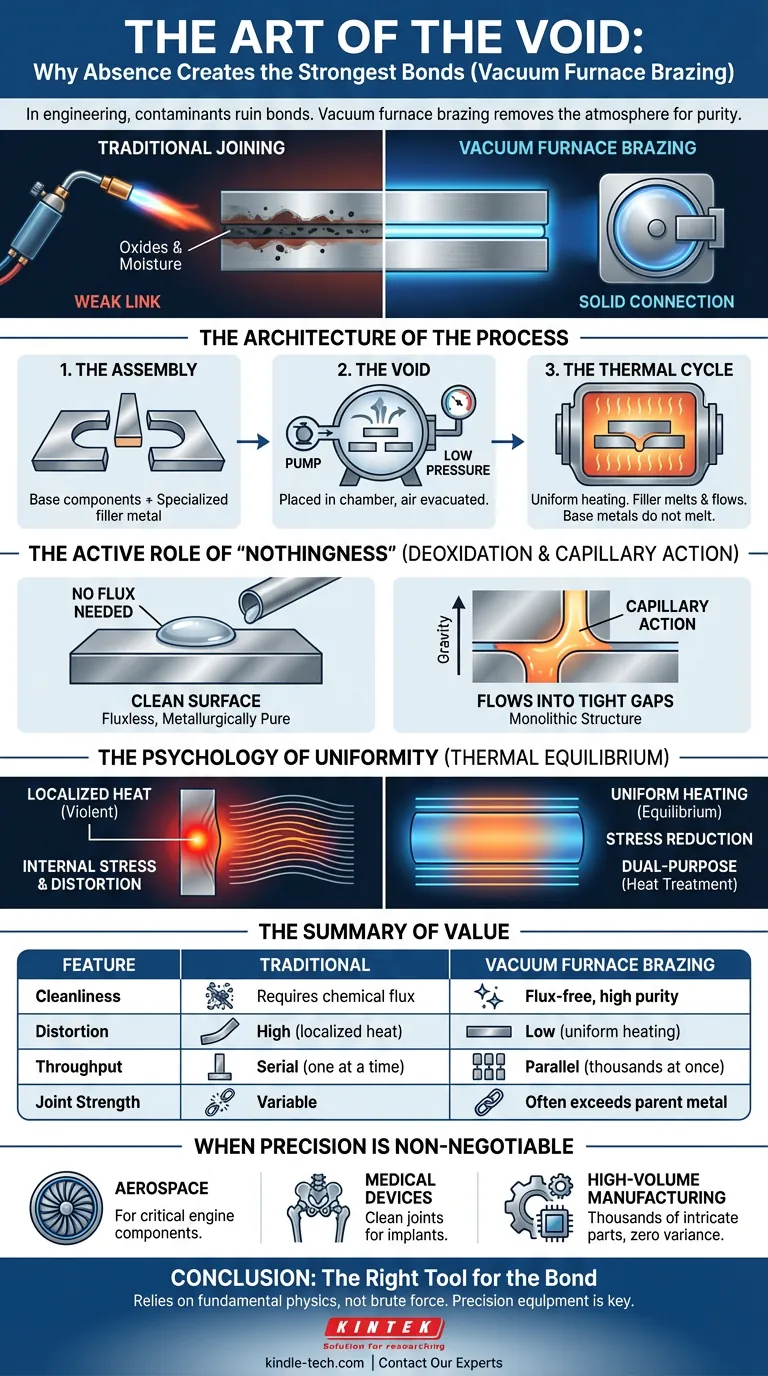
In engineering, as in life, the presence of contaminants often ruins the bond.
When we try to join two metals using traditional heat, the atmosphere becomes an adversary. Oxygen creates oxides. Moisture introduces hydrogen. These invisible variables turn what should be a solid connection into a weak link.
Vacuum furnace brazing flips this problem on its head.
It does not fight the atmosphere; it removes it entirely. By creating a high-purity environment, it allows physics—specifically capillary action and thermal diffusion—to do the heavy lifting.
Here is why the strongest connections are made in a vacuum.
The Architecture of the Process
Vacuum furnace brazing is deceptively simple in concept but sophisticated in execution. It is a high-purity metal joining process that creates joints often stronger than the parent materials themselves.
The mechanism relies on three distinct phases:
- The Assembly: Base metal components are fitted together with a specialized filler metal (an alloy with a lower melting point).
- The Void: The assembly is placed in a chamber, and the air is evacuated to extremely low pressures.
- The Thermal Cycle: The furnace heats the assembly uniformly. The filler melts, flows, and solidifies.
Unlike welding, the base metals never melt. They merely accept the bond.
The Active Role of "Nothingness"
We tend to think of a vacuum as a passive setting—an empty stage. In brazing, the vacuum is an active participant.
Its primary role is deoxidation.
In standard brazing, you need chemical flux to clean the metal surfaces. Flux is messy. It creates residues. It can corrode the part later if not perfectly removed.
In a vacuum furnace, the low pressure causes surface oxides to dissociate or evaporate. The environment itself cleans the metal. This results in a "fluxless" process, ensuring the joint is metallurgically pure.
The Power of Capillary Action
Once the environment is clean and the temperature rises, the filler metal liquefies.
Because the vacuum has removed the resistance of surface oxides, the liquid alloy is drawn into the tightest gaps between components via capillary action.
It flows against gravity. It penetrates deep into the joint. It diffuses slightly into the atomic structure of the base metal. Upon cooling, it forms a monolithic structure.
The Psychology of Uniformity
Most joining methods, like torch brazing or localized welding, are violent. They blast heat at a single point.
This creates a temperature gradient. Hot spots expand; cold spots resist. The result is internal stress and distortion.
Vacuum furnace brazing offers thermal equilibrium.
- Uniform Heating: The entire assembly rises in temperature simultaneously.
- Stress Reduction: Because the part expands and contracts as a unit, distortion is minimized.
- Dual-Purpose: The heating cycle can often double as a heat treatment (annealing or hardening), saving time and cost.
Strategic Trade-offs
Every engineering choice has a cost. While vacuum brazing offers unmatched quality, it is not a universal solution.
It requires a shift in mindset from "repair" to "production."
The Limitations
- Capital Intensity: High-vacuum furnaces are complex, expensive systems requiring skilled operation.
- The Batch Constraint: This is not a quick fix. It involves pumping down, heating, soaking, and cooling. It is designed for planned batches, not one-off emergency repairs.
- Material Science: The base metals must withstand the brazing temperatures without degrading.
The Summary of Value
| Feature | Traditional Welding/Brazing | Vacuum Furnace Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Cleanliness | Requires chemical flux | Flux-free, high purity |
| Distortion | High (localized heat) | Low (uniform heating) |
| Throughput | Serial (one at a time) | Parallel (thousands of joints at once) |
| Joint Strength | Variable | Often exceeds parent metal |
When Precision is Non-Negotiable
You do not use vacuum brazing to fix a garden gate. You use it when the cost of failure is catastrophic.
- Aerospace: For turbine blades where oxide inclusions could lead to engine failure.
- Medical Devices: For implants where flux residue could cause biological rejection.
- High-Volume Manufacturing: When you need to join thousands of intricate parts simultaneously with zero variance.
Conclusion: The Right Tool for the Bond
The beauty of vacuum furnace brazing lies in its reliance on fundamental physics rather than brute force. By removing the air, we allow the metal to do what it naturally wants to do: bind together.
However, achieving this level of purity requires precise equipment.
KINTEK understands the rigor required for high-performance laboratories and manufacturing environments. We specialize in the lab equipment and consumables that make these advanced thermal processes possible.
Whether you are joining dissimilar metals or scaling up production for aerospace components, precision begins with the right setup.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
Related Articles
- The Hidden Variable: Why Your Vacuum Furnace Results Are Inconsistent, and How to Fix Them for Good
- Dental Sintering Furnaces The Impact on Restoration Quality and Durability
- Why Your High-Temperature Processes Fail: The Hidden Enemy in Your Vacuum Furnace
- Dos and don'ts during the installation of molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating element
- Your Vacuum Furnace Hits the Right Temperature, But Your Process Still Fails. Here’s Why.




















