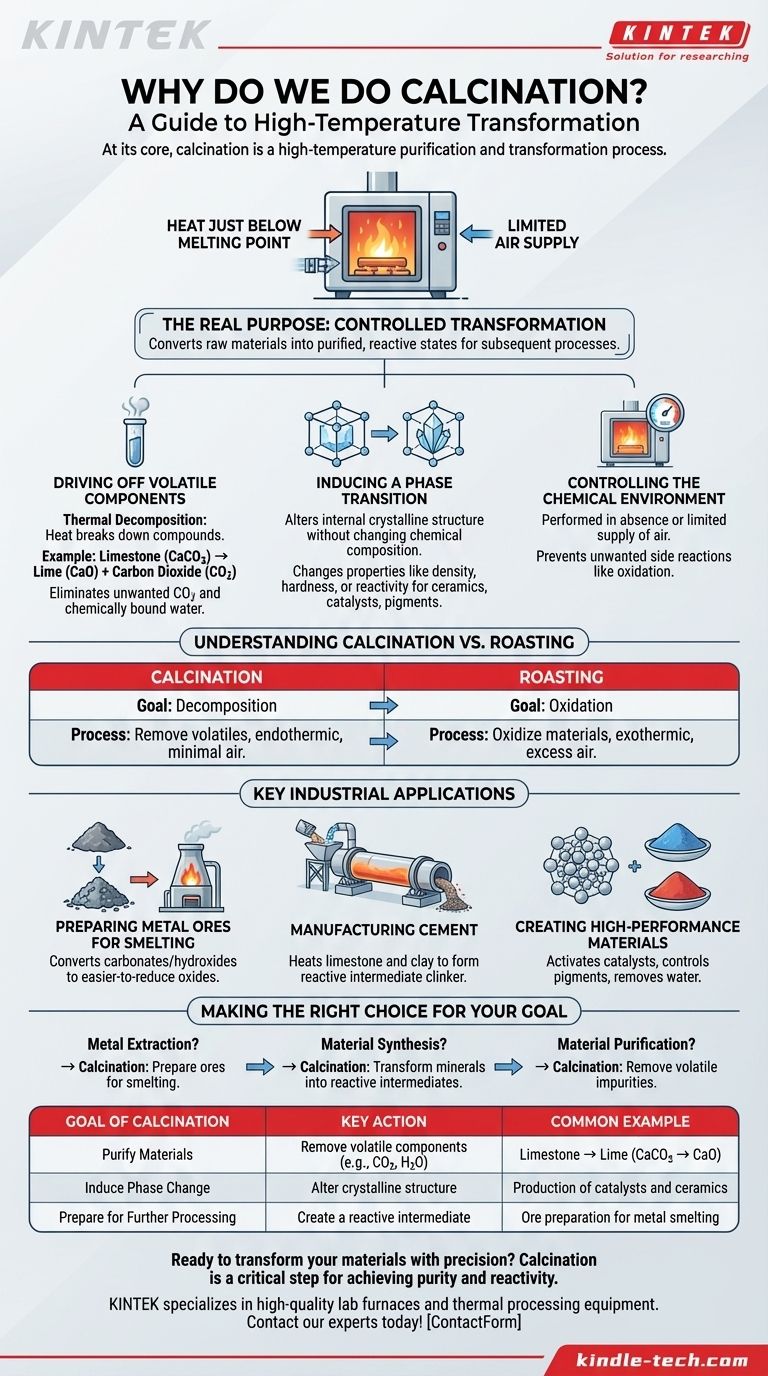
At its core, calcination is a high-temperature purification and transformation process. It involves heating a solid material to a temperature just below its melting point, typically with a limited supply of air. This intense heat is used to drive off volatile substances, cause thermal decomposition, or trigger a change in the material's physical structure, preparing it for its next use.
The real purpose of calcination is not just heating, but controlled transformation. It is the critical step that converts raw, often inert materials like mineral ores into a purified and more chemically reactive state, making subsequent processes like metal extraction or cement production possible and efficient.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand why calcination is so fundamental in material science and industry, you must first understand the changes it induces. The process is not merely about drying a substance; it's about causing a fundamental chemical or physical change.
Driving Off Volatile Components
The most common purpose of calcination is thermal decomposition. This is a chemical reaction where heat breaks down a compound into two or more simpler substances.
A classic example is the production of lime from limestone. Limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO3) is heated, causing it to decompose into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and driving off carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.
This process eliminates the volatile CO2, which is unwanted in the final product, and leaves behind the useful, reactive lime. The same principle applies to removing chemically bound water (hydrates) from minerals.
Inducing a Phase Transition
Sometimes, the goal isn't to change the chemical composition but to alter the material's internal crystalline structure. This is known as a phase transition.
Heating can rearrange the atoms in a solid, changing its properties like density, hardness, or reactivity without removing any part of it. This is a crucial step in producing certain ceramics, catalysts, or pigments where a specific crystal structure is required for performance.
Controlling the Chemical Environment
Calcination is almost always performed in the absence or limited supply of air. This is a critical distinction. The goal is to break the material down with heat, not to burn or oxidize it.
By controlling the atmosphere inside the furnace—whether it's inert, reducing, or has very little oxygen—engineers can prevent unwanted side reactions and ensure the desired transformation occurs cleanly.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Calcination vs. Roasting
The term "roasting" is often used alongside calcination, but they are fundamentally different processes with opposing goals. Mistaking one for the other leads to process failure.
The Goal of Calcination: Decomposition
As discussed, calcination aims to break a material down, often by removing a volatile component like CO2 or H2O. It is typically an endothermic process (it requires energy input) and is conducted with minimal air to prevent oxidation.
The Goal of Roasting: Oxidation
Roasting, in contrast, is performed with an excess of air or oxygen. Its specific purpose is to oxidize the material. This is common in metallurgy for converting metal sulfide ores into metal oxides, which are easier to reduce to pure metal later on. The process is often exothermic (it releases heat).
Key Industrial Applications
Calcination is not an obscure laboratory technique; it is a cornerstone of several massive global industries.
Preparing Metal Ores for Smelting
In metallurgy, many metals are found in nature as carbonates or hydroxides. Calcination is the essential first step to convert these ores into their oxide forms. These oxides are much more easily reduced (the oxygen is removed) in a smelter to produce the pure metal.
Manufacturing Cement
The production of Portland cement is one ofthe largest scale applications of calcination. Raw materials, primarily limestone and clay, are heated in a massive rotary kiln.
The intense heat calcines the limestone into lime and allows it to react with the other minerals to form a new substance called clinker. This clinker is the reactive intermediate that, when ground into a powder, becomes cement.
Creating High-Performance Materials
Calcination is also used on a smaller scale to produce specialized materials. It can be used to activate catalysts, control the final color and properties of pigments, or remove water from materials like gypsum to create Plaster of Paris.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of calcination is always tied to a specific transformation goal.
- If your primary focus is metal extraction: Calcination is the essential preparatory step to convert carbonate or hydroxide ores into oxides, which are much easier to reduce into pure metal.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis (like cement): Calcination is the core chemical engine that transforms raw, inactive minerals into a highly reactive intermediate like clinker.
- If your primary focus is material purification: Calcination serves to remove volatile impurities, such as bound water or carbon-based compounds, to create a stable and pure final product.
Ultimately, calcination is the foundational thermal process for converting raw materials into valuable, functional products.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Calcination | Key Action | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purify Materials | Remove volatile components (e.g., CO2, H2O) | Limestone → Lime (CaCO3 → CaO) |
| Induce Phase Change | Alter crystalline structure | Production of catalysts and ceramics |
| Prepare for Further Processing | Create a reactive intermediate | Ore preparation for metal smelting |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? Calcination is a critical step for achieving purity and reactivity in your products. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for reliable calcination processes. Whether you're in metallurgy, cement production, or advanced material synthesis, our solutions ensure controlled, efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific thermal processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















