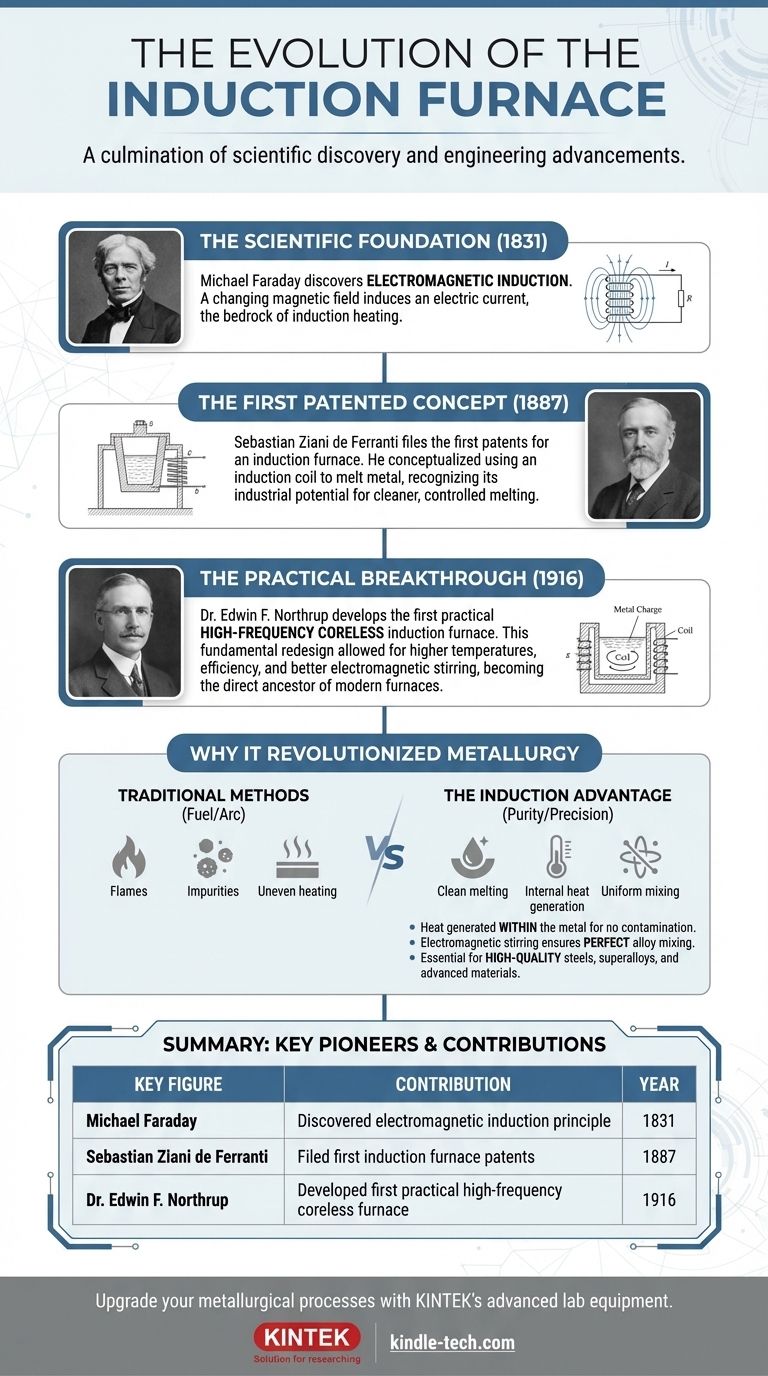
The first patents for an induction furnace were filed by Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti in 1887. While he is credited with the invention, this breakthrough was the culmination of scientific discovery and was followed by critical engineering advancements that made the technology practical for industrial use.
The invention of the induction furnace was not a single event but a progression. It began with Michael Faraday's discovery of the underlying scientific principle, was first conceptualized as a furnace by Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, and was later perfected for industrial use by Dr. Edwin F. Northrup.

The Scientific Foundation: More Than One Mind
Understanding who invented the furnace requires looking at the scientific bedrock it was built upon. The core concept is not the furnace itself, but the method of heating.
Michael Faraday and Induction's Principle
In 1831, scientist Michael Faraday discovered the principle of electromagnetic induction. He demonstrated that a changing magnetic field could induce an electric current in a nearby conductor.
This discovery is the absolute foundation of the technology. Without Faraday's work, the induction furnace would not exist.
The Core Concept of Induction Heating
Induction heating applies Faraday's principle directly. An alternating current is passed through a coil, creating a rapidly changing magnetic field.
When a conductive material (like metal) is placed inside this coil, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates immense heat, causing it to melt without any external flame or electric arc.
From Concept to Patent: The First Furnace
The leap from a scientific principle to a specific industrial application required an inventor's vision.
Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti's Breakthrough
Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, a British electrical engineer and inventor, was the first to conceptualize and patent the application of this principle for melting metal.
His 1887 patents laid out the design for a furnace that used an induction coil to heat and melt a metal charge. This was the first time the idea was formally documented as an invention.
Why Ferranti's Design Was Foundational
Ferranti's genius was in seeing the industrial potential. He recognized that induction could provide a cleaner and more controlled melting process compared to the fuel-fired furnaces of the era. His work established the core engineering concept.
The Leap to Practicality: The Modern Furnace Takes Shape
Ferranti's initial designs had limitations. The technology truly became a cornerstone of modern metallurgy thanks to developments in the United States.
Dr. Edwin F. Northrup's Contribution
In 1916, working at Princeton University, Dr. Edwin F. Northrup developed and built the first practical high-frequency coreless induction furnace.
This was not a minor tweak; it was a fundamental redesign that solved many of the problems of earlier concepts and unlocked the technology's true power.
What Made the Coreless Furnace a Game-Changer
Northrup's design is the direct ancestor of most modern induction furnaces. By removing the iron core that linked the coil and the metal charge, his furnace became far more versatile and efficient.
This "coreless" design prevented contamination, allowed for better electromagnetic stirring of the molten metal (improving alloy quality), and enabled much higher operating temperatures and power levels.
Why This Invention Revolutionized Metallurgy
The induction furnace wasn't just a new way to get metal hot; it was a fundamentally better way to control metallurgical processes.
Before Induction: The Limits of Other Furnaces
Traditional fuel-fired or arc furnaces introduced impurities into the metal from combustion byproducts or the graphite electrodes used to create the arc. Heating was often uneven, and controlling the melt's chemistry was difficult.
The Induction Advantage: Purity and Precision
The induction furnace offered a revolutionary level of control. Since the heat is generated within the metal itself, there is no contamination from external sources.
The electromagnetic forces also naturally stir the molten bath, ensuring alloys are mixed perfectly and uniformly. This combination of purity and precision is why induction furnaces are essential for producing high-quality steels, superalloys, and other advanced materials.
Key Figures in the Story of Induction
To properly attribute the invention, you must recognize the distinct contribution of each pioneer.
- If your primary focus is the scientific principle: Michael Faraday is the key figure whose discovery of electromagnetic induction made it all possible.
- If your primary focus is the original patented concept: Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti is credited with inventing and patenting the first induction furnace.
- If your primary focus is the first practical, industrial-scale furnace: Dr. Edwin F. Northrup's development of the coreless high-frequency furnace was the pivotal moment for its commercial success.
Ultimately, technological progress is rarely the work of a single individual but rather a chain of linked innovations.
Summary Table:
| Key Figure | Contribution | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Michael Faraday | Discovered electromagnetic induction (scientific principle) | 1831 |
| Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti | Filed first patents for induction furnace design | 1887 |
| Dr. Edwin F. Northrup | Developed first practical high-frequency coreless furnace | 1916 |
Upgrade your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced lab equipment!
Just as the pioneers of induction technology revolutionized metal melting, KINTEK provides the precision equipment your laboratory needs to achieve superior results. Our induction furnaces and lab consumables ensure the purity, control, and efficiency required for high-quality metallurgy.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and production capabilities. Get in touch via our Contact Form and let KINTEK power your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















