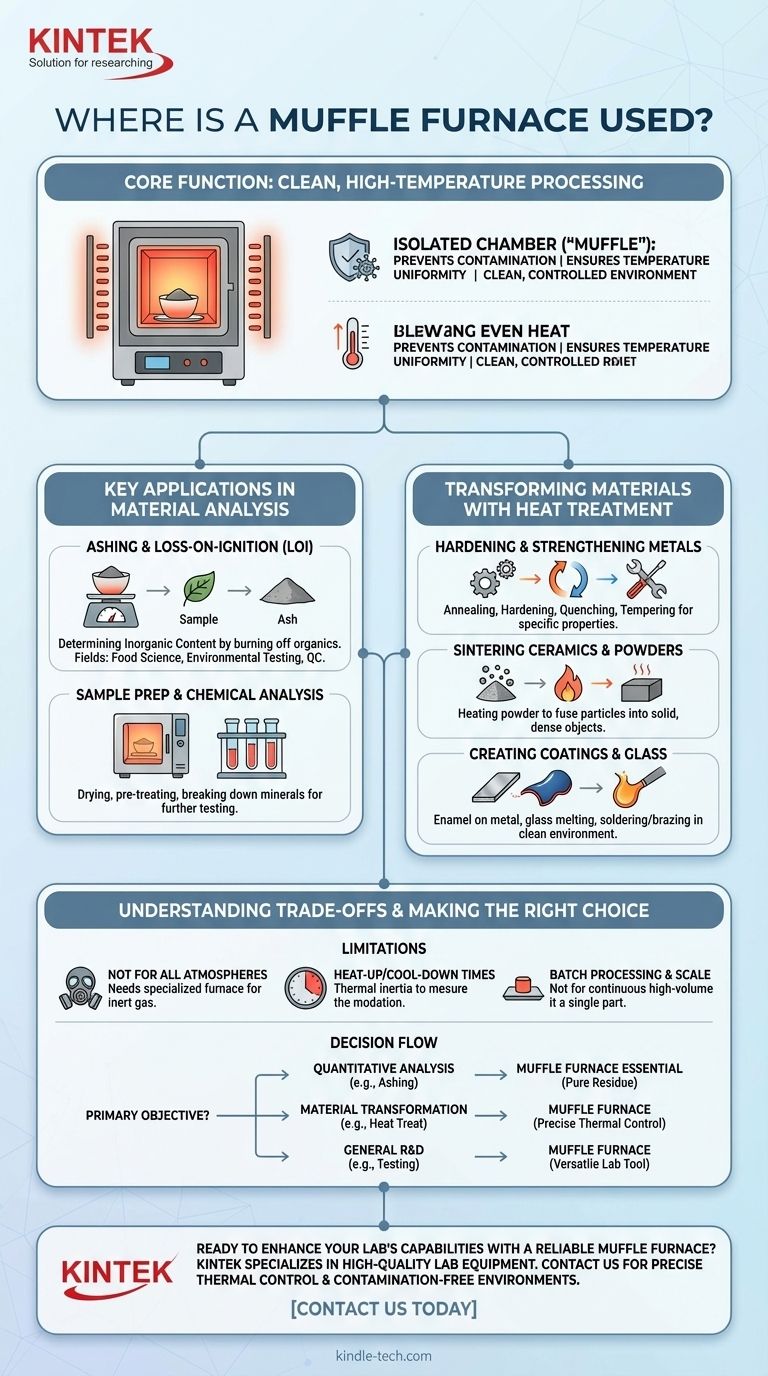
In essence, a muffle furnace is used anywhere a sample needs to be heated to a high temperature in a clean, controlled environment. Its applications span across quantitative analysis, materials science, and industrial production. They are fundamental tools for tasks like ashing organic matter, heat-treating metals to alter their properties, and sintering ceramics to create solid forms.
A muffle furnace's value comes not just from its ability to reach high temperatures, but from its core design: an enclosed "muffle" chamber that isolates the sample. This prevents contamination from heating elements or combustion byproducts, ensuring the purity and integrity of the process.

The Core Function: Clean, High-Temperature Processing
The name "muffle furnace" reveals its primary advantage. The internal chamber, or muffle, separates the material being heated from the actual heating elements and the external environment.
Preventing Contamination
This isolation is critical. In analytical applications, it ensures that the only thing being measured is the sample itself, without any impurities introduced by the heating process. In materials synthesis, it prevents unwanted chemical reactions that could alter the final product's properties.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The enclosed nature of the muffle promotes even heat distribution. This ensures the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is vital for consistent results in both scientific analysis and material heat treatment.
Key Applications in Material Analysis
A major use for muffle furnaces is determining the composition of a sample by burning away its volatile or combustible components.
Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
Ashing is the most common analytical application. A sample is heated to a high temperature to burn off all organic substances, leaving behind only the non-combustible ash (inorganic content).
This is used in fields like food science, environmental testing, and material quality control to determine the ash percentage of a sample. Loss-on-ignition (LOI) is a similar process used to determine the volatile content of a material.
Sample Preparation and Chemical Analysis
Muffle furnaces are used to prepare samples for further analysis. This includes drying samples to determine moisture content, pre-treating medical or environmental samples, or breaking down refractory minerals for chemical testing.
Transforming Materials with Heat Treatment
Muffle furnaces are central to metallurgy and materials science for altering the physical and mechanical properties of materials.
Hardening and Strengthening Metals
Processes like annealing, hardening, quenching, and tempering all rely on precise thermal cycles. A muffle furnace provides the controlled environment needed to heat a metal part and then cool it at a specific rate to achieve desired properties like hardness or ductility.
Sintering Ceramics and Powders
Sintering is the process of heating powdered material to a temperature just below its melting point. This causes the particles to fuse together, creating a solid, dense object. This is fundamental to the production of technical ceramics and certain metal parts.
Creating Coatings and Glass
The furnace's clean environment is perfect for creating enamel coatings on metal, melting glass for artistic or technical purposes, and soldering or brazing components without introducing contaminants that could weaken the bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, a muffle furnace is not the solution for every heating application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not for All Atmospheres
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere inside the chamber. If your process requires an inert (like argon) or reactive gas atmosphere, you will need a specialized furnace designed for that purpose.
Batch Processing and Scale
Muffle furnaces are typically designed for batch processing, where individual samples or small groups of parts are loaded, heated, and removed. They are not suited for continuous, high-volume industrial production lines, which require larger tunnel kilns or belt furnaces.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Times
Due to their robust insulation, muffle furnaces can have significant heat-up and cool-down times. This thermal inertia must be factored into your workflow, as they do not provide instantaneous heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the right tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: A muffle furnace is essential for any test requiring a pure, uncontaminated residue, such as ashing or loss-on-ignition.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: A muffle furnace provides the precise thermal control needed to achieve specific properties in metals, ceramics, and other materials through heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is general research and development: The furnace's versatility makes it an invaluable lab tool for testing new materials and high-temperature processes on a small, controlled scale.
Understanding its function as a controlled, clean heating chamber allows you to leverage its power for any high-temperature task requiring precision and purity.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) | Prevents contamination for accurate results |
| Metallurgy | Annealing, hardening, tempering | Controlled environment for property alteration |
| Ceramics & Powders | Sintering | Fuses particles into solid, dense objects |
| General R&D | Sample preparation, testing | Versatile tool for controlled high-temperature processes |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable muffle furnace?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise thermal control and contamination-free environment your applications demand. Whether you're in materials science, quality control, or research and development, our muffle furnaces are designed to deliver consistent, accurate results for ashing, heat treatment, sintering, and more.
Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs and achieve superior high-temperature processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the four steps to the heat treating process? Master the 3 Core Stages for Superior Results
- What temperature is required for calcination? Master Material-Specific Thermal Decomposition
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- Can calcination be done in a muffle furnace? Yes, for precise air-atmosphere heating.
- What is the difference between cold type and hot type? Uncover the Printing Revolution



















