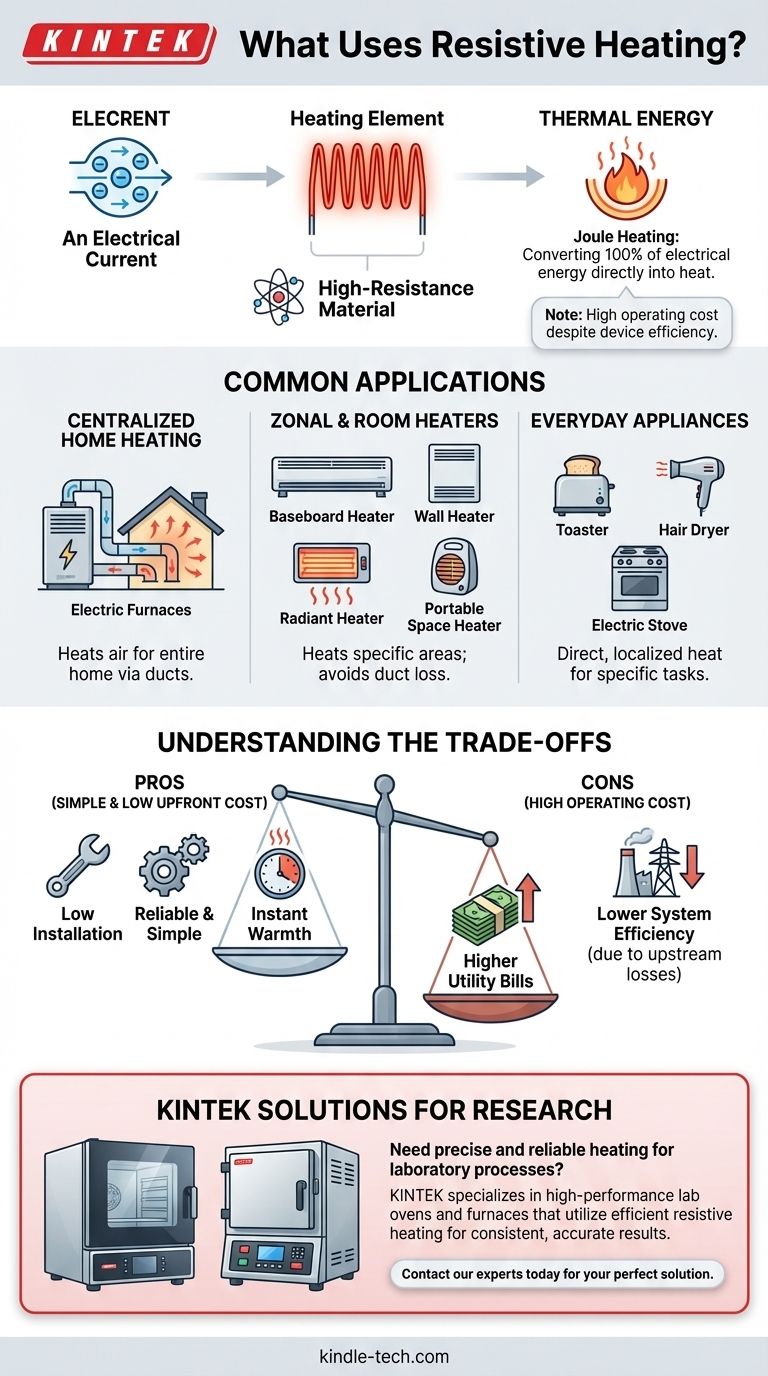
At its core, resistive heating is the simple process of creating heat by passing electricity through an object that resists the flow. You encounter this technology every day in common appliances like toasters, hair dryers, and electric stoves. In home heating, it is the principle behind centralized forced-air electric furnaces as well as individual room heaters, including electric baseboards, wall heaters, and portable space heaters.
Resistive heating works by converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. While this conversion is nearly 100% efficient, the high cost of electricity often makes it a more expensive heating method compared to alternatives like natural gas or heat pumps.

How Resistive Heating Works
Resistive heating is one of the most fundamental applications of electricity. Its simplicity is its greatest strength, making it reliable and inexpensive to manufacture.
The Fundamental Principle
The scientific principle behind resistive heating is known as Joule heating. When an electric current flows through a material, the electrons in the current collide with the atoms of that material.
In materials with high electrical resistance, these collisions are frequent and intense, causing the atoms to vibrate. This increased vibration is what we perceive as heat.
The Heating Element
The core of any resistive heater is the heating element—a specialized component designed to have high electrical resistance.
These elements are typically made from alloys like nichrome (a mix of nickel and chromium), which can get extremely hot without degrading or oxidizing quickly.
The Efficiency of Conversion
A key characteristic of resistive heating is that it is nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat energy.
Virtually every watt of electricity that flows through the heating element is transformed directly into heat. However, this figure can be misleading when considering the total cost of heating a space.
Common Applications of Resistive Heating
This technology is found in two main categories: centralized systems for entire buildings and smaller, localized heaters for specific areas or appliances.
Centralized Forced-Air Systems
An electric furnace is a central heating system that uses large resistive heating coils to warm air. A blower then pushes this heated air through the home's ductwork.
These systems are simple and reliable but are often the most expensive type of central heating to operate.
Zonal and Room Heaters
These devices provide heat to a single room or zone, avoiding the energy loss associated with ductwork.
- Baseboard Heaters: These long, low-profile units contain heating elements and rely on natural convection to circulate warm air throughout a room.
- Wall Heaters: Similar to baseboard heaters, these are installed in a wall and often include a fan to distribute heat more quickly.
- Radiant Heaters: These devices heat objects and people directly in their line of sight, rather than heating the air. They provide instant warmth, much like the sun.
- Portable Space Heaters: These common household devices are a prime example of resistive heating, offering a simple way to add supplemental heat to any area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While simple and effective, resistive heating comes with significant practical considerations, primarily revolving around cost and overall energy consumption.
The "Efficiency" Misconception
The claim of 100% efficiency only refers to the device itself. It doesn't account for the energy lost when generating and transmitting the electricity from the power plant to your home.
When these upstream losses are factored in, the total system efficiency is often much lower than that of a natural gas furnace or an electric heat pump.
High Cost of Operation
Electricity is typically a more expensive fuel per unit of heat (BTU) than natural gas. This means that heating a home with resistive heat usually results in a significantly higher utility bill.
Simplicity and Low Installation Cost
The primary advantage of resistive heating systems is their mechanical simplicity. They have few moving parts, which makes them very reliable, long-lasting, and inexpensive to purchase and install.
This low upfront cost is why they are still a common choice for supplemental heating or in regions with low electricity rates and mild winters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heating technology depends entirely on balancing upfront costs with long-term operational expenses.
- If your primary focus is low installation cost for a smaller area: Electric baseboard, wall, or space heaters are an excellent and affordable choice for supplemental or infrequent use.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term energy bills for a whole home: A high-efficiency heat pump or natural gas furnace will almost always be the more economical solution.
- If your primary focus is instant, targeted warmth: A portable radiant heater provides on-demand heat exactly where you need it without wasting energy on an entire room.
Ultimately, knowing when to leverage the simplicity of resistive heating versus a more complex system is key to creating a comfortable and cost-effective environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Home Heating | Electric Furnaces | Heats air for entire home via ductwork; high operating cost. |
| Zonal/Room Heaters | Baseboard, Wall, Radiant, Space Heaters | Heats specific areas; low installation cost, instant warmth. |
| Common Appliances | Toasters, Hair Dryers, Electric Stoves | Direct, localized heat for specific tasks; highly reliable. |
Need precise and reliable heating for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including ovens and furnaces that utilize efficient resistive heating for consistent, accurate results. Whether you need a standard drying oven or a high-temperature furnace for advanced materials testing, our solutions are designed for durability and precision. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your laboratory's unique requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra-Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Electrode Lead for High-Precision Applications
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research



















