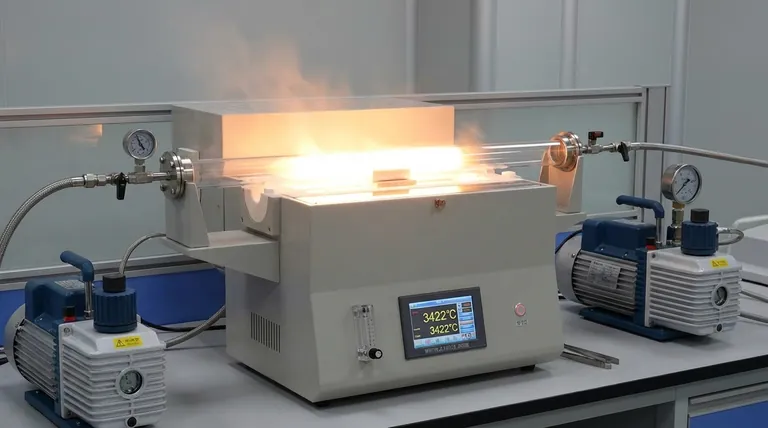
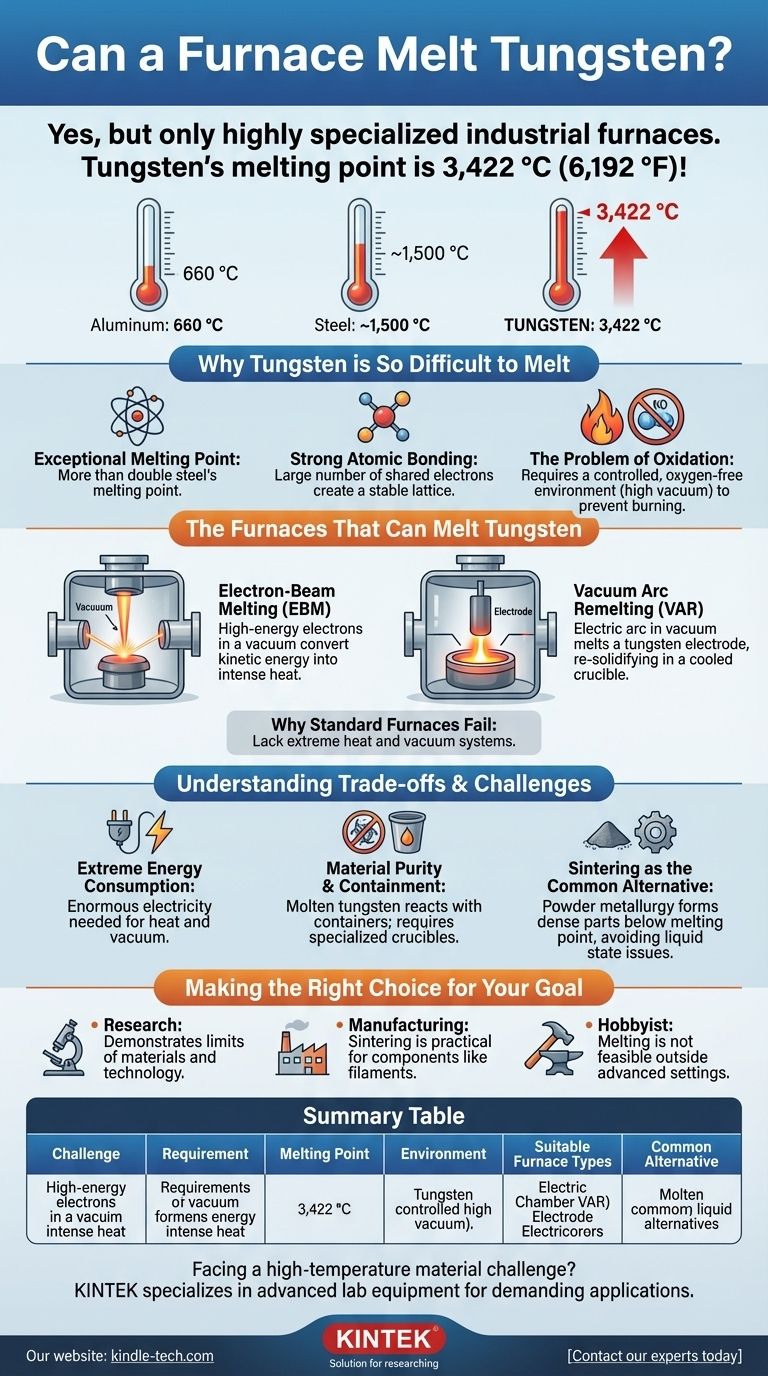
Yes, a furnace can melt tungsten, but only a highly specialized industrial one. Tungsten has the highest melting point of any pure metal at an astonishing 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). This temperature is far beyond the capability of any standard furnace, such as those used for steel or even a blacksmith's forge. Melting tungsten requires advanced technology designed specifically to generate and contain such extreme heat in a controlled environment.
The ability to melt tungsten is not a question of simply "getting it hot enough." It is an industrial challenge that requires overcoming its extreme melting point, preventing its rapid oxidation at high temperatures, and using specialized furnaces like electron-beam or vacuum arc systems that are fundamentally different from conventional equipment.

Why Tungsten is So Difficult to Melt
To appreciate the challenge, we must first understand the unique properties of the metal itself. Tungsten’s resilience is rooted in its fundamental atomic structure.
The Exceptional Melting Point
Tungsten's melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F) sets it apart from nearly all other materials. For context, this is more than double the melting point of steel (around 1,500 °C) and five times that of aluminum (660 °C).
Strong Atomic Bonding
The "why" behind this high melting point lies in its atomic structure. Tungsten atoms are held together by incredibly strong metallic bonds. The large number of shared electrons creates a highly stable and dense lattice that requires an immense amount of thermal energy to break apart.
The Problem of Oxidation
Even if you could generate the required heat, you cannot melt tungsten in the open air. At elevated temperatures, tungsten reacts very quickly with oxygen and would essentially burn away (oxidize) before it ever reached a liquid state. This mandates a controlled, oxygen-free environment, typically a high vacuum.
The Furnaces That Can Melt Tungsten
Because of these challenges, melting tungsten is reserved for specific industrial processes using purpose-built equipment.
Electron-Beam Melting (EBM)
This is a highly precise method. In a high vacuum, a beam of high-energy electrons is aimed at the tungsten. The kinetic energy from the electrons is instantly converted into intense heat, melting the material. The vacuum environment is perfect for preventing oxidation.
Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
In this process, a large tungsten electrode is positioned inside a vacuum chamber above a water-cooled copper crucible. An electric arc is struck between the electrode and the crucible, creating intense heat that melts the tip of the electrode. The molten tungsten drips down and re-solidifies in the crucible, forming a purified ingot.
Why Standard Furnaces Fail
A blast furnace for iron ore only reaches about 1,650 °C. A typical industrial heat-treating furnace may reach 1,300 °C. These temperatures are not even halfway to what is needed to melt tungsten. Furthermore, they lack the vacuum systems necessary to prevent catastrophic oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Melting tungsten is not just difficult; it is also resource-intensive and presents unique engineering problems.
Extreme Energy Consumption
Generating the temperatures and high vacuums required for EBM or VAR furnaces consumes an enormous amount of electricity. This contributes significantly to the high cost of processing tungsten.
Material Purity and Containment
At 3,422 °C, molten tungsten is highly reactive. It can dissolve or react with almost any container (crucible) holding it, leading to contamination. This is why water-cooled copper crucibles or "crucible-less" EBM methods are used, as they keep the molten pool contained without direct contact with a meltable material.
Sintering as the Common Alternative
Because of these complexities, the vast majority of tungsten products are not made by melting and casting. Instead, they are formed through powder metallurgy. Tungsten powder is compressed into a desired shape and then heated to a high temperature—but below its melting point—in a process called sintering. The atoms bond together, creating a solid, dense object without ever becoming liquid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to tungsten depends entirely on your objective, as working with it in its molten state is rarely the practical solution.
- If your primary focus is research or academics: Understand that melting tungsten is a benchmark for extreme material processing, demonstrating the limits of both material science and furnace technology.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or design: Recognize that tungsten parts are almost exclusively made via sintering (powder metallurgy), which is a more practical and cost-effective method for creating components like filaments or electrical contacts.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist metalworking: Acknowledge that melting tungsten is not feasible outside of a major industrial or advanced research setting due to the prohibitive temperature, vacuum, and safety requirements.
Understanding the immense difficulty of melting tungsten gives you a clear appreciation for why it is one of our most vital high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 3,422 °C (6,192 °F) |
| Environment | High Vacuum (to prevent oxidation) |
| Suitable Furnace Types | Electron-Beam Melting (EBM), Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) |
| Common Alternative | Powder Metallurgy / Sintering |
Facing a high-temperature material challenge? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for demanding applications. Whether you're in R&D or manufacturing, our expertise can help you select the right technology for your specific material processing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What is a tube furnace used for? Achieve Precise, Controlled Thermal Processing
- How does a tubular furnace work? A Guide to Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- What material are furnace tubes? Choosing the Right Material for High-Temperature Success



















