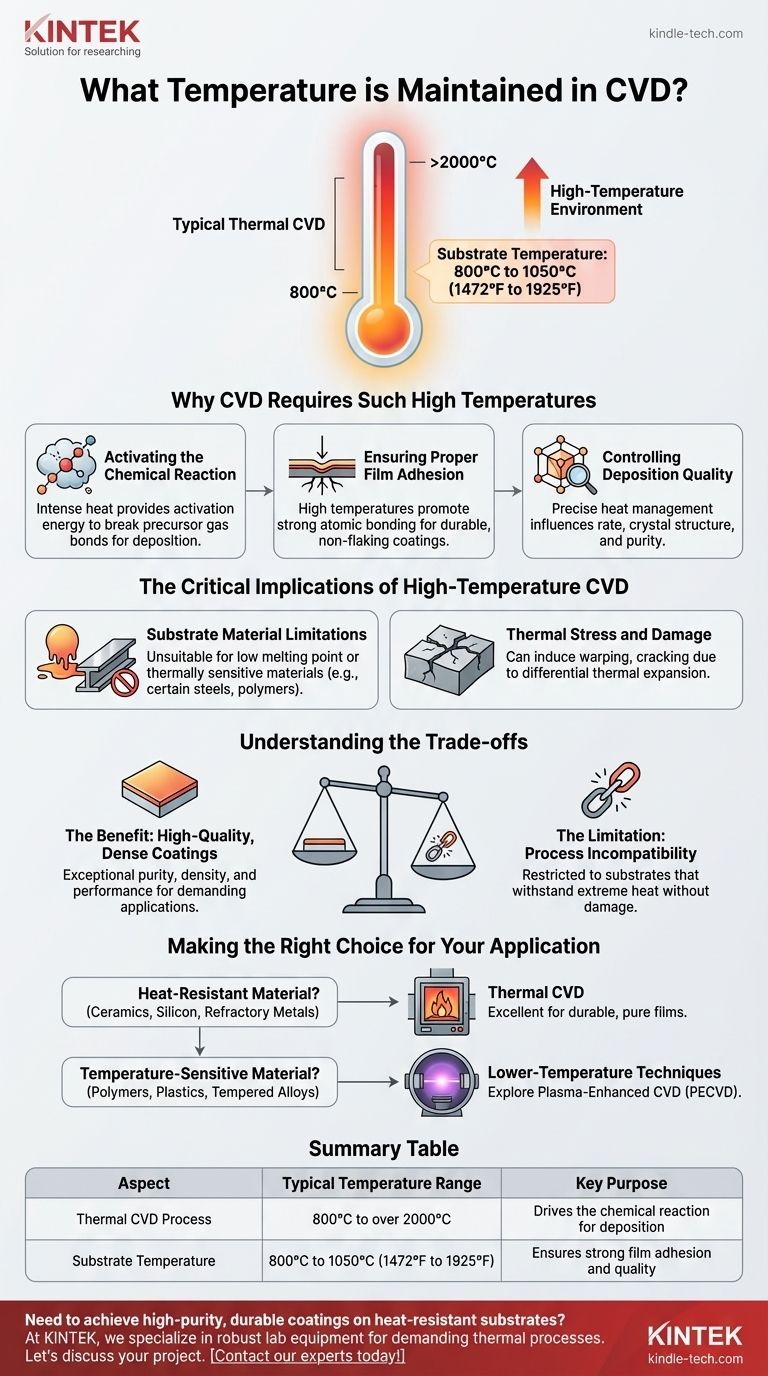
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the process is defined by its high-temperature environment. Typical thermal CVD operates in a range of 800°C to over 2000°C, with the substrate being coated often reaching temperatures between 800°C and 1051.6°C (1472°F to 1925°F).
The extremely high temperature in CVD is not an incidental byproduct; it is the fundamental energy source required to drive the chemical reactions that form the coating. This requirement is also the process's primary limitation, restricting its use to substrates that can withstand intense heat.

Why CVD Requires Such High Temperatures
Understanding the role of heat is crucial to understanding the entire CVD process. The temperature is a carefully controlled variable that directly influences the outcome.
Activating the Chemical Reaction
The core of CVD involves introducing precursor gases into a chamber. The intense heat provides the necessary activation energy to break the chemical bonds within these gases.
This decomposition allows the desired elements to be released and then deposit onto the substrate surface as a solid thin film.
Ensuring Proper Film Adhesion
High substrate temperatures promote strong atomic bonding between the coating material and the substrate itself.
This results in a film with excellent adhesion, which is critical for creating durable and reliable coatings that will not flake or peel.
Controlling Deposition Quality
Temperature is one of the most critical parameters for controlling the final properties of the film.
By precisely managing the heat, engineers can influence the deposition rate, crystal structure, and purity of the resulting coating.
The Critical Implications of High-Temperature CVD
The reliance on extreme heat creates significant constraints and challenges that must be considered before selecting CVD for an application.
Substrate Material Limitations
The most significant consequence is the limited range of materials that can be coated. The process is unsuitable for any material with a low melting point or that is sensitive to thermal changes.
For example, since the process temperature often exceeds the tempering temperature of steel, it can alter the mechanical properties of certain steel alloys, making them unsuitable substrates.
Thermal Stress and Damage
Exposing a substrate to such high temperatures can induce thermal stress. This can lead to warping, cracking, or other forms of damage, especially if the substrate and coating have different coefficients of thermal expansion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use CVD involves a clear trade-off between the quality of the result and the demands of the process.
The Benefit: High-Quality, Dense Coatings
The primary reason to accept the challenges of high-temperature CVD is the exceptional quality of the films it produces.
These coatings are typically very dense, pure, and uniform, offering superior performance in demanding applications like semiconductor manufacturing and wear-resistant tooling.
The Limitation: Process Incompatibility
The main trade-off is that this quality comes at the cost of compatibility. You can only apply these superior coatings to substrates that can survive the extreme processing environment without being damaged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on the material you need to coat.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-resistant material (e.g., ceramics, silicon, refractory metals): Thermal CVD is an excellent choice for producing highly durable, pure, and strongly adhered films.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material (e.g., polymers, plastics, tempered alloys): You must explore lower-temperature deposition techniques, such as Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD).
Ultimately, the high temperature of CVD is both its greatest strength and its most significant constraint.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Typical Temperature Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD Process | 800°C to over 2000°C | Drives the chemical reaction for deposition |
| Substrate Temperature | 800°C to 1050°C (1472°F to 1925°F) | Ensures strong film adhesion and quality |
Need to achieve high-purity, durable coatings on heat-resistant substrates? The precise temperature control required for successful CVD is critical. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and expert solutions for demanding thermal processes. Whether you're working with semiconductors, ceramics, or refractory metals, our systems are designed for reliability and performance. Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















