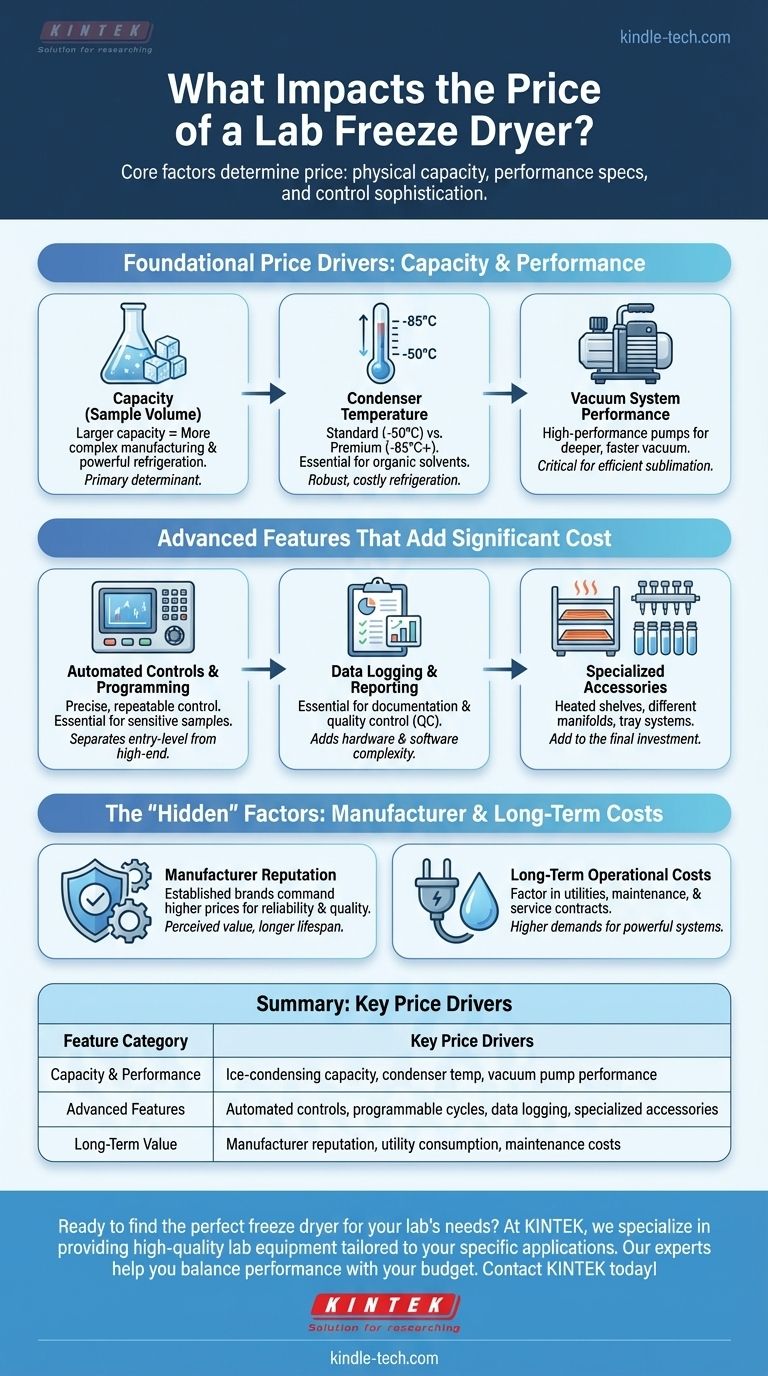
The price of a lab freeze dryer is determined by three core factors: its physical capacity, its core performance specifications, and the sophistication of its control and data features. While a larger machine naturally costs more, features like ultra-low condenser temperatures and automated data logging can add significantly to the final investment.
Choosing a freeze dryer isn't about finding the cheapest option; it's about understanding the total cost of ownership and precisely matching the machine's capabilities to your scientific application to avoid costly errors.

Foundational Price Drivers: Capacity and Performance
The most significant factors influencing a freeze dryer's base price are its physical size and the power of its core cooling and vacuum systems. These elements determine the fundamental capabilities of the machine.
Capacity (Sample Volume)
Capacity refers to the amount of material the freeze dryer can process in a single cycle. It's often measured by the total ice-condensing capacity of the unit.
Larger capacity models require more complex manufacturing and more powerful refrigeration systems, making them a primary determinant of price.
Condenser Temperature
The cold trap, or condenser, temperature is a critical performance metric. Standard models typically reach -50°C, which is sufficient for samples with a high water content.
More expensive units can achieve -85°C or lower. This capability is essential for samples containing organic solvents or materials with very low freezing points, as it requires a much more robust and costly refrigeration system.
Vacuum System Performance
The vacuum pump is another core component. High-performance pumps that can achieve a deeper vacuum level more quickly contribute to a higher overall system price.
The right vacuum level is crucial for efficient sublimation and must be matched to the specific requirements of your application.
Advanced Features That Add Significant Cost
Beyond the basic hardware, software and automation features can substantially increase the price. These are often what separate entry-level models from high-end, specialized systems.
Automated Controls and Programming
Basic models may have manual controls, but advanced freeze dryers feature automatic controls and programmable cycles.
This allows for precise, repeatable control over shelf temperature and vacuum levels throughout a run, which is critical for sensitive biological samples and process optimization.
Data Logging and Reporting
Features for data logging and reporting are essential for research and production environments that require documentation for quality control or regulatory compliance.
The ability to track and export run data like temperature and pressure adds both hardware and software complexity, increasing the cost.
Specialized Accessories
The price of the base unit is only part of the total investment. Specialized accessories like heated shelves, different manifold types for flasks, or tray systems for vials all add to the final cost.
The "Hidden" Factors: Manufacturer and Long-Term Costs
The sticker price doesn't tell the whole story. The manufacturer's reputation and the projected operational costs are crucial considerations that indirectly influence the value and total investment.
Manufacturer Reputation
Established brands with a proven history of reliability, innovation, and support often command higher prices.
This premium is tied to the perceived value of their engineering expertise and the quality of their components, which can lead to better performance and a longer lifespan for the equipment.
Long-Term Operational Costs
A comprehensive evaluation includes future costs. Consider the water and electricity consumption, as more powerful systems will have higher utility demands.
Furthermore, factor in the potential costs of future maintenance, service contracts, and the labor required to operate the unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the goal is to purchase a freeze dryer that meets your specific needs without paying for capabilities you will never use. A clear understanding of your application is the best guide.
- If your primary focus is basic research with aqueous samples: A standard capacity unit with a -50°C condenser and manual controls is likely the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing samples with organic solvents: You must invest in a unit with a low-temperature condenser (-85°C or lower) to ensure efficient trapping and prevent pump damage.
- If your primary focus is process development or regulated production: Prioritize a system with advanced automation, programmable cycles, and comprehensive data logging from a reputable manufacturer.
Making an informed decision requires looking beyond the price tag to the specific features that will enable your work successfully and reliably.
Summary Table:
| Feature Category | Key Price Drivers |
|---|---|
| Capacity & Performance | Ice-condensing capacity, condenser temperature (-50°C vs. -85°C), vacuum pump performance |
| Advanced Features | Automated controls, programmable cycles, data logging, specialized accessories |
| Long-Term Value | Manufacturer reputation, utility consumption (water/electricity), maintenance costs |
Ready to find the perfect freeze dryer for your lab's needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific applications. Whether you're processing aqueous samples, working with organic solvents, or require full regulatory compliance, our experts will help you select a system that balances performance with your budget—ensuring you get the best value and avoid costly mismatches.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our reliable freeze dryers can enhance your research and streamline your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- How does freeze drying benefit dairy products? Unlock Premium Quality and Shelf Stability
- What should be considered when choosing a lab freeze dryer? Match Your Samples and Workflow for Success
- What are the key reasons to use a freeze dryer in laboratories? Preserve Sample Integrity for Reliable Research
- What are the steps to use a laboratory freeze dryer? Master Lyophilization for Superior Sample Preservation
- What benefits do laboratory freeze dryers provide in chemical and biotechnological processes? Preserve Purity & Stability



















