Articles

Application of Isostatic Graphite in the Photovoltaic Industry
1 year agoAn overview of the use of isostatic graphite in various stages of photovoltaic production and its market demand.
Learn More
Isostatic Pressing Technology for Solid-State Batteries
1 year agoFocus on isostatic pressing to commercialize next-gen batteries.
Learn More
Isostatic Pressing Technology in Solid-State Battery Production
1 year agoExploring the role of isostatic pressing technology in manufacturing solid electrolytes for next-generation solid-state batteries.
Learn More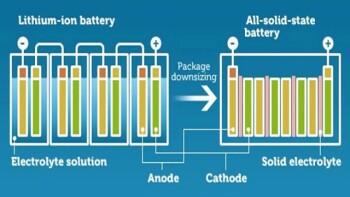
Essential Equipment for Mass Production of Solid-State Batteries: Isostatic Press
1 year agoDiscusses the role of isostatic pressing technology in enhancing solid-state battery performance and production efficiency.
Learn More
Sample Preparation Techniques for Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
1 year agoComprehensive guide on selecting and applying sample preparation methods for infrared spectroscopy.
Learn More
XPS Powder Sample Preparation and Precautions
1 year agoGuidelines for preparing and handling powder samples for XPS analysis.
Learn More
Overview of Basic Laboratory Pumps
1 year agoAn overview of various types of laboratory pumps including constant flow, oil-free vacuum, rotary vane, diaphragm, chemical hybrid, molecular, injection, and circulating water pumps.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Test Chamber Equipment
1 year agoOverview of essential lab test chambers for various environmental simulations.
Learn More
Basic Constant Temperature Heating Equipment in Laboratories
1 year agoOverview of various constant temperature heating devices used in laboratories.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Culture Equipment
1 year agoOverview of essential laboratory equipment for biological and microbiological research.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Drying Equipment
1 year agoOverview of various drying equipment used in laboratories, including vacuum, blast, electric heating, hot air disinfection, and infrared drying ovens.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Refrigeration Equipment
1 year agoOverview of essential refrigeration tools for labs.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Reaction Equipment
1 year agoOverview of essential lab equipment for chemical reactions under various conditions.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Centrifuge Equipment
1 year agoOverview of different types of centrifuges used in laboratories.
Learn More
Laboratory Sample Preparation and Digestion Equipment
1 year agoOverview of essential lab equipment for sample preparation and digestion.
Learn More
Basic Cleaning and Disinfection Equipment in the Laboratory
1 year agoOverview of essential lab cleaning and disinfection tools and their operational principles.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Extraction Equipment
1 year agoOverview of various extraction methods used in laboratories.
Learn More
Basic Laboratory Purification Equipment Overview
1 year agoAn overview of essential purification equipment used in laboratories, including water purification, solvent evaporation, and waste treatment systems.
Learn More
Basic Mixing Equipment in the Laboratory
1 year agoOverview of essential laboratory mixing devices and their functionalities.
Learn More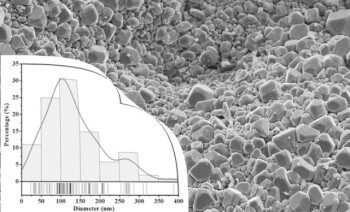
Sample Preparation Methods in X-ray Fluorescence and Their Impact on Test Results
1 year agoExplores the tablet and melting methods in X-ray fluorescence, detailing their advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations.
Learn More
Preparation Techniques for Solid Samples in Infrared Spectroscopy
1 year agoA detailed guide on various methods for preparing solid samples for infrared spectroscopy, including plate pressing, paste, and thin film methods.
Learn More
X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry: Powder Tableting Sample Preparation
1 year agoA comprehensive guide on the powder tableting method for sample preparation in X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, detailing grinding, pressing, and application scope.
Learn More
IR (Tablet Pressing Method) Operation
1 year agoDetailed guide on the IR tablet pressing method, including instruments, reagents, sample preparation, and testing procedures.
Learn More
Issues with Poor Demoulding in Manual Tablet Presses
1 year agoAnalyzes the causes of poor demoulding in manual tablet presses, focusing on powder, mold, machine body, and operator factors.
Learn More
X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Analysis Method | Sample preparation method: tableting sample preparation
1 year agoDetailed guide on XRF analysis, focusing on sample preparation and powder sample methods.
Learn More
Manual Lab Hydraulic Pellet Press: Comprehensive Guide to High-Quality Pellet Preparation
1 year agoExplore the detailed guide on using a Manual Lab Hydraulic Pellet Press for high-quality pellet preparation in spectral analyses. Learn about features, operation, and maintenance for optimal performance.
Learn More
Optimizing Laboratory Analysis with Split Automatic Heated Lab Pellet Press
1 year agoExplore the advanced features and benefits of split automatic heated lab pellet presses for precise pellet preparation in various analytical applications. Ideal for high-throughput laboratories.
Learn More
Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press (CIP): Applications, Benefits, and Customization
1 year agoExplore the versatile world of Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) technology. Learn about its applications in various industries, benefits, and customization options for tailored solutions.
Learn More
Exploring the Capabilities and Applications of Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP)
1 year agoDive into the comprehensive guide on Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP), its technology, applications, and benefits in material processing. Discover how WIP enhances material properties and its role in advanced manufacturing.
Learn More
Why Most PELLET PRESS XRF SAMPLE PREPARATION Fail: Common Issues and Solutions
1 year agoDiscover the common pitfalls in PELLET PRESS XRF SAMPLE PREPARATION and learn effective solutions to ensure accurate results. Covers particle size, contamination, binder choice, and more.
Learn More