Heater wire is designed with high resistance because resistance is the very property that allows the wire to convert electrical energy into thermal energy. According to Joule's law of heating, the amount of heat produced is directly proportional to the wire's electrical resistance for a given electrical current. A low-resistance wire would allow current to pass through it efficiently, producing very little heat, which defeats the purpose of a heater.
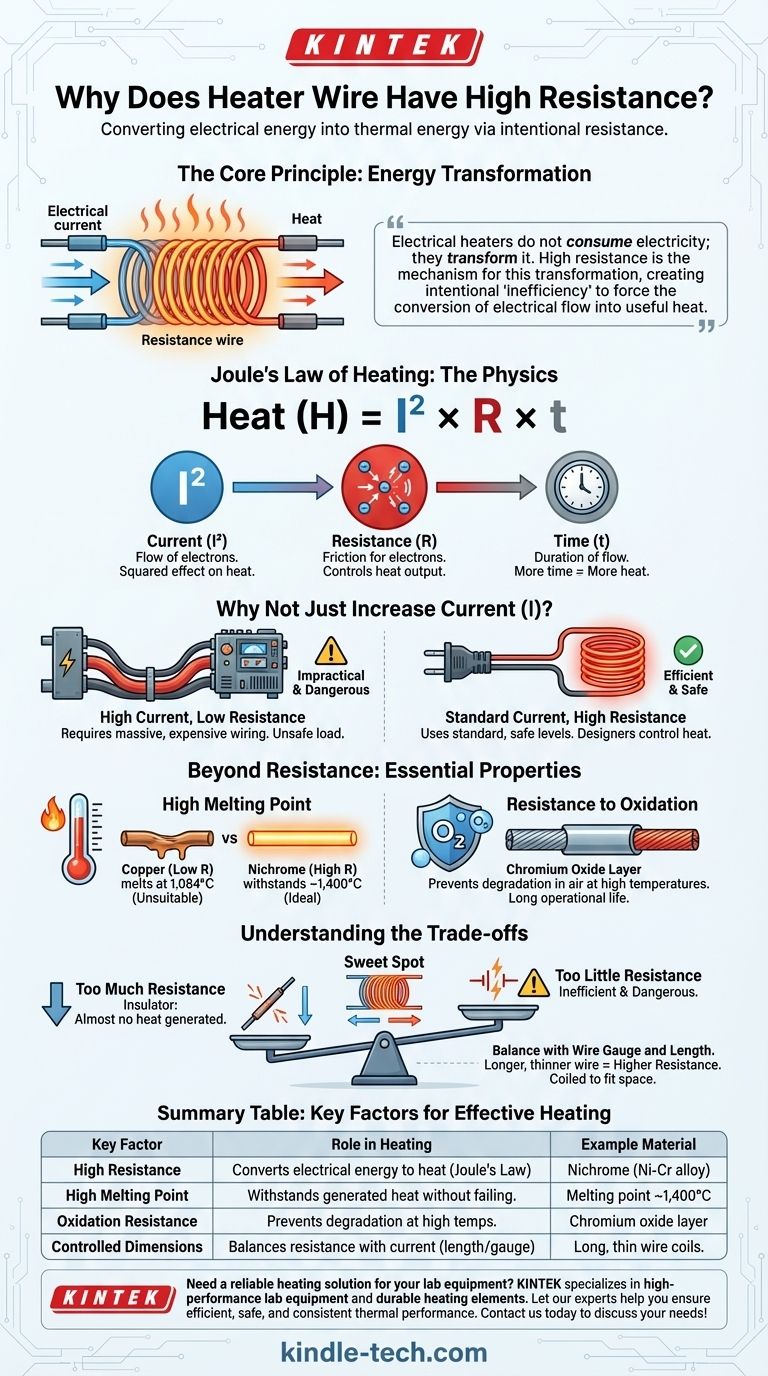
The core principle is that electrical heaters do not consume electricity; they transform it. High resistance is the mechanism for this transformation, creating intentional "inefficiency" to force the conversion of electrical flow into useful heat.

The Physics of Electrical Heating
To understand why high resistance is essential, we must first look at the fundamental law governing this process.
Introducing Joule's Law of Heating
At its heart, electrical heating is described by a simple and powerful formula: Heat = I² x R x t.
This is Joule's First Law. It states that the heat (H) generated by a conductor is the product of the square of the current (I), the conductor's resistance (R), and the amount of time (t) the current is flowing.
The Critical Role of Resistance (R)
In this equation, resistance (R) is the key variable that a designer can control through material choice. For any given current flowing through the circuit, doubling the resistance will double the heat produced.
Think of electrical resistance as a form of friction for electrons. As electrons are forced through a high-resistance material, they collide with the atoms of that material, transferring their energy and causing the atoms to vibrate. This increased vibration is what we perceive as heat.
Why Not Just Increase Current (I)?
You might notice the current (I) is squared in the formula, meaning it has an even greater impact on heat. However, simply increasing the current is often impractical and dangerous.
High current requires thicker, more expensive supply wiring and can put an unsafe load on the building's electrical system. By using a high-resistance material, designers can generate significant heat using the standard, safe levels of current available from a wall outlet.
Beyond Resistance: Properties of an Effective Heater Wire
While high resistance is the primary requirement, several other properties are just as crucial for a safe and durable heating element.
High Melting Point
The wire must be able to withstand the very heat it generates. If the temperature produced exceeds the material's melting point, the wire will fail instantly.
This is why heater elements are made from specialized alloys like Nichrome (an alloy of nickel and chromium), which has a high melting point of around 1,400°C (2,550°F). Copper, an excellent conductor with low resistance, would melt at 1,084°C and is completely unsuitable.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals react rapidly with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation (the same process that causes rust). This degrades the wire, changing its resistance and eventually causing it to crumble and break.
Nichrome is exceptionally good at resisting oxidation. When heated, it forms a protective outer layer of chromium oxide that prevents the rest of the wire from deteriorating, giving it a long operational life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing a heating element isn't as simple as choosing the material with the highest possible resistance. It's a careful balancing act.
The Problem of Too Much Resistance
If a wire's resistance is excessively high, it begins to act like an insulator. It will impede the flow of current so much that very little current can pass through.
According to Joule's law (Heat = I² x R), if the current (I) drops to nearly zero, almost no heat will be generated, regardless of how high the resistance (R) is. The goal is to find a "sweet spot" that provides enough resistance to generate heat without crippling the current flow.
The Balance with Wire Gauge and Length
The resistance of a wire is also determined by its length and thickness (gauge). A longer, thinner wire has higher resistance. However, a thinner wire is also more fragile and can't handle as much current before it overheats and breaks.
Engineers must therefore balance the material's resistivity with the physical dimensions of the wire to achieve the target heat output for a specific voltage and current. This is why you see heater elements coiled up—to fit a very long wire into a small space.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this principle allows you to see the deliberate engineering behind common household and industrial devices.
- If your primary focus is efficient power transmission: You need the lowest possible resistance, which is why power lines and extension cords use thick copper or aluminum wire.
- If your primary focus is generating light: You need extreme resistance in a vacuum, forcing a tungsten filament to incandescence, as in an old-style light bulb.
- If your primary focus is generating controlled heat: You need a material with high, stable resistance and excellent oxidation protection, which is the role of Nichrome in toasters, space heaters, and electric stoves.
By choosing a material with high resistance, engineers intentionally harness a property that is undesirable in most electrical circuits to create useful heat on demand.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Heating | Example Material |
|---|---|---|
| High Resistance | Converts electrical energy to heat via Joule's law | Nichrome (Nickel-Chromium alloy) |
| High Melting Point | Withstands generated heat without failing | Melting point ~1,400°C |
| Oxidation Resistance | Prevents degradation at high temperatures | Chromium oxide layer |
| Controlled Dimensions | Balances resistance with current flow (length/gauge) | Long, thin wire coils |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable heating elements designed for precision and longevity. Let our experts help you select the right components to ensure efficient, safe, and consistent thermal performance in your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating

















