The Psychology of Maintenance
In the laboratory, we often treat maintenance as a chore—a tax we pay for doing the real work. But there is a deeper reality to materials science: the state of your equipment is a direct reflection of the discipline of your process.
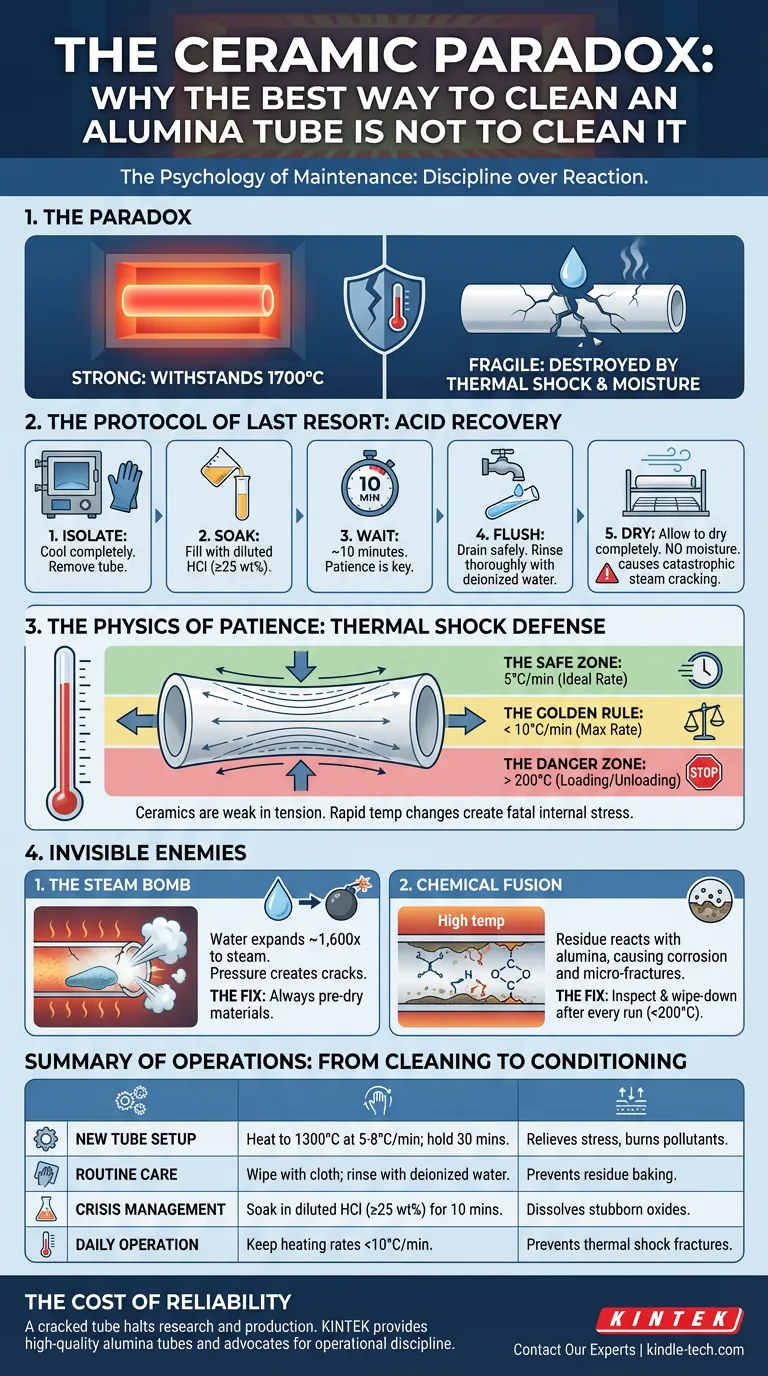
An alumina tube is an engineering paradox. It is capable of withstanding 1700°C, yet it can be destroyed by a drop of cold water or a wet sample.
When researchers ask, "How do I clean my alumina tube?", they are often asking the wrong question. They are looking for a reactive solution to a process failure. While chemical cleaning is sometimes necessary, the true engineering challenge is not removing the residue. It is preventing the conditions that allowed the residue to fuse with the ceramic in the first place.
Here is how to manage the lifecycle of your furnace tube, from the protocol of last resort to the art of prevention.
The Protocol of Last Resort: Acid Recovery
If you are reading this because your tube is already heavily contaminated, you are past the point of routine maintenance. You are now in a recovery operation.
When significant residue remains baked onto the tube walls, physical wiping is insufficient. You must use chemistry to reset the system.
The Acid Wash Procedure
This process uses Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) to dissolve metallic oxides without aggressively attacking the alumina structure. Treat this as surgery, not a daily wash.
- Isolate the Component: Ensure the furnace is completely cool. Remove the tube and place it on a chemically resistant surface.
- The Soak: Fill the tube with diluted hydrochloric acid (≥25 wt%).
- The Wait: Let it soak for approximately 10 minutes. Patience is key here; let the chemistry do the work.
- The Flush: Drain the acid safely. Rinse the interior thoroughly with deionized water. You must remove all traces of acid.
- The Dry: Allow the tube to dry completely. Reheating a wet tube will generate steam pressure that causes catastrophic cracking.
The Physics of Patience
The single greatest threat to your alumina tube is not dirt. It is Thermal Shock.
Ceramics are strong in compression but weak in tension. When a tube heats up or cools down too quickly, the temperature gradient creates internal stress. If the expansion of the inner wall outpaces the outer wall, the material snaps.
Physics does not negotiate. To preserve your equipment, you must adopt a philosophy of slowness.
- The Golden Rule: Never exceed a heating or cooling rate of 10°C per minute.
- The Safe Zone: A conservative rate of 5°C per minute is the hallmark of a careful operator.
- The Danger Zone: Never load or unload samples when the furnace is above 200°C.
The Invisible Enemies
Beyond heat, two factors silently degrade your equipment: Moisture and Chemistry.
1. The Steam Bomb
Water expands roughly 1,600 times when it turns to steam. If you place a sample with high moisture content or crystal water into a sealed, hot environment, you are essentially creating a pressure bomb inside a ceramic vessel.
** The Fix:** Always pre-dry materials. If your sample holds water, the furnace is not the place to remove it.
2. Chemical Fusion
Residue is not passive. At high temperatures, left-over sample material can react with the alumina, creating new compounds. This is chemical corrosion. It etches the tube walls, creating micro-fractures that weaken the structural integrity over time.
The Fix: Inspect the tube after every run (once cooled below 200°C). A simple wipe-down prevents today's residue from becoming tomorrow's permanent corrosion.
Summary of Operations
To ensure longevity, move your focus from "cleaning" to "conditioning."
| Operational Phase | Action Required | The "Why" |
|---|---|---|
| New Tube Setup | Heat to 1300°C at 5-8°C/min; hold 30 mins. | Relieves manufacturing stress and burns off pollutants. |
| Routine Care | Wipe with cloth; rinse with deionized water. | Prevents residue from baking into the ceramic. |
| Crisis Management | Soak in diluted HCl (≥25 wt%) for 10 mins. | Dissolves stubborn metallic oxides. |
| Daily Operation | Keep heating rates <10°C/min. | Prevents thermal shock and stress fractures. |
The Cost of Reliability
A cracked tube stops research. It halts production. It costs time, which is often more expensive than the hardware itself.
At KINTEK, we understand that a furnace is only as reliable as the consumables inside it. We provide high-quality alumina tubes designed to withstand rigorous laboratory environments, but we also advocate for the operational discipline that makes them last.
Whether you need a replacement tube or advice on optimizing your thermal process, our engineering team is ready to assist.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
Related Articles
- Cracked Tubes, Contaminated Samples? Your Furnace Tube Is The Hidden Culprit
- Rotary Furnaces: Advanced Materials Processing and Applications
- Entropy and the Alumina Tube: The Art of Precision Maintenance
- Exploring the Key Characteristics of Tube Heating Furnaces
- Installation of Tube Furnace Fitting Tee




















