Graphite is the material of choice for furnaces because of its exceptional ability to withstand extreme temperatures while remaining chemically inert and structurally stable. It can handle heat up to 5000°F without reacting with common process gases like nitrogen or argon, making it uniquely suited for high-purity, high-temperature environments.
The decision to use graphite in furnaces is not based on a single trait, but on a powerful combination of extreme thermal stability, chemical inertness, and energy efficiency. This trifecta makes it uniquely capable of handling demanding industrial processes while reducing operational costs and cycle times.
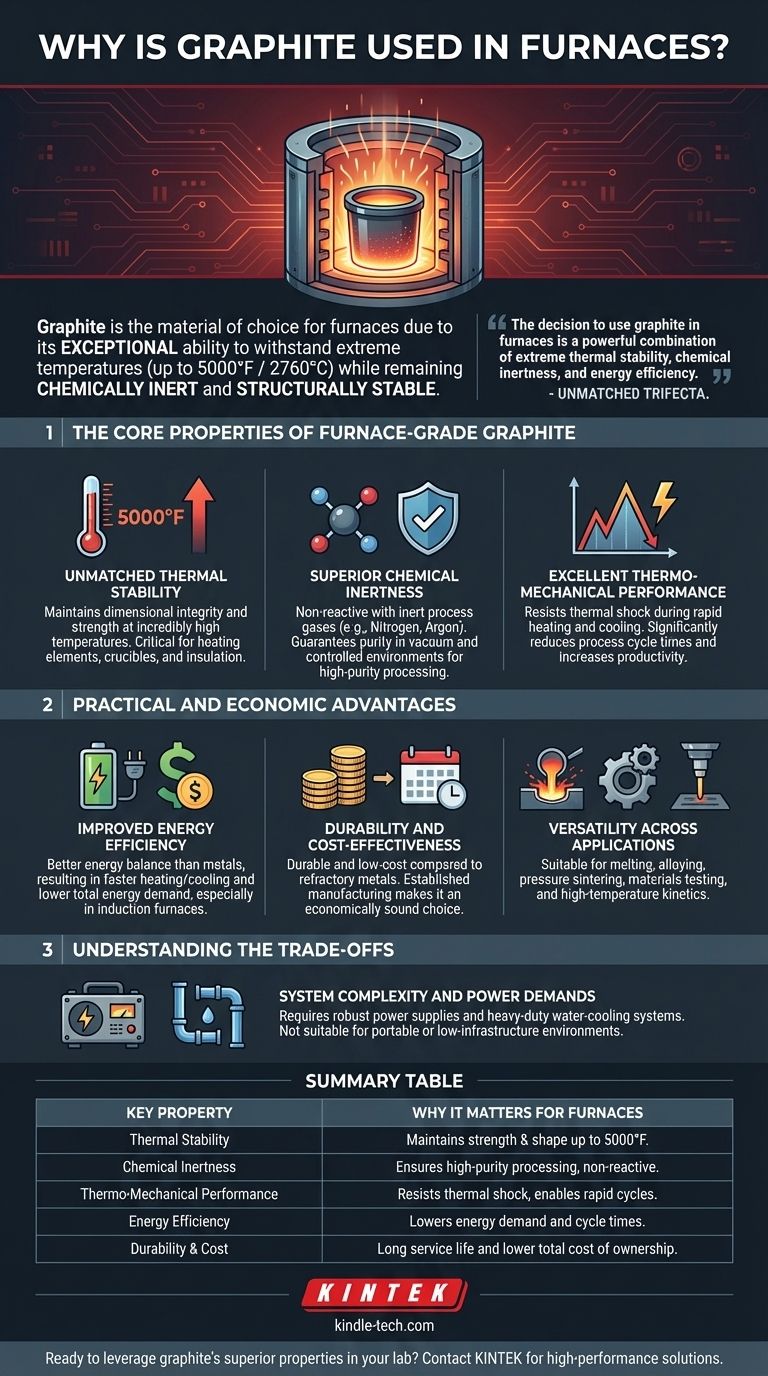
The Core Properties of Furnace-Grade Graphite
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Graphite maintains its dimensional integrity and strength at incredibly high temperatures. This stability is critical in furnace applications where other materials would melt, warp, or degrade.
This property ensures that components like heating elements, crucibles, and insulation retain their shape and function through repeated, intense heating cycles.
Superior Chemical Inertness
In controlled environments like vacuum furnaces, preventing contamination is paramount. Graphite is valued for being non-reactive with inert process gases such as nitrogen and argon.
This inertness guarantees that the material being processed is not contaminated by the furnace components, which is essential for applications like high-temperature sintering and heat treatment.
Excellent Thermo-Mechanical Performance
Graphite can be heated and cooled very rapidly without suffering from thermal shock or damage.
This capability significantly reduces the time required for each process cycle, directly increasing furnace productivity and operational throughput.
Practical and Economic Advantages
Improved Energy Efficiency
While graphite can absorb a high amount of heat, it provides a better overall energy balance than comparable metals.
This efficiency results in faster heating and cooling times, which lowers the total energy demand of the furnace, especially in power-intensive induction furnaces.
Durability and Cost-Effectiveness
Graphite hot zones are known for being durable and low-cost compared to refractory metal alternatives.
Its wide availability and established manufacturing processes make it an economically sound choice for a vast range of industrial heating applications.
Versatility Across Applications
The unique properties of graphite make it suitable for a diverse set of processes.
It is commonly used for melting and alloying metals, pressure sintering, materials testing, and investigating high-temperature reaction kinetics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
System Complexity and Power Demands
While the graphite components themselves are effective, the furnaces built around them are not simple systems.
Graphite furnaces require heavy-duty power supplies and robust water-cooling systems to manage the immense energy involved, making them unsuitable for portable or low-infrastructure environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing graphite is often the default for high-temperature processes, but understanding why ensures it aligns with your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is process purity and speed: Graphite's chemical inertness and rapid thermal cycling make it the ideal choice for vacuum and inert gas furnaces.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and efficiency: Graphite's excellent energy balance, durability, and lower material cost provide a low total cost of ownership.
- If your primary focus is system design: You must account for the significant power and cooling infrastructure required to support a graphite furnace, as this is a key system-level consideration.
Ultimately, graphite's unique blend of properties makes it an indispensable material for advancing modern high-temperature technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for Furnaces |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Maintains strength and shape at temperatures up to 5000°F (2760°C). |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive with inert gases, ensuring high-purity processing. |
| Thermo-Mechanical Performance | Resists thermal shock, enabling rapid heating and cooling cycles. |
| Energy Efficiency | Lowers total energy demand and reduces process cycle times. |
| Durability & Cost | Offers a long service life and lower total cost of ownership. |
Ready to leverage graphite's superior properties in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces and components that harness the power of graphite. Whether your priority is process purity, operational efficiency, or system design, our experts can help you select the right solution for your high-temperature applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite-based furnace solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of surface hardening? Achieve Superior Wear Resistance and Toughness
- What is the process of sintering in the iron and steel industry? A Key Step for Efficient Blast Furnace Operation
- What is the negative effect of quenching steel? Manage Internal Stress and Prevent Cracking
- What is plasma pyrolysis in waste management? Achieve Complete Waste Destruction with Plasma Technology
- What are the categories of heat treatment? A Guide to Softening, Hardening, and Refining Metals
- What are the advantages of a vacuum drying oven for nZVI? Preserve Chemical Reactivity & Prevent Oxidation
- How is vacuum created in a furnace? A Guide to Achieving a Contamination-Free Heat Treatment Environment
- Why is a vacuum drying oven recommended for processing wet gels of Erbium-doped titanium dioxide? | KINTEK



















