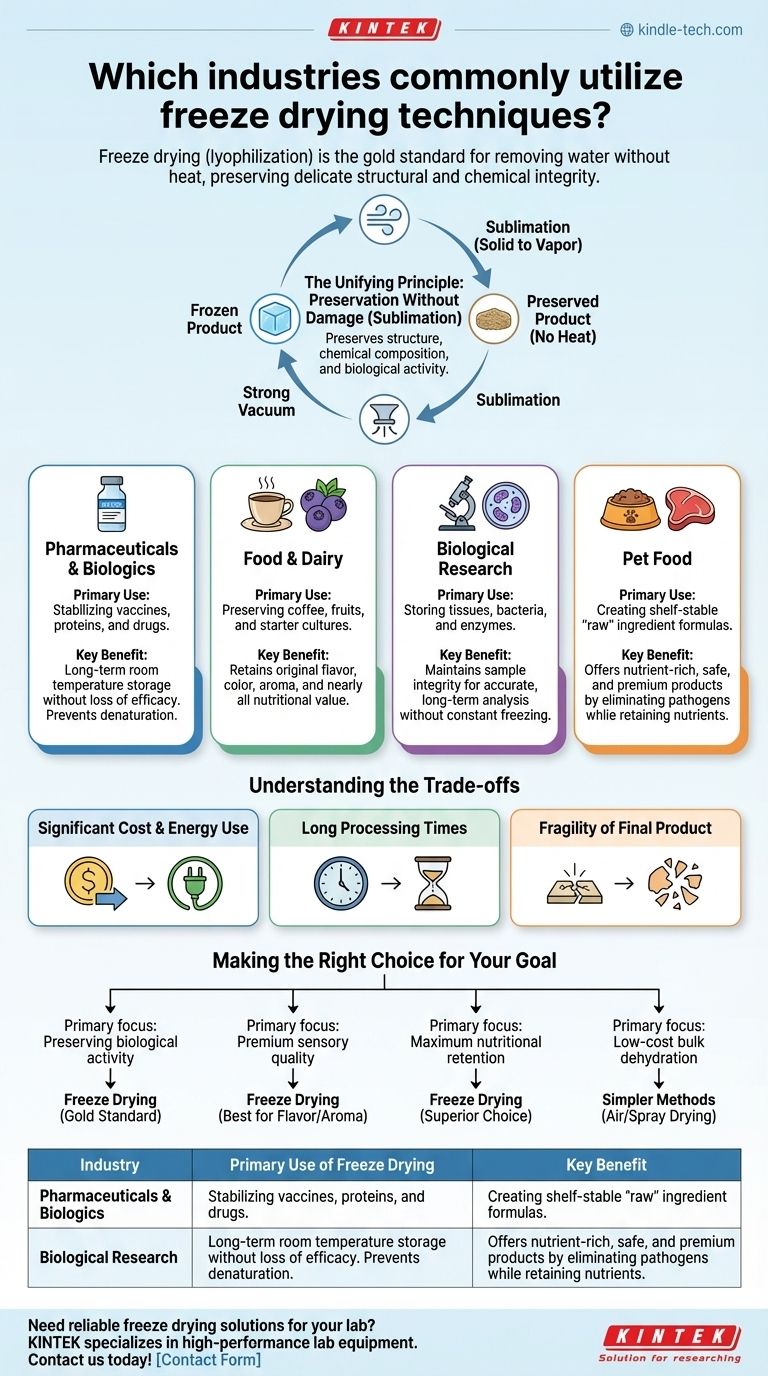
At its core, freeze drying is a critical process for a surprisingly diverse range of fields. The technique, formally known as lyophilization, is the gold standard in the pharmaceutical, food and dairy, biological research, and high-end pet food industries. Its unique ability to remove water without heat is the common thread that makes it indispensable across these seemingly unrelated sectors.
The unifying value of freeze drying is its ability to preserve the delicate structural and chemical integrity of a substance. By turning frozen water directly into vapor, it avoids the damage caused by heat or liquid-phase drying, making it the preferred method for high-value, sensitive materials.

The Unifying Principle: Preservation Without Damage
Freeze drying works through a process called sublimation. A product is first frozen solid, and then placed in a strong vacuum. This causes the frozen water crystals to transform directly into water vapor, bypassing the liquid phase entirely.
This gentle removal of water is what preserves a product's original structure, chemical composition, and biological activity.
Pharmaceuticals and Biologics: Ensuring Efficacy and Stability
In the pharmaceutical world, many modern drugs, especially biologics like vaccines, antibodies, and proteins, are incredibly fragile. Exposing them to heat would denature them, rendering them useless.
Freeze drying stabilizes these active ingredients in a solid state. This allows them to be stored for years at room temperature and then quickly rehydrated for use, a critical factor for global distribution and stockpiling.
Food and Dairy: Locking in Flavor, Color, and Nutrition
The "fresh" taste of instant coffee or the vibrant color of freeze-dried berries is a direct result of lyophilization. Traditional heat-drying methods degrade vitamins, break down flavor compounds, and alter texture.
By preserving the food's cellular structure, freeze drying retains nearly all of its original nutritional value, aroma, and taste. It is also used to preserve starter cultures for yogurt and cheese, keeping the delicate probiotic bacteria alive.
Biological Research: Stabilizing Specimens for Study
For scientists, preserving the integrity of a biological sample is non-negotiable. Whether it's tissue, bacteria, or purified enzymes, any structural change can compromise research results.
Freeze drying allows for the long-term storage of these specimens without the need for constant freezing. This makes it easier to transport, share, and analyze samples over time without degradation.
Pet Food: Meeting Demand for "Raw" and Premium Ingredients
The high-end pet food market increasingly favors "raw" or minimally processed ingredients. Freeze drying allows manufacturers to offer the nutritional benefits of raw meat, fish, and organs in a safe, shelf-stable format.
This process eliminates pathogens by removing water, yet retains the nutrient profile that would be lost through conventional high-heat cooking or rendering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, freeze drying is not a universal solution. It involves significant trade-offs that limit its use to specific applications where its benefits outweigh its drawbacks.
Significant Cost and Energy Use
Freeze drying equipment is expensive to purchase and operate. The process of maintaining a deep freeze and a strong vacuum is highly energy-intensive, making it one of the most expensive methods of dehydration.
Long Processing Times
Unlike rapid spray drying or tunnel drying, a freeze-drying cycle can take anywhere from several hours to multiple days. This low throughput means it is not practical for high-volume, low-margin commodities.
Fragility of the Final Product
The resulting lyophilized product is porous and often quite brittle. It must be handled and packaged carefully to prevent it from crushing into a powder, which adds another layer of cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use freeze drying ultimately depends on whether the integrity of the end product is your highest priority.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze drying is the gold standard for sensitive materials like vaccines, enzymes, and cell cultures.
- If your primary focus is premium sensory quality: This is the best method for retaining the flavor, color, and aroma of high-end food products like coffee and fruit.
- If your primary focus is maximum nutritional retention: It is the superior choice for creating nutrient-dense products, from health supplements to premium pet food.
- If your primary focus is low-cost bulk dehydration: Simpler, faster methods like air drying or spray drying are almost always a more economical choice.
Ultimately, freeze drying is the definitive solution when the cost of damaging a product is far greater than the cost of preserving it.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use of Freeze Drying | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals & Biologics | Stabilizing vaccines, proteins, and drugs | Long-term room temperature storage without loss of efficacy |
| Food & Dairy | Preserving coffee, fruits, and starter cultures | Retains original flavor, color, and nutritional value |
| Biological Research | Storing tissues, bacteria, and enzymes | Maintains sample integrity for accurate analysis |
| Pet Food | Creating shelf-stable raw ingredient formulas | Offers nutrient-rich, safe, and premium products |
Need reliable freeze drying solutions for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including freeze dryers tailored for pharmaceuticals, food science, and biological research. Our expertise ensures your sensitive materials are preserved with precision and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific industry needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
People Also Ask
- How is freeze-drying applied in the pharmaceutical industry? Stabilize Delicate Drugs for Long-Term Efficacy
- What is the primary technique used by lab freeze dryers to process materials? Lyophilization for Superior Sample Preservation
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a freeze dryer? Match Your Needs for Optimal Performance & Value
- What are the main components of a lab freeze dryer? Unlock the Secrets of Lyophilization
- What is the role of the refrigeration system in a freeze dryer? It's the Heart of the Sublimation Process



















