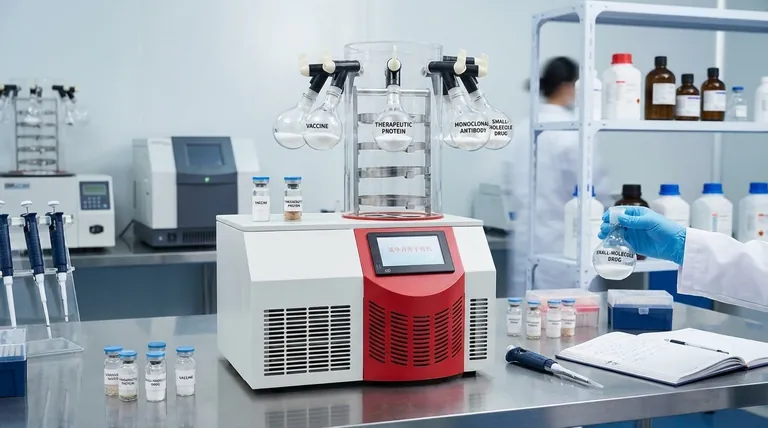
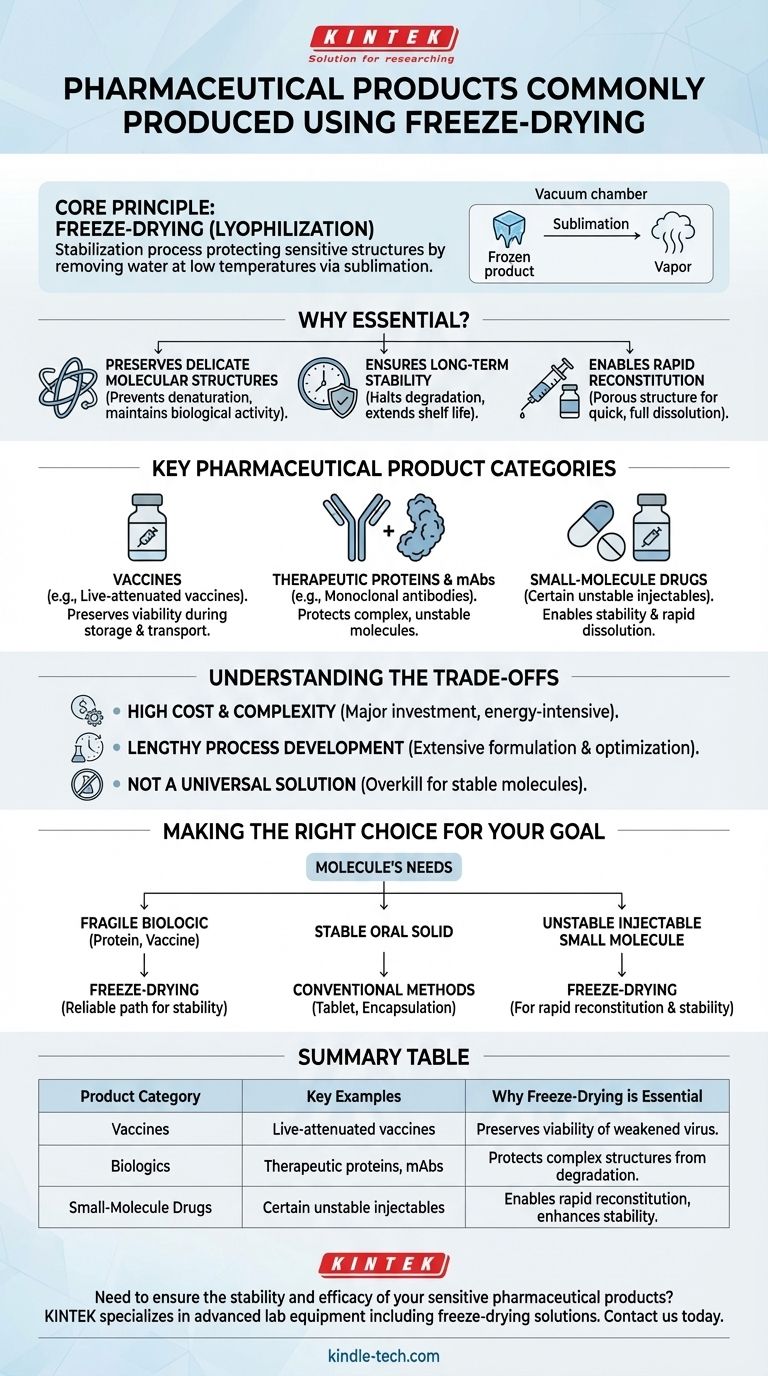
In pharmaceuticals, freeze-drying is the definitive technology for preserving the integrity of sensitive and unstable products. The most common categories include complex biologics like vaccines, therapeutic proteins, and monoclonal antibodies, as well as certain unstable small-molecule drugs that cannot survive in a liquid state or withstand traditional heat-based drying methods.
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is not merely a drying technique. It is a stabilization process designed to protect a drug's critical molecular structure and biological activity by removing water at low temperatures, ensuring its efficacy and extending its shelf life far beyond what is possible in a liquid formulation.

The Core Principle: Why Freeze-Drying is Essential
The decision to freeze-dry a pharmaceutical product is driven by one primary factor: instability. Many of modern medicine's most powerful drugs, particularly biologics, are incredibly fragile and will degrade quickly in a liquid solution or if exposed to heat.
Preserving Delicate Molecular Structures
Heat-based drying methods can cause denaturation, a process where complex molecules like proteins unfold and lose their specific three-dimensional shape. This structural change is often irreversible and renders the drug biologically inactive and therefore useless.
Freeze-drying bypasses this by first freezing the product, then applying a deep vacuum. This allows the frozen water to turn directly into a vapor—a process called sublimation—without ever passing through a destructive liquid phase at high temperatures.
Ensuring Long-Term Stability
By removing water, which is a key medium for chemical degradation reactions, freeze-drying effectively halts the processes that cause a drug to lose its potency over time.
This creates a stable, solid "cake" (or lyophile) that can often be stored for years, sometimes even at room temperature. This simplifies the cold-chain logistics required for many liquid biologics, making distribution and storage easier and more cost-effective.
Enabling Rapid Reconstitution
A well-formulated freeze-dried product is highly porous. When a clinician is ready to administer the drug, they simply add a sterile liquid (like water for injection).
The porous structure allows the liquid to penetrate the cake quickly and completely, ensuring the drug is rapidly and fully reconstituted into a clear solution, ready for injection. This is a critical quality attribute for safe and effective use.
Key Pharmaceutical Product Categories
While the technology is versatile, it is most heavily concentrated in product categories where molecular fragility is the central challenge.
Vaccines
Many live-attenuated vaccines, which contain weakened but living viruses, rely on freeze-drying to remain viable during storage and transport. The process preserves the virus without killing it, ensuring it can elicit the necessary immune response upon administration.
Therapeutic Proteins and Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
This is the largest and fastest-growing category. Proteins, enzymes, and especially monoclonal antibodies are large, complex molecules that are notoriously unstable in solution. Freeze-drying is the gold-standard method for creating a stable, long-lasting drug product from these biologics.
Small-Molecule Drugs
While less common, freeze-drying is also used for certain small-molecule drugs. This is typically done when the drug is highly unstable in the presence of water or when a specific porous structure is needed to achieve rapid dissolution upon reconstitution for injectable formulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. It is a highly specialized process with significant trade-offs that must be carefully considered.
High Cost and Complexity
Freeze-drying equipment is a major capital investment, and the process itself is energy-intensive. A single lyophilization cycle can take several days to complete, making it one of the most expensive and time-consuming manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical industry.
Lengthy Process Development
Developing a robust freeze-drying cycle is not trivial. It requires extensive formulation work to select the right cryoprotectants (substances that protect the drug during freezing) and rigorous optimization of the cycle's temperature, pressure, and time parameters for each specific product.
Not a Universal Solution
For drug molecules that are inherently stable, freeze-drying is often overkill. Simpler and more cost-effective preservation methods, such as spray drying or simple crystallization, are preferable when the product's stability allows for them.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use freeze-drying must be based on a deep understanding of your molecule's inherent properties and your final product's requirements.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fragile biologic (protein, antibody, vaccine): Freeze-drying is almost certainly the required and most reliable path to ensure long-term stability and activity.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective oral solid dosage form for a stable molecule: Conventional tableting or encapsulation methods are far more appropriate and economical.
- If your primary focus is an injectable small molecule with stability or solubility issues: Freeze-drying is a powerful option to consider for creating a stable product that can be rapidly reconstituted before use.
Ultimately, choosing the right preservation technology is about matching the process to the specific needs of the drug molecule to guarantee its safety, efficacy, and stability.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Key Examples | Why Freeze-Drying is Essential |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccines | Live-attenuated vaccines | Preserves the viability of the weakened virus for long-term storage and transport. |
| Biologics | Therapeutic proteins, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) | Protects complex, fragile molecular structures from degradation, ensuring biological activity. |
| Small-Molecule Drugs | Certain unstable injectable drugs | Enables rapid reconstitution and enhances stability for drugs that degrade in liquid form. |
Need to ensure the stability and efficacy of your sensitive pharmaceutical products? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored for pharmaceutical development, including freeze-drying solutions. Our expertise helps you preserve the integrity of complex biologics, vaccines, and more. Let us support your R&D and manufacturing goals—contact us today to discuss how we can meet your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What occurs during the secondary drying phase? Master the Final Step for Product Stability
- What are amorphous materials in freeze drying? The Key to Preventing Product Collapse
- What role does freeze drying play in scientific research? Preserve Sample Integrity for Reliable Results
- What types of biological materials are suitable for freeze drying? Preserve Stability and Activity
- What is the distillate extraction method? Achieve Peak Purity in Cannabis Concentrates



















