Table of Contents
- Unveiling the Automatic Hydraulic Press: A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Laboratory Applications
- Introduction to automatic hydraulic presses and their significance in various industries and laboratories
- Exploring the diverse applications of automatic hydraulic presses, from XRF analysis to polymer processing
- Advantages of automatic hydraulic presses: precision, repeatability, and autonomous operation
- The Mechanics of Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Unlocking the Power of Precision and Efficiency
- Revolutionizing Sample Preparation: The Role of Automatic Hydraulic Presses in Laboratories
- Industrial Applications of Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Shaping Diverse Materials and Processes
- Maintaining and Troubleshooting Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Ensuring Optimal Performance
- Future Advancements in Automatic Hydraulic Press Technology: A Glimpse into Innovation
Unveiling the Automatic Hydraulic Press: A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Laboratory Applications
Introduction to automatic hydraulic presses and their significance in various industries and laboratories
Automatic hydraulic presses are invaluable tools in many industries and laboratories, offering precision and versatility for a wide range of applications. These machines utilize high pressure to condense and mold materials, powered by an electric motor or hand-operated levers. Compared to other manufacturing equipment, hydraulic presses are relatively affordable and offer immense versatility for producing objects with precision.

Exploring the diverse applications of automatic hydraulic presses, from XRF analysis to polymer processing
The applications of automatic hydraulic presses are diverse and span multiple industries and laboratories. In scientific laboratories, they are often used for preparing powder samples for analysis, such as in XRF (X-ray fluorescence) analysis. The use of hydraulic presses has significantly improved the speed and efficiency of XRF sample preparation, particularly in hand-fed hydraulic systems. Additionally, these presses are beneficial for high-volume sample preparation, increasing the overall sampling speed.
The versatility of hydraulic presses extends beyond XRF sample preparation. They are also commonly used for sample manipulation activities in laboratories and in industrial settings for small and large-scale manufacturing practices. Some specific applications include hot embossing, laminating, and melting polymers for thin films.
Advantages of automatic hydraulic presses: precision, repeatability, and autonomous operation
Automatic hydraulic presses offer several advantages over manual presses, including increased precision, repeatability, and autonomous operation. These presses are controlled by a switch or automated controller, ensuring consistent and accurate pressure application every time. This level of precision is crucial in various applications where consistency is paramount.
Furthermore, automatic hydraulic presses, such as the APEX 400, enhance laboratory workflow by operating autonomously once programmed. This allows technicians to focus on other tasks while the press completes its operation. Not only are automatic presses less laborious to operate compared to manual counterparts, but they also provide greater accuracy and consistency due to the elimination of variable factors during use.
In conclusion, automatic hydraulic presses are versatile and powerful tools used in various industries and laboratories. Their ability to apply high pressure with precision and repeatability makes them ideal for applications such as XRF sample preparation, sample manipulation, and a range of manufacturing processes. The autonomous operation of automatic hydraulic presses further enhances their utility, allowing technicians to focus on other tasks while the press efficiently completes its operation.
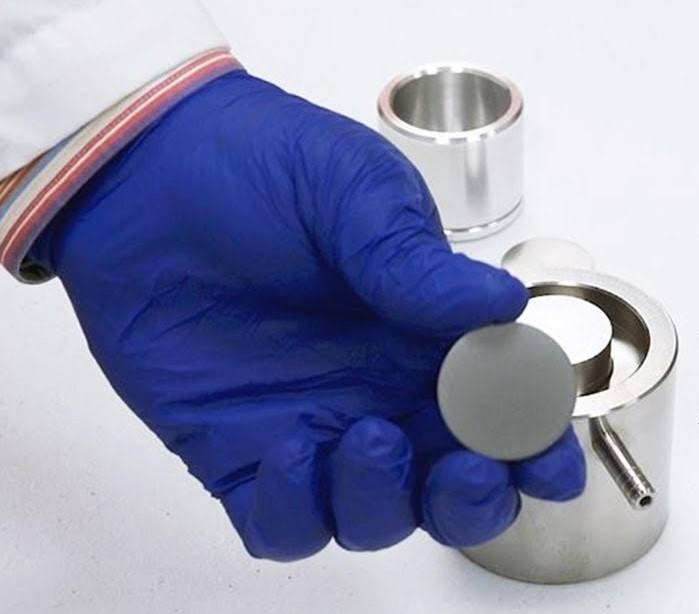

The Mechanics of Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Unlocking the Power of Precision and Efficiency
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Automatic Hydraulic Press Operation
Automatic hydraulic presses utilize a pump to elevate a piston containing air or liquid pressure. This configuration enables precise force application by releasing the piston's pressure onto a target object positioned beneath it. The combination of hydraulic power and controlled pressure ensures consistent and accurate results, making these presses ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments like the automotive industry.
Comparing Automatic Hydraulic Presses with Manual Presses: Key Differences and Advantages
Unlike manual hydraulic presses that rely on physical effort for operation, automatic hydraulic presses employ either a switch or automated controller to regulate the piston's movement. This automation provides enhanced accuracy and repeatability, ensuring consistent pressure application with each use. Furthermore, automatic hydraulic presses significantly reduce labor requirements, freeing up technicians to focus on other tasks while the press operates autonomously.
Examining the Components of an Automatic Hydraulic Press: Hydraulic System, Touchscreen Interface, and Die
A typical automatic hydraulic press comprises several key components:
-
Hydraulic System: The core of the press, the hydraulic system generates and transmits pressurized fluid to the piston. It ensures precise force application and control.
-
Touchscreen Interface: Modern automatic hydraulic presses feature user-friendly touchscreen interfaces that allow for intuitive programming and operation. Technicians can easily set parameters, monitor progress, and troubleshoot issues through the interface.
-
Die: The die, a crucial component of the press, performs the intended task, such as pressing, cutting, or forming. Automatic presses often incorporate dies capable of automated actions like pressing and releasing materials.

In conclusion, automatic hydraulic presses revolutionize laboratory and manufacturing processes by providing precise, efficient, and consistent force application. Their automation capabilities and user-friendly interfaces make them an invaluable asset for various applications, including sample preparation, XRF analysis, and polymer processing.
Revolutionizing Sample Preparation: The Role of Automatic Hydraulic Presses in Laboratories
Automatic hydraulic presses have transformed sample preparation in laboratories, offering accuracy, consistency, and ease of use. These versatile machines are used in various applications, including material testing, powder compaction, and XRF analysis.
Applications of Automatic Hydraulic Presses in Laboratory Settings
Automatic hydraulic presses are widely used in laboratories for a variety of applications, including:
- Material testing: Automatic hydraulic presses are used to test the mechanical properties of materials, such as tensile strength, compressive strength, and hardness.
- Powder compaction: Automatic hydraulic presses are used to compact powders into pellets or briquettes for further analysis.
- XRF analysis: Automatic hydraulic presses are used to prepare XRF pellets for elemental analysis.
- Other applications: Automatic hydraulic presses are also used in a variety of other laboratory applications, such as sample preparation for chromatography, spectroscopy, and microscopy.
Advantages of Using Automatic Hydraulic Presses for Sample Preparation
Automatic hydraulic presses offer several advantages over manual hydraulic presses and other sample preparation methods. These advantages include:
- Accuracy: Automatic hydraulic presses provide precise and consistent force control, ensuring accurate and reproducible results.
- Consistency: Automatic hydraulic presses eliminate human error, resulting in consistent sample preparation and reliable results.
- Ease of use: Automatic hydraulic presses are easy to operate, with intuitive controls and user-friendly interfaces.
- Efficiency: Automatic hydraulic presses can be programmed to operate autonomously, freeing up laboratory personnel for other tasks.
- Safety: Automatic hydraulic presses are equipped with safety features to protect users from potential hazards.

Industrial Applications of Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Shaping Diverse Materials and Processes
Automatic hydraulic presses are indispensable tools in many industrial settings, contributing significantly to the efficiency and versatility of manufacturing processes. Their wide-ranging applications encompass metalworking, plastics processing, and woodworking industries, where they excel in performing various operations, including forging, punching, blanking, deep drawing, and forming.
Unveiling the Role of Automatic Hydraulic Presses in Diverse Industries
Metalworking: In the metalworking industry, automatic hydraulic presses are extensively used for forging, a process that involves shaping metal components by applying high pressure. This technique allows for the creation of complex shapes and enhances the strength and durability of metal parts. Additionally, hydraulic presses are employed in punching and blanking operations, where they precisely cut and form metal sheets into desired shapes.
Plastics Processing: The plastics processing industry relies heavily on automatic hydraulic presses for molding and forming plastic components. These presses apply controlled pressure and heat to shape thermoplastic materials into a myriad of products, ranging from intricate automotive parts to everyday consumer goods. The versatility of hydraulic presses enables the production of complex shapes and intricate details, catering to diverse industry needs.
1.Capacity and Size:
- Determine the maximum force required for the intended application. Presses are typically rated in tons or kilonewtons, and selecting a model with sufficient capacity is essential to avoid overloading and potential damage.
- Consider the size of the samples and the available workspace. Choose a press with a platen size and working area that accommodate the intended sample dimensions comfortably.
2. Automation Features:
- Evaluate the level of automation required for the intended application. Some presses offer semi-automatic operation with manual loading and unloading, while fully automatic models can perform the entire process autonomously.
- Consider features such as programmable cycles, automatic pressure control, and data logging capabilities to enhance efficiency and consistency.
3. Control Systems:
- Choose a press with an intuitive and user-friendly control system. Clear displays, easy-to-use interfaces, and customizable settings contribute to efficient operation and minimize the learning curve for technicians.
- Consider the availability of safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents.
4. Safety Mechanisms:
- Ensure the selected press complies with relevant safety standards and regulations. Look for features such as guarding, light curtains, and safety enclosures to protect operators from potential hazards.
- Consider the availability of safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents.
5. Versatility and Compatibility:
- Evaluate the versatility of the press to accommodate various applications. Consider the availability of interchangeable platens, tooling, and accessories to expand the range of processes that can be performed.
- Ensure compatibility with existing laboratory equipment, such as sample holders, dies, and molds, to avoid the need for additional purchases or modifications.

6. Maintenance and Service:
- Consider the maintenance requirements and service availability for the chosen press. Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Choose a press with easily accessible components, clear maintenance instructions, and readily available spare parts to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Automatic Hydraulic Presses: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Maintaining and troubleshooting automatic hydraulic presses are crucial for ensuring longevity, reliability, and optimal performance. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to prevent issues and maximize press performance.
-
Best Practices for Maintaining Automatic Hydraulic Presses:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the press clean and free of contaminants. Clean the press exterior and internal components regularly to prevent dirt, dust, and debris buildup.
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication of moving parts and hydraulic components. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for the type and frequency of lubrication.
- Hydraulic Fluid Maintenance: Regularly check and change the hydraulic fluid according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Monitor fluid levels and ensure there's no contamination.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections for leaks, loose connections, worn components, and other signs of wear and tear. Early detection and repair can prevent major issues.
- Calibration: Calibrate the press periodically to ensure accurate readings and consistent performance. Calibration should be performed by qualified technicians.
-
Common Troubleshooting Tips for Resolving Issues:
- No Pressure or Insufficient Pressure: Check the hydraulic fluid level, pump, and filter. Inspect for leaks, loose connections, or faulty components.
- Press Not Functioning Properly: Verify the power supply and electrical connections. Check for any error codes or messages on the press control panel.
- Excessive Noise or Vibration: Inspect for worn or damaged components, such as bearings, gears, or couplings. Tighten loose bolts or connections.
- Uneven or Inconsistent Pressure: Check the pressure gauge and calibrate the press if necessary. Inspect for leaks or blockages in the hydraulic system.
- Slow Operation or Lack of Power: Inspect the hydraulic pump, motor, and valves for proper function. Check for leaks, contamination, or worn components.

-
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Calibration:
- Increased Reliability: Regular maintenance and calibration enhance the reliability of the press, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime.
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: Proper maintenance and calibration ensure accurate readings and consistent performance, leading to reliable and reproducible results.
- Extended Lifespan: A well-maintained and calibrated press has a longer lifespan, providing a cost-effective investment in the long run.
- Safety: Regular maintenance and calibration help identify potential safety hazards, such as leaks or worn components, preventing accidents and injuries.
Future Advancements in Automatic Hydraulic Press Technology: A Glimpse into Innovation
Automatic hydraulic presses have revolutionized industries and laboratories, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more remarkable advancements in automatic hydraulic press technology, shaping the future of various sectors.
1. Automation and Robotics Integration:
The future of automatic hydraulic presses lies in the seamless integration of automation and robotics. Advanced control systems will enable presses to operate autonomously, performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention. This integration will streamline production processes, reduce labor costs, and enhance overall productivity.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity:
The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) will transform automatic hydraulic presses into interconnected devices capable of communicating with each other and with central control systems. This connectivity will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote troubleshooting, maximizing uptime and minimizing downtime.
3. Improved Control Systems:
Future automatic hydraulic presses will feature sophisticated control systems that provide precise control over force, speed, and pressure. These systems will utilize advanced algorithms and sensors to optimize performance and ensure consistent, high-quality results. Additionally, intuitive user interfaces will simplify operation and make these presses accessible to a wider range of users.

4. Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Techniques:
Advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques will lead to the development of stronger, lighter, and more durable components for automatic hydraulic presses. These improvements will enhance the overall performance, longevity, and reliability of these machines, reducing maintenance requirements and increasing productivity.
5. Industry-Specific Customization:
The future of automatic hydraulic presses will witness increased customization to meet the unique requirements of specific industries. Tailored designs, specialized features, and industry-specific software will enable these presses to seamlessly integrate into diverse manufacturing and laboratory environments, delivering optimal performance and efficiency.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
As the world becomes increasingly conscious of environmental concerns, automatic hydraulic presses will incorporate energy-efficient technologies to minimize their environmental impact. These presses will utilize regenerative braking systems, variable-speed drives, and optimized hydraulic circuits to reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs.
The future of automatic hydraulic press technology holds immense promise, with advancements in automation, IoT integration, improved control systems, advanced materials, industry-specific customization, and sustainability driving innovation. These advancements will revolutionize industries, enhance productivity, and open up new possibilities for research and development, shaping the future of manufacturing and laboratory practices.
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
Related Articles
- How to choose a laboratory hot press
- An In-Depth Guide on Laboratory Presses and KBr Pellets Production
- Applications and Importance of Hydraulic Press in Laboratories
- A Comprehensive Guide on Pressing XRF Pellets Using a KinTek Automatic Hydraulic Press
- Fully automatic tablet press operating steps and replacement accessories