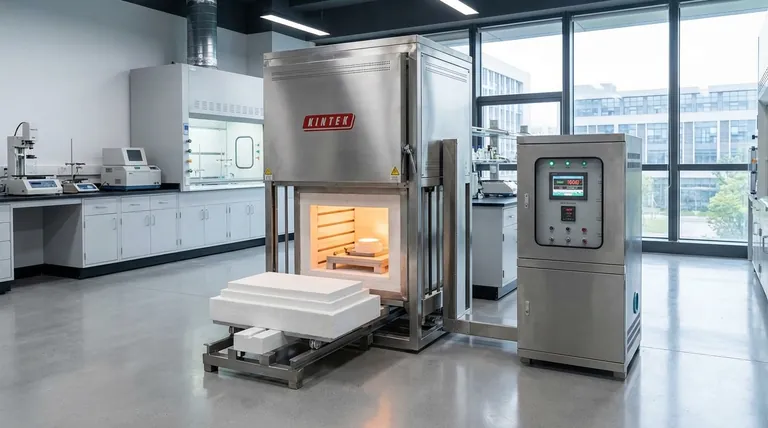
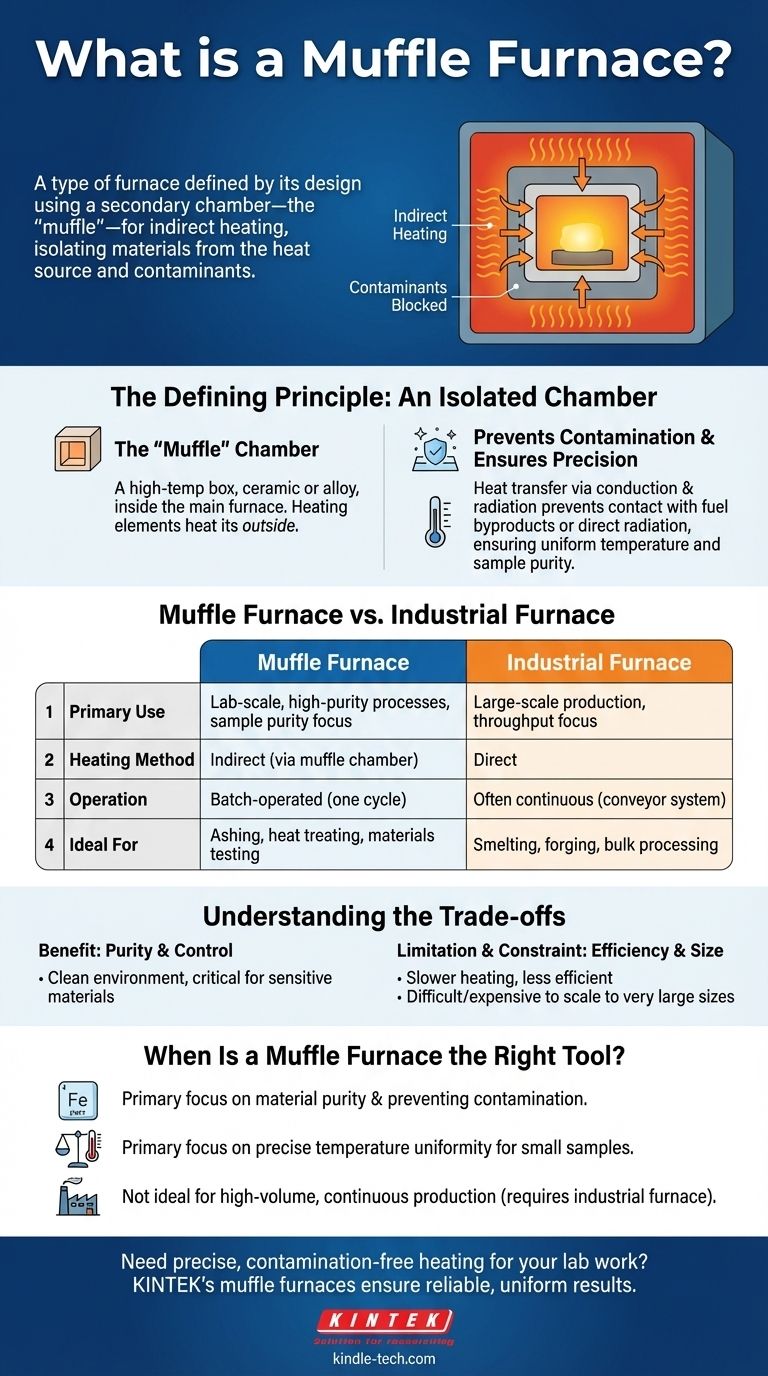
A muffle furnace is a type of furnace defined by its design, which uses a secondary chamber—the "muffle"—to isolate the material being heated from the direct heat source and any contaminants. This design ensures that byproducts of combustion or direct radiation do not interact with the sample, making it essential for processes requiring high purity and precise temperature control, especially in laboratory settings.
The core principle of a muffle furnace isn't its size or temperature range, but its method of indirect heating. By placing the workload inside a separate, sealed chamber, it guarantees a clean environment free from contamination by the fuel or heating elements.

The Defining Principle: An Isolated Chamber
A muffle furnace's entire purpose revolves around the concept of isolation. It is, in effect, a furnace within a furnace.
The "Muffle" Chamber
The muffle is a box-like container, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or a metallic alloy. This chamber sits inside the main furnace, and the heating elements heat the outside of the muffle.
How It Prevents Contamination
Heat is transferred through the muffle's walls to the sample inside via conduction and radiation. This separation prevents any gases, soot, or other byproducts from a fuel-fired heat source from touching the sample. In electric furnaces, it prevents direct radiation from the heating elements from causing uneven heating or reactions.
Precision and Uniformity
This indirect heating method allows for exceptionally uniform temperature distribution within the chamber. This makes muffle furnaces ideal for sensitive processes like ashing, heat treating, or materials research where precise temperature cycles are critical.
Muffle Furnace vs. Industrial Furnace: A Matter of Purpose
While both are furnaces, their intended applications are fundamentally different, which dictates their design and operation.
Application: Laboratory vs. Production
A muffle furnace is primarily a tool for laboratory-scale work. Its focus is on sample purity, controlled atmospheres, and precision for testing, analysis, or creating small, high-value components.
An industrial furnace, by contrast, is built for large-scale production. Its goal is throughput and efficiency in processes like smelting, forging, or large-batch heat treating.
Operation: Batch vs. Continuous
Muffle furnaces are almost always batch-operated. You place a sample inside, run a complete heating and cooling cycle, and then remove it.
Industrial furnaces are often continuous, with materials moving through different temperature zones on a conveyor system to maximize output.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The unique design of a muffle furnace presents clear advantages but also inherent limitations.
The Benefit: Purity and Control
The primary advantage is an impeccably clean heating environment. When you cannot risk any external element affecting your material, the muffle design is non-negotiable.
The Limitation: Heat Transfer Efficiency
Heating a sample indirectly through the walls of a secondary chamber is inherently less efficient than direct heating. It can lead to slower heating rates and potentially higher energy consumption compared to a direct-fired furnace of similar size.
The Constraint: Size and Volume
The chamber-within-a-chamber design makes it difficult and expensive to scale to very large sizes. This is why muffle furnaces are typically reserved for smaller, high-value applications rather than bulk industrial processing.
When Is a Muffle Furnace the Right Tool?
Your choice depends entirely on the requirements of your heating process.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing contamination: A muffle furnace is the correct and often only choice.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature uniformity for small samples: A muffle furnace excels at providing a stable, even thermal environment for research and analysis.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A dedicated industrial furnace design is necessary to achieve the required scale and efficiency.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision for high-purity heating where the integrity of your sample is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Industrial Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Laboratory-scale, high-purity processes | Large-scale production |
| Heating Method | Indirect (via a muffle chamber) | Direct |
| Operation | Batch | Often continuous |
| Key Advantage | Superior material purity and precise temperature control | High throughput and efficiency |
| Ideal For | Ashing, heat treating, materials testing | Smelting, forging, bulk processing |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your lab work?
A muffle furnace from KINTEK is the ideal solution for applications where sample purity and precise temperature control are non-negotiable. Whether you're performing ashing, heat treatment, or materials research, our lab equipment ensures reliable, uniform results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the inside material of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lining for Your Application
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the objective of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the tolerance of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Accuracy & Uniformity



















