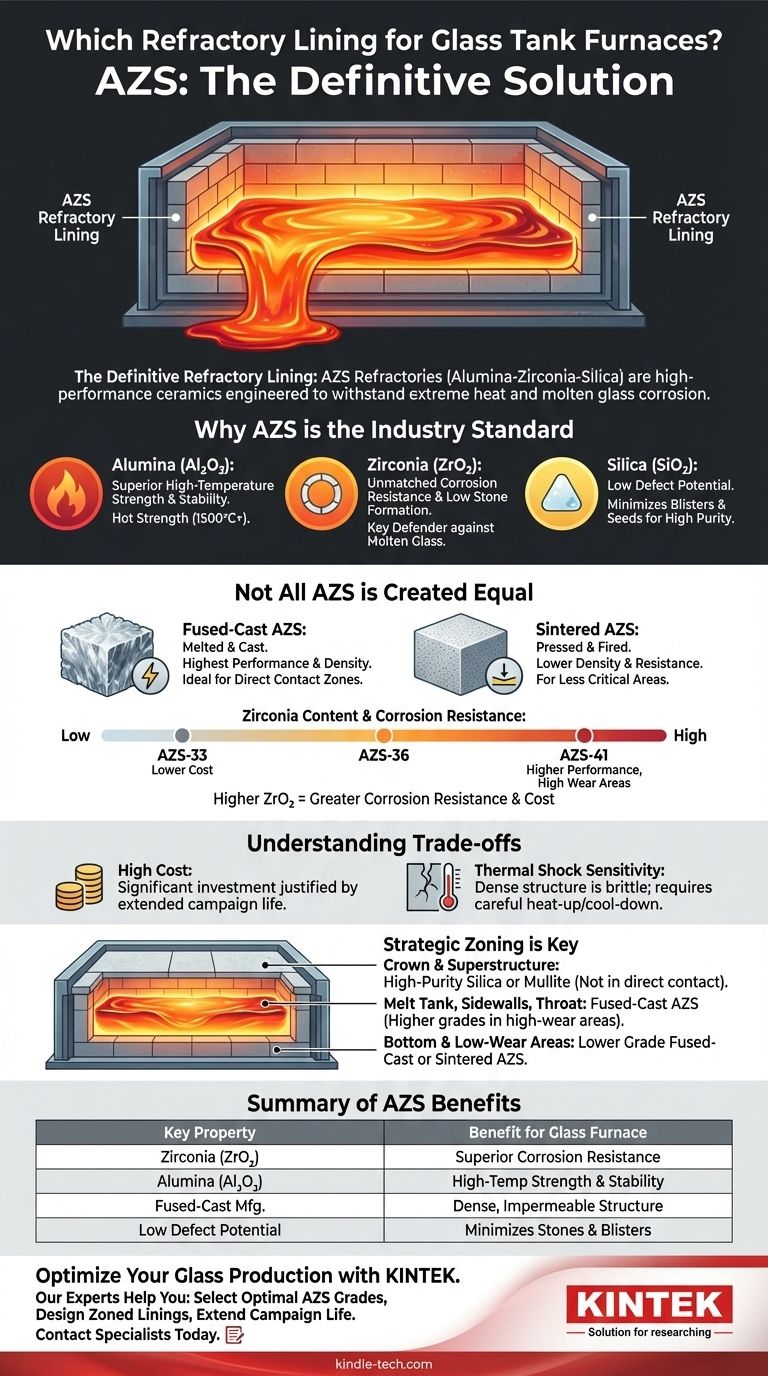
The definitive refractory lining used in the high-contact zones of a glass tank furnace is a family of materials known as AZS refractories. These are high-performance ceramics composed primarily of alumina (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), and silica (SiO2), specifically engineered to withstand the extreme conditions of molten glass production.
The core challenge in lining a glass furnace is not just containing extreme heat, but also resisting the intense chemical corrosion from molten glass. AZS refractories are the industry standard because their unique composition provides the best possible defense against this corrosion, preventing contamination and ensuring the quality of the final glass product.

Why AZS is the Industry Standard
The environment inside a glass furnace is one of the most demanding industrial applications. The refractory lining must act as a stable container, withstanding temperatures often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F) while being in constant contact with a chemically aggressive molten liquid.
Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
Molten glass is a powerful solvent that actively dissolves most materials it touches. The zirconia (ZrO2) component in AZS is the key to its exceptional performance.
Zirconia is highly resistant to chemical attack from the molten glass and its alkali vapors. This property minimizes the rate at which the furnace lining wears away and, crucially, reduces the risk of refractory particles breaking off and causing defects known as "stones" in the finished glass.
Superior High-Temperature Strength
The structural integrity of the furnace depends on the lining's ability to bear loads at extreme temperatures without deforming.
This is the primary role of the alumina (Al2O3) content. Alumina provides the high-temperature mechanical strength, or "hot strength," needed to keep the furnace structure stable throughout its long operational campaign.
Low Defect Potential
A successful refractory lining must be non-reactive with the melt. The goal is to avoid introducing impurities or bubbles into the glass.
The carefully balanced formulation of AZS, including its silica (SiO2) glassy phase, is designed to have very low potential for creating "blisters" (gas bubbles) or "seeds" in the glass. This ensures a high-purity, high-quality final product.
Not All AZS is Created Equal
AZS is not a single product but a category of materials. The specific manufacturing process and composition are tailored for different zones within the furnace to balance performance and cost.
Fused-Cast vs. Sintered AZS
The most common and highest-performing type is fused-cast AZS. The raw materials are melted in an electric arc furnace and cast into molds, creating a very dense, impermeable structure with superior corrosion resistance. This is the material of choice for areas in direct contact with molten glass.
Sintered AZS is produced by pressing and firing powders. While still a capable refractory, it is less dense and less corrosion-resistant than its fused-cast counterpart, making it suitable for less critical, lower-wear areas.
The Role of Zirconia Content
Fused-cast AZS is typically categorized by its zirconia percentage. Common grades include AZS-33, AZS-36, and AZS-41, with the number indicating the approximate ZrO2 content.
Higher zirconia content directly translates to greater corrosion resistance. Therefore, the most aggressive areas of the furnace, like the throat and melt-line, will use a high-zirconia material like AZS-41, while less demanding sidewalls might use AZS-33.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While AZS is the optimal solution for glass contact, it is not without its challenges. Acknowledging these is key to proper furnace design and operation.
The Primary Factor: Cost
High-performance materials come at a high price. Fused-cast AZS, particularly high-zirconia grades, represents a significant portion of the furnace construction cost. This expense is justified by the furnace's extended lifespan and the quality of the glass produced.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
The dense, rigid structure of fused-cast AZS makes it somewhat brittle and susceptible to cracking if heated or cooled too rapidly. Furnace heat-up and cool-down schedules must be managed with extreme care to prevent thermal shock damage to the lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct refractory is a zoning exercise, matching the material's properties and cost to the specific demands of each area within the furnace.
- If your primary focus is the melt tank, sidewalls, and throat: Fused-cast AZS is the only viable choice, with higher-zirconia grades used in the highest-wear areas.
- If your primary focus is the furnace crown and superstructure: These areas are not in direct contact with molten glass, so other materials like high-purity silica or mullite refractories are often used for their thermal stability and lower cost.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and budget: A zoned lining is essential, strategically placing the highest-grade (and most expensive) AZS only where absolutely necessary and using more economical materials elsewhere.
Ultimately, a successful glass furnace campaign is built upon a lining that strategically combines materials to maximize lifespan while protecting the purity of the glass.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Glass Furnace |
|---|---|
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) Content | Provides superior corrosion resistance against molten glass. |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) Content | Ensures high-temperature mechanical strength and stability. |
| Fused-Cast Manufacturing | Creates a dense, impermeable structure for maximum durability. |
| Low Defect Potential | Minimizes stones and blisters in the final glass product. |
Optimize Your Glass Production with the Right Refractory Solution
Choosing the correct refractory lining is critical to the longevity of your furnace and the quality of your glass. The experts at KINTEK specialize in high-performance lab and industrial equipment, including refractories for demanding thermal processes.
We can help you:
- Select the optimal AZS grade (e.g., AZS-33, AZS-41) for your specific furnace zones.
- Balance performance with budget through strategic, zoned lining designs.
- Extend your furnace campaign life and protect your product purity.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your project needs and ensure your furnace is built for success. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















