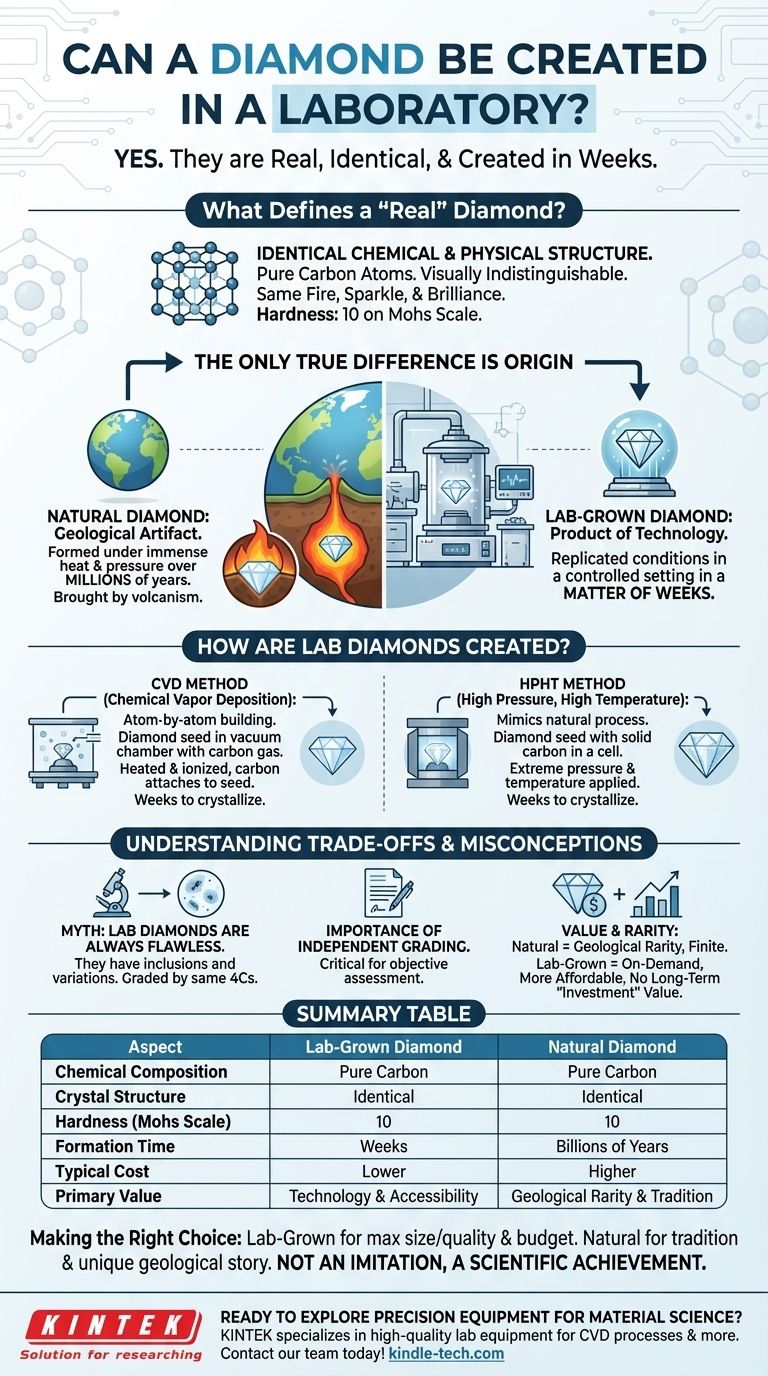
Yes, a diamond can be created in a laboratory. These are not fakes or imitations like cubic zirconia, but are chemically, physically, and optically identical to diamonds mined from the Earth. The only fundamental difference between a lab-grown diamond and a natural diamond is its origin.
A lab-grown diamond is a real diamond, possessing the same carbon crystal structure as its mined counterpart. The primary distinction lies in its creation process—condensed into a matter of weeks in a controlled environment rather than occurring over millions of years deep within the Earth.

What Defines a "Real" Diamond?
To understand lab-grown diamonds, we must first define what a diamond is. At its core, a diamond is a specific crystal structure made of pure carbon atoms.
An Identical Chemical and Physical Structure
A lab-created diamond shares the exact same chemical composition and crystal structure as a natural one. This means they are visually indistinguishable.
They exhibit the same fire, sparkle, and brilliance. Furthermore, they possess the same hardness, making them—along with natural diamonds—the hardest known natural material on the Mohs scale.
The Only True Difference is Origin
The journey is the only thing that separates the two. A natural diamond is a geological artifact, formed under immense pressure and heat millions of years ago, and brought to the surface by volcanic eruptions.
A lab-grown diamond is a product of technology, created by replicating those same conditions in a highly controlled setting.
How Are Lab Diamonds Created?
Scientists have developed two primary methods to grow diamonds, both of which begin with a tiny diamond "seed," which is a minuscule slice of a pre-existing diamond.
The CVD Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
This process is akin to building the diamond atom by atom. The diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with a carbon-rich gas.
The chamber is heated to extreme temperatures, causing the gas to ionize. These carbon particles then attach to the diamond seed, slowly building up layers and crystallizing into a complete diamond over several weeks.
The HPHT Method (High Pressure, High Temperature)
This method more directly mimics the natural process inside the Earth. The diamond seed is placed in a cell with solid carbon and subjected to a combination of extreme pressure and very high temperatures.
Under these conditions, the carbon melts and forms around the seed, crystallizing into a diamond. The entire process takes approximately six to ten weeks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
While physically identical, the context surrounding lab-grown diamonds involves important considerations and common misunderstandings.
Myth: Lab Diamonds Are Always Flawless
The controlled environment of a lab does not guarantee perfection. Just like natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds can have inclusions and variations in color.
They are graded using the exact same "4 Cs" standard (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat) as natural diamonds. Their quality can vary significantly, so a thorough inspection is always necessary.
The Importance of Independent Grading
Because quality varies, it is critical that any significant lab-grown diamond purchase is accompanied by an independent grading report from a reputable gemological institute. This ensures an objective assessment of its quality.
Value and Rarity
The key trade-off is between technological accessibility and geological rarity. Natural diamonds are a finite resource, and their value is tied to that scarcity.
Lab-grown diamonds can be produced on demand, which generally makes them more affordable but also means they do not hold the same long-term "investment" value associated with rare, natural gems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a lab-grown and a natural diamond is a personal one, based on your priorities and values.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the maximum size and quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond delivers the same physical beauty and durability as a natural diamond, often at a significantly lower price point.
- If your primary focus is the tradition and unique story of a geological artifact: A mined diamond, with its billion-year history, holds a romanticism and sense of rarity that technology cannot replicate.
Ultimately, lab-grown diamonds are not an imitation but a remarkable achievement of science, offering a genuine and compelling alternative to their earth-mined counterparts.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Identical | Identical |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Formation Time | Weeks | Billions of Years |
| Typical Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Primary Value | Technology & Accessibility | Geological Rarity & Tradition |
Ready to explore precision equipment for material science? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're researching CVD processes or need reliable tools for your laboratory, our expertise can help you achieve your goals. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















