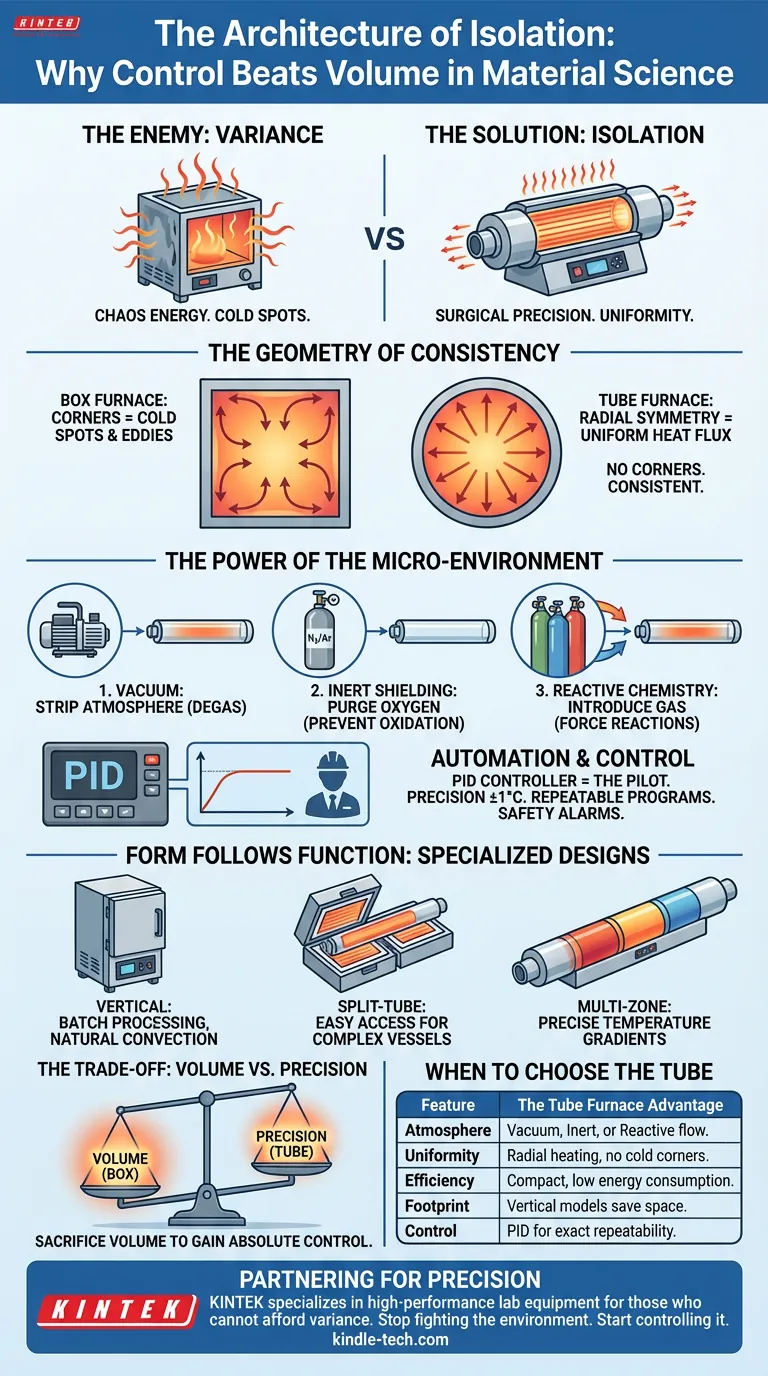
The Enemy of Science is Variance
In any laboratory, the battle is never really against the material. The battle is against the variables.
When you heat a sample, "getting it hot" is the easy part. A campfire can get things hot. A standard box furnace can get things hot. But in advanced material processing, heat without control is just chaos energy.
The difference between a failed experiment and a breakthrough often comes down to the quality of the environment surrounding the sample.
This is where the Tube Furnace separates itself from the pack. It is not designed for bulk; it is designed for isolation. It offers a level of "surgical" precision that general-purpose equipment simply cannot replicate.
The Geometry of Consistency
Consider the shape of a standard furnace. It is a box. Boxes have corners. In thermal dynamics, corners are where uniformity goes to die. They create cold spots and airflow eddies that result in uneven thermal history across a sample.
The tube furnace embraces a different philosophy: Radial Symmetry.
By arranging heating elements around a central cylindrical tube, the furnace creates a radially balanced heat source. There are no corners.
- Uniformity: The heat flux is consistent from all sides.
- Insulation: Advanced materials like polycrystalline fiber lock that heat in.
- Result: An exceptionally uniform temperature field along the heated zone.
For a materials engineer, this means that the edge of your sample experiences the exact same history as the center. Reliability is no longer a variable; it is a constant.
The Power of the Micro-Environment
The true "romance" of the tube furnace lies in its ability to create a world within a world.
In a standard muffle furnace, your sample is often at the mercy of the ambient air. Even with vents closed, the atmosphere is uncontrolled.
The tube furnace changes the rules of engagement. Because the work tube can be sealed, you are not just controlling temperature; you are acting as the architect of the atmosphere.
This capability allows for three distinct modes of operation:
- Vacuum: You can strip away the atmosphere entirely to degas materials.
- Inert Shielding: You can purge oxygen and introduce nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation.
- Reactive Chemistry: You can introduce specific gases to force chemical reactions that wouldn't occur in nature.
This is the definition of a controlled micro-environment. It turns the furnace from a heater into a reactor.
Automation is the Ultimate Safety Feature
There is a psychological comfort in repeatability.
Modern tube furnaces have moved beyond simple "on/off" switches. They utilize PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers.
Think of a PID controller as a pilot landing a plane. It doesn't just look at where the temperature is; it looks at where it's going and how fast. It adjusts the power constantly to prevent overshooting.
This allows for complex, multi-segment programs. You can ramp up, dwell, cool down, and ramp up again—automatically.
- Precision: Control often falls within ±1°C.
- Safety: Alarms for thermocouple failure and over-temperature limits protect the equipment (and the scientist).
Form Follows Function: Specialized Designs
The tube furnace is not a monolith; it adapts to the gravity of the situation—literally.
The Vertical Furnace
Sometimes, gravity is a tool. Vertical orientation is ideal for batch processing and leverages natural convection to enhance uniformity even further.
The Split-Tube
Convenience matters. A split-tube design is hinged, opening like a book. This is essential for complex reactor vessels with large flanges that simply won't fit through a standard tube opening.
The Multi-Zone
For the most demanding applications, such as crystal growth, uniform heat isn't enough—you need a specific lack of uniformity. Multi-zone furnaces allow you to create a precise temperature gradient, controlling exactly how a material cools and crystallizes across its length.
The Trade-Off: Volume vs. Precision
In engineering, there are no solutions, only trade-offs.
The tube furnace is not perfect for everyone. The constraint is in the name: the tube.
- Size: You are limited by the diameter of the tube.
- Throughput: You cannot stack dozens of large beakers inside as you might in a box furnace.
- Complexity: Managing gas flow and vacuum pressures adds layers to the setup.
However, this trade-off is intentional. You are sacrificing volume to gain absolute control.
Summary: When to Choose the Tube
If your work relies on "good enough" heating for large batches, use a box furnace. But if your work relies on the purity of the result, the tube furnace is the only logical choice.
| Feature | The Tube Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Ability to run Vacuum, Inert, or Reactive gas flows. |
| Uniformity | Radial heating eliminates cold corners. |
| Efficiency | Compact thermal mass reduces energy consumption. |
| Footprint | Vertical models save critical bench space. |
| Control | Programmable PID for exact repeatability. |
Partnering for Precision
At KINTEK, we understand that for many researchers, the equipment is not just a tool—it is the environment where discovery happens.
We specialize in high-performance lab equipment designed for those who cannot afford variance. Whether you need the complex gradients of a multi-zone system or the strict atmospheric control of a vacuum tube furnace, our solutions are built to eliminate the variables so you can focus on the science.
Stop fighting the environment. Start controlling it.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
Related Articles
- Installation of Tube Furnace Fitting Tee
- The Silent Partner in Pyrolysis: Engineering the Perfect Thermal Boundary
- Beyond the Spec Sheet: The Hidden Physics of a Tube Furnace's True Limit
- Entropy and the Alumina Tube: The Art of Precision Maintenance
- Why Your Furnace Components Keep Failing—And the Material Science Fix




















