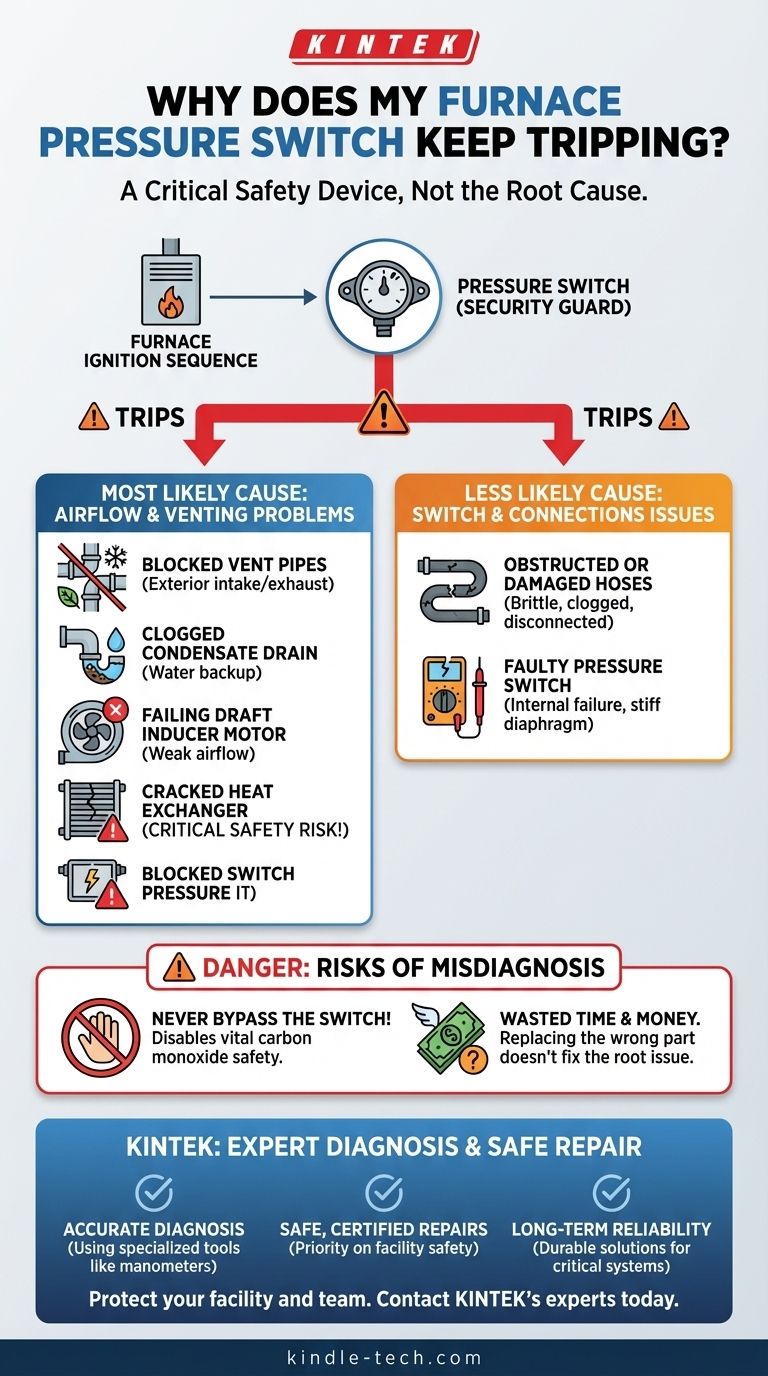
In almost all cases, a furnace pressure switch trips for one of two reasons: either the switch itself has failed, or it is correctly detecting a problem with your furnace's drafting and venting system. While it's possible the switch is faulty, it is far more likely that it's doing its job by signaling a genuine safety concern that must be investigated.
Your furnace's pressure switch is a critical safety device. A "tripping" switch is most often a symptom of an underlying airflow or venting problem, not the cause of the failure. Simply replacing the switch without diagnosing the root cause is often ineffective and can be dangerous.

What a Pressure Switch Does (And Why It Matters)
Think of the pressure switch as a security guard for your furnace. Its only job is to ensure the furnace's exhaust vent path is clear before allowing the main gas burners to ignite.
The Critical Safety Sequence
When you call for heat, a specific sequence begins. First, the draft inducer motor kicks on. This is a small fan that creates a negative pressure (a vacuum) to pull toxic exhaust gases like carbon monoxide safely out of your home through the flue pipe.
The pressure switch monitors this vacuum. Once it detects the correct negative pressure, it closes an electrical circuit, sending an "all clear" signal to the furnace's control board. Only after receiving this signal will the board proceed to ignite the gas burners.
A Signal of a Deeper Issue
If the switch does not detect the proper vacuum, it will not close the circuit, and the furnace will shut down the ignition sequence to prevent a dangerous buildup of exhaust gases in your home. The control board will then typically flash an error code indicating a pressure switch fault.
This means the "tripping" you're experiencing is the switch performing its function perfectly. It's telling you something is wrong with the venting process.
Common Causes for a Tripping Pressure Switch
Investigating a pressure switch problem means looking at the entire system it monitors. The issue usually falls into one of two categories.
Category 1: Venting & Airflow Problems (The Most Likely Cause)
These issues prevent the draft inducer motor from creating the necessary vacuum.
- Blocked Vent Pipes: This is the most common culprit. Check the PVC intake or exhaust pipes on the outside of your home for blockage from snow, ice, leaves, or animal nests.
- Clogged Condensate Drain: High-efficiency furnaces produce water (condensate) that must drain away. If the drain line or trap becomes clogged, water can back up into the inducer motor housing and obstruct airflow.
- Failing Draft Inducer Motor: The motor itself may be weak or failing. If it doesn't spin fast enough, it can't generate the required vacuum for the switch to close.
- A Cracked Heat Exchanger: While less common, a crack in the heat exchanger can alter the pressure within the system and prevent the switch from closing. This is a serious safety hazard that leaks carbon monoxide and requires immediate professional attention.
Category 2: Issues with the Switch & Its Connections
Sometimes, the problem lies with the switch or its immediate connections, even if the venting is clear.
- Obstructed Hoses: The small rubber or silicone hoses connecting the pressure switch to the inducer motor assembly can become brittle, cracked, or clogged with debris. They can also sag and fill with condensate water, blocking the pressure reading.
- A Faulty Pressure Switch: The switch itself can fail. The internal rubber diaphragm can rupture or become stiff with age, or the electrical contacts can wear out. A soft flapping or clicking sound can sometimes indicate a failed diaphragm.
Understanding the Pitfalls: The Danger of Misdiagnosis
It can be tempting to assume the part named in the error code is the part that needs replacing, but this often leads to wasted time and money.
The Risk of Bypassing the Switch
Under no circumstances should you ever bypass a pressure switch to get the furnace to run. You are disabling a vital safety feature designed to prevent deadly carbon monoxide from filling your home. It is a dangerous and potentially fatal shortcut.
The Cost of Replacing the Wrong Part
If you replace a pressure switch without addressing a blocked vent pipe, the new switch will also trip for the exact same reason. You will have spent money on a part you didn't need and will still be left without heat and a problem to solve.
How to Diagnose the Problem Safely
Your approach should be determined by your comfort level with inspecting the equipment.
- If you are comfortable with basic inspection: Start with the safest and most obvious checks. Visually inspect the exterior vent pipes for any blockages and check the clear plastic condensate drain line for visible clogs or backed-up water.
- If the issue is not obvious or you are unsure: Your safest and most effective option is to call a qualified HVAC technician. They have the tools, like a manometer, to precisely measure the vacuum and determine if the problem is inadequate draft or a faulty switch.
- If you suspect the switch itself is faulty: A technician can test the switch directly with a multimeter to see if it's closing the circuit when a manual vacuum is applied. This definitively proves whether the switch or the system is the source of the problem.
Understanding that the pressure switch is a messenger, not the message, is the key to a safe and effective repair.
Summary Table:
| Potential Cause | Symptoms & Key Indicators | Urgency / Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Blocked Vent Pipes | Error code, no visible draft from exterior vent | High - Requires immediate clearing |
| Clogged Condensate Drain | Water in inducer motor housing, gurgling sounds | Medium - Can cause water damage |
| Failing Draft Inducer Motor | Weak airflow, unusual noises, motor struggles to spin | High - Needs professional diagnosis |
| Cracked Heat Exchanger | Strange odors, soot, carbon monoxide risk | Critical - Shut off furnace and call a professional immediately |
| Faulty Pressure Switch/Hose | Switch fails to click, damaged/cracked hoses | Medium - Can be tested with a multimeter |
Don't Risk Your Safety – Let KINTEK's Experts Diagnose Your Furnace
A tripping pressure switch is a serious warning sign that should never be ignored. Improper diagnosis can lead to wasted money on unnecessary parts or, worse, expose your home to dangerous carbon monoxide.
KINTEK specializes in maintaining critical laboratory equipment, including industrial furnaces and environmental control systems. Our technicians use specialized tools like manometers to accurately measure vacuum pressure and pinpoint the exact cause of your furnace's safety shutdown—whether it’s a blocked vent, failing inducer motor, or faulty switch.
We ensure:
- Accurate Diagnosis: No guesswork. We identify the root cause, not just the symptom.
- Safe, Certified Repairs: Your safety is our priority. We follow strict protocols to prevent hazardous conditions.
- Long-Term Reliability: We provide durable solutions to keep your lab or facility running safely and efficiently.
Protect your lab, your team, and your investment. Contact our expert team today for a professional assessment and reliable repair.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a magnetic stirrer in a fuel cell electrolyte system? Enhance Stability and Accuracy
- What material is used for furnace insulation? Key Materials for Maximum Efficiency & Performance
- How do high-precision PID controllers ensure the accuracy of process optimization data? Master Dynamic Temperature Ramps
- What are the primary functions of a high-purity quartz tube? Ensure Peak Microwave Plasma Reactor Performance
- What types of vacuum pumps are commonly found in laboratories? Choose the Right Pump for Your Lab's Needs
- Is quartz chemically resistant? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Inertness for Demanding Applications
- What is a furnace retort? Your Guide to Precision Atmosphere Control for Heat Treatment
- Why are cemented carbide balls selected as the grinding media? Optimize Graphene-Reinforced Alumina Ceramics

















