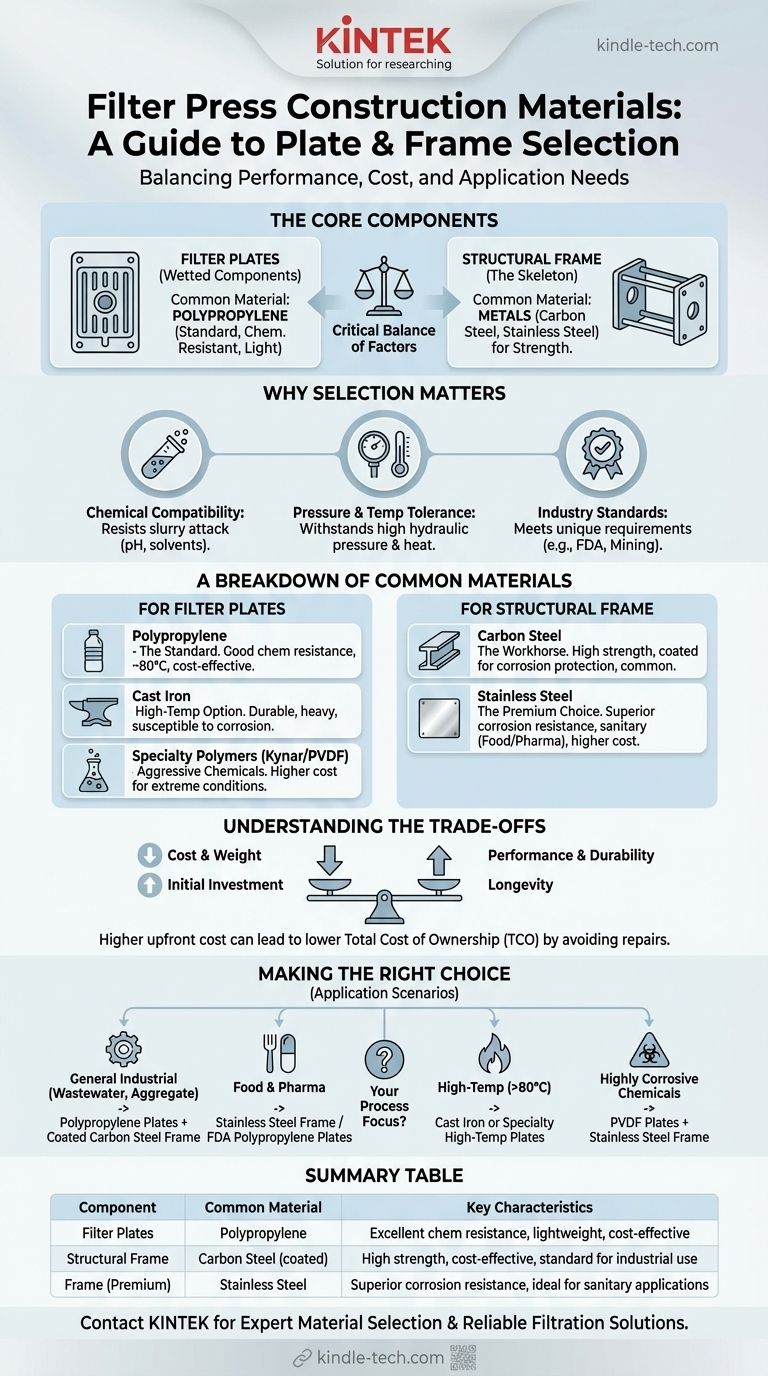
The most common material of construction for modern filter press plates is polypropylene. This polymer has become the industry standard due to its exceptional chemical resistance, light weight, and cost-effectiveness. However, the structural frame of the press is typically made from robust metals like carbon steel or stainless steel to withstand the immense pressures involved in operation.
The choice of material for a filter press is not a single decision but a critical balance of factors. It is dictated by the chemical nature of the slurry, operating temperature, pressure requirements, and specific industry standards, with different materials often used for the plates versus the structural frame.

Why Material Selection is Paramount
A filter press operates under demanding conditions. The material must not only provide structural integrity but also endure constant contact with the process fluid. Making the wrong choice can lead to equipment failure, product contamination, and safety hazards.
Chemical Compatibility
The primary consideration for the filter plates is their ability to resist chemical attack from the slurry being processed. The material must be inert to the specific pH, solvents, or abrasive particles involved.
Pressure and Temperature Tolerance
The structural frame must be strong enough to handle the high hydraulic pressures used to clamp the plates together, while the plates themselves must resist flexing. Both components must also maintain their integrity at the process operating temperature.
Industry and Application Standards
Different industries have unique requirements. A press used in mining needs to be rugged and abrasion-resistant, while one used in pharmaceuticals must meet strict sanitary standards (e.g., FDA-approved materials) to prevent contamination.
A Breakdown of Common Materials
Different components of the filter press are optimized with different materials. The "wetted" parts (plates and cloths) have different requirements than the structural skeleton.
For Filter Plates (The "Wetted" Components)
- Polypropylene (The Standard): This is the default choice for a vast range of applications. It offers a broad spectrum of chemical resistance, good temperature tolerance (up to ~180°F / 80°C), and is relatively inexpensive and easy to mold.
- Cast Iron (The High-Temp Option): Before the advent of modern polymers, cast iron was the standard. It is still used for applications involving high temperatures or specific solvents that are incompatible with polypropylene. However, it is extremely heavy and susceptible to corrosion from certain chemicals.
- Specialty Polymers (Kynar/PVDF): For extremely aggressive chemical applications (e.g., strong acids, bases, or solvents) where polypropylene is unsuitable, more advanced and costly polymers like PVDF are used.
For the Structural Frame (The Skeleton)
- Carbon Steel (The Workhorse): The vast majority of filter press frames are constructed from carbon steel due to its high tensile strength and low cost. It is almost always epoxy-coated or painted to protect it from corrosion in the plant environment.
- Stainless Steel (The Premium Choice): In sanitary applications like food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals, or in highly corrosive environments, stainless steel is the preferred material. It offers superior corrosion resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost. Sometimes, a carbon steel frame is "clad" with a thin layer of stainless steel to provide a corrosion-resistant surface at a lower cost than a full stainless steel build.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material is an exercise in balancing performance, lifespan, and cost. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Cost vs. Performance
A standard filter press with polypropylene plates and a coated carbon steel frame offers the best value for most general industrial applications. Upgrading to stainless steel or specialty polymers dramatically increases the initial capital cost but may be necessary for process compatibility and longevity.
Weight vs. Durability
Polypropylene plates are lightweight, making them easier for operators to handle during cleaning or maintenance. Cast iron plates are exceptionally durable but are incredibly heavy, often requiring lifting equipment for removal and installation.
Longevity vs. Initial Investment
Investing in a more chemically resistant material like stainless steel for the frame in a corrosive environment can prevent premature failure. While the upfront cost is higher, it can lead to a lower total cost of ownership by avoiding costly repairs or an early replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection should be guided entirely by your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general industrial dewatering (e.g., wastewater, aggregate fines): A polypropylene plate pack with a coated carbon steel frame is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is food-grade or pharmaceutical processing: A full stainless steel construction or a stainless-steel-clad frame with FDA-approved polypropylene plates is essential for compliance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature applications (above 180°F / 80°C): You must specify cast iron or specialty high-temperature polymer plates designed for these conditions.
- If your primary focus is highly corrosive chemical filtration: A detailed chemical compatibility review is required, likely pointing toward specialty polymers like PVDF for plates and a stainless steel or fiberglass-reinforced frame.
Ultimately, a successful filtration operation depends on correctly matching the equipment's materials to the demands of the process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Material | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Plates | Polypropylene | Excellent chemical resistance, lightweight, cost-effective |
| Structural Frame | Carbon Steel (coated) | High strength, cost-effective, standard for industrial use |
| Frame (Premium) | Stainless Steel | Superior corrosion resistance, ideal for sanitary applications |
Selecting the right filter press material is critical for efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including filter presses tailored to your specific laboratory and industrial needs. Our experts can help you navigate material selection based on your chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Contact us today for a consultation and let us help you build a reliable filtration solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- What is an example of a hydraulic press? Discover the Power of Laboratory Sample Preparation
- What is the hydraulic forging process? Master the Art of High-Strength Metal Forming
- What is the purpose of a laboratory hydraulic press for LATP electrolyte pellets? Achieve Optimal Density & Conductivity
- What core conditions does a laboratory hydraulic press provide for solid-state electrolyte pellets? Enhance Density!



















